What is 'passive salt water cooling' that improves CPU performance by about 33%?
In addition to general air cooling, there are
Membrane-encapsulated, moisture-desorptive passive cooling for high-performance, ultra-low-cost, and long-duration electronics thermal management - ScienceDirect
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2666998623001801
Passive Salt Water Cooling Boosts CPU Performance by Almost 33% | Tom's Hardware
https://www.tomshardware.com/pc-components/cooling/passive-salt-water-cooling-boosts-cpu-performance-by-almost-33
Cheap salty solution cools computers and boosts performance by a third | New Scientist
https://www.newscientist.com/article/2400457-cheap-salty-solution-cools-computers-and-boosts-performance-by-a-third/
Salt solution cools computers, boosts performance
https://techxplore.com/news/2023-11-salt-solution-cools-boosts.html
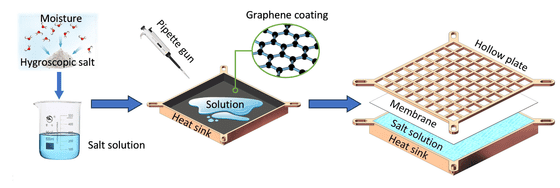
The formal name of the cooling system developed by Mr. Wei Wu of the Department of Energy and Environment, City University of Hong Kong and others is 'hygroscopic salt-containing membrane encapsulated heat sink (HSMHS)', which removes moisture from a solution of hygroscopic lithium bromide salt. It is a mechanism that cools the CPU through the process of evaporation.
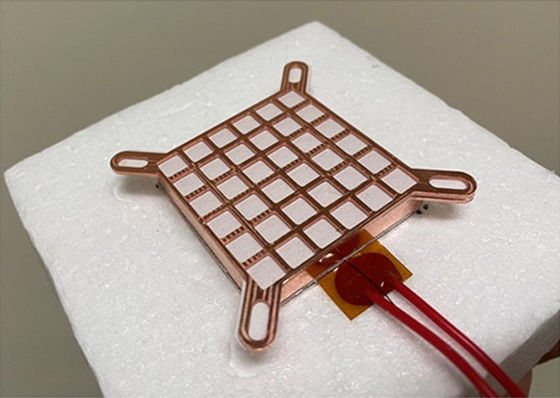
The lithium bromide salt is trapped in a porous membrane that allows only water vapor to pass through, and is sandwiched between plates to prevent the salt from coming into contact with electronic equipment, while a metal heat sink allows heat to escape efficiently. It is designed to.
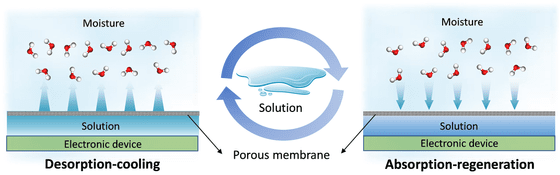
HSMHS's passive cooling system works in two stages: a 'desorption cooling process' and an 'absorption regeneration process.' First, the withdrawal cooling process removes heat by evaporating water from the solution. After cooling, the system enters an absorption regeneration process, where the highly concentrated salt solution absorbs moisture from the surrounding air and automatically restores its cooling capacity.
'This device can spontaneously and quickly restore its cooling capacity by absorbing water vapor from the air during periods of non-operation, similar to how mammals rehydrate and prepare to sweat again,' said Wu. 'I'll do it,' he said.
Cooling costs are a major issue for computer processors, especially in large-scale facilities such as data centers. Passive cooling systems, which have no moving parts like fans and do not require electricity like water cooling pumps, are attractive, but traditional passive cooling systems quickly reach thermal saturation and suffer from performance issues such as
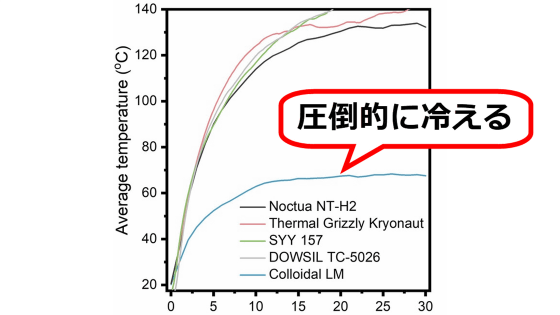
Meanwhile, in tests conducted by the research team using HSMHS, they succeeded in improving device performance by 32.65% compared to using a regular heat sink.

One of the major features of HSMHS is its long effective cooling time. In the aforementioned tests, HSMHS was able to cool processors below 64 degrees for about 400 minutes, which is 10 times better than the most advanced material, metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). About. In addition, lithium bromide salts are inexpensive and therefore have high cost performance, approximately 1000 times more cost-effective than chromium-based MOFs.
Regarding HSMHS, Mr. Wu said, ``This cooling strategy is cost-effective and highly scalable, so there are fewer technical barriers and can be used in a variety of cooling applications.''
◆Forum now open
A forum related to this article has been set up on the GIGAZINE official Discord server . Anyone can write freely, so please feel free to comment! If you do not have a Discord account, please create one by referring to the article explaining how to create an account!
• Discord | 'Is the cooling method of the PC you are currently using air cooling? Water cooling? Or?' | GIGAZINE
https://discord.com/channels/1037961069903216680/1173910643481526363
Related Posts:
in Hardware, Posted by log1l_ks