Was Intel's 11th generation Core processor 'Rocket Lake' so bad?
Intel adopted a hybrid architecture that combines high-performance cores and high-efficiency cores in the 12th-generation Core processor `` Alder Lake '' released in September 2021, achieving `` outstanding performance '' compared to the previous generation. The information site
Was Rocket Lake Power Efficient? – Chips and Cheese
https://chipsandcheese.com/2022/12/17/was-rocket-lake-power-efficient/
Suggestions when searching for 'Rocket Lake' on Google are like this, with harsh words such as 'failure', 'garbage' and 'black history'. When you actually go to look at the search results, it's not straight up described as a 'failure'.
On the premise of Chips and Cheese, Alder Lake's high-performance core, Golden Cove, is a new architecture with a new process, and it is natural that it has a big advantage over Rocket Lake, saying that as a 'appropriate comparison', the same I'm doing a comparison with the CPU of the process rule. In comparison, Intel processors are looking at package power instead of core power because important components such as L3 cache, ring bus, and memory controller are not on the core power plane. Also, all tests were run with 4 threads active and the workload was limited to 4 cores on CPUs with more cores.
The first targets were the 6th generation Core processor Skylake and the 7th generation Core processor Kaby Lake with the same 14 nm process rule.
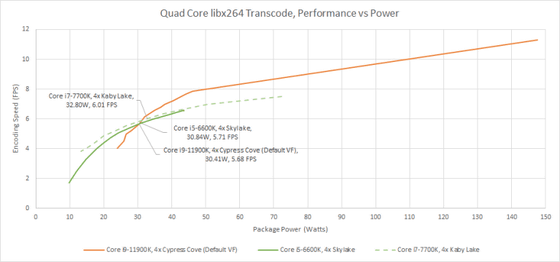
Rocket Lake is well known for its 'too high power consumption'. However, Chips and Cheese, which did a comparison with 4K encoding, said, 'Moderate power isn't too bad.' As a matter of fact, Rocket Lake's Cypress Cove core performed better than Skelake when the power consumption was 30 W or more. In order to demonstrate high performance with Rocket Lake, four cores consume a total of 147W, but it seems that efficiency will be very poor as expected. On the other hand, Chips and Cheese states that 'the inability to scale down at low power consumption' is the biggest weakness of Rocket Lake, and in fact, when the power consumption drops below 30W, the performance drops, and the score loses to Skylake and Kaby Lake. It is In the graph below, the orange solid line indicates Rocket Lake, the green solid line indicates Skelake, and the green dotted line indicates Kaby Lake.
In addition, we also measured 7Zip compression, which does not fully load 4 cores because it rarely uses vector units and is not as parallelized as libx264 encoding. Power consumption exceeds Kaby Lake at around 35W, and score close to Golden Cove at 75W.
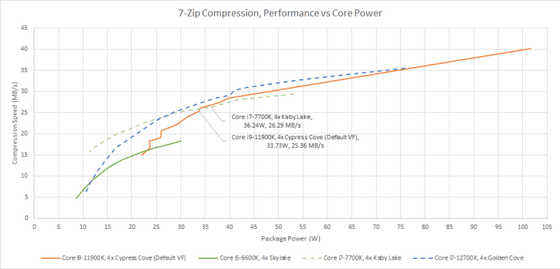
From this result, Chips and Cheese can say that Rocket Lake certainly has high power consumption in some cases, and while it has the weakness that it cannot be scaled down to a power level as low as Alder Lake, at the power level of middle-sized desktops over 30W It is rated as the most efficient 14nm process processor. This indicates that efficiency can be improved by using a large, high IPC core that operates at a low clock, even if it is not a new process rule. However, he points out that Rocket Lake's efficiency advantage is unfortunately very narrow.

Related Posts:
in Hardware, Posted by logc_nt