What impact will the Bank of Japan's sudden de facto interest rate hike have on the Japanese economy and foreign bonds in the future?

by
The Bank of Japan held amonetary policy meeting on Tuesday, December 20, 2022, and announced that it had expanded the fluctuation range of long-term interest rates from about 0.25% to about 0.5% ( PDF file) . The economic news site ' The Macro Compass ' explains the reason and impact.
What The Heck Is Happening In Japan?
https://themacrocompass.substack.com/p/bank-of-japan-surprise#details
Until now, the Bank of Japan has been actively implementing monetary easing with an emphasis on economic expansion. By introducing yield curve control in September 2016, the volatility of long-term government bond interest rates was expanded from 0% to 0.25%.
However, at the Monetary Policy Meetings held on December 19 and 20, the volatility of long-term government bond interest rates was expanded to around 0.5%. Alfonso Peccatiello of The Macro Compass points out that this decision could significantly change the economy of Japan, a capital exporting country .
[Results of the December Monetary Policy Meeting]
— Bank of Japan (@Bank_of_Japan_j) December 20, 2022
The Bank of Japan held its Monetary Policy Meeting today and released the 'Monetary Policy Conduct for the Near Time.' https://t.co/DafrhdJWES pic.twitter.com/jsayPGGCMl
As for the reason for expanding the fluctuation range, Bank of Japan Governor Haruhiko Kuroda said, 'It is not a rate hike , it is aimed at improving market function due to global inflation.' Featured in various media outlets .
Mr. Pecatiello said about the expansion of the volatility at this timing, 'Because Kuroda's term expires in April 2023, it is necessary to lay the foundation for the next governor's monetary policy.' increase. In addition, Mr. Pecatiello said that in the current situation where Japan's core inflation rate continues to rise, a tight monetary policy that emphasizes price stability is required. I predict that The graph below shows the rise in Japan's core inflation rate. It is shown that the core inflation rate, which continued to rise from around November 2021, will reach 2% from December 2022 to January 2023.
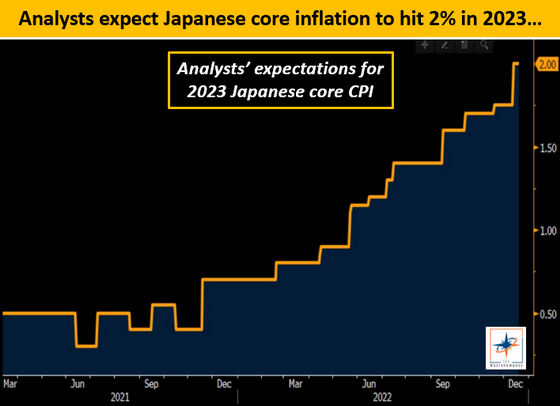
In addition, Mr. Pecatiello analyzed the future of the Japanese economy, predicting the possibility of an interest rate hike of 30
As a further impact, it has been pointed out that the yen will appreciate faster because the interest rate hike will not provide additional yield when purchasing foreign government bonds. The graph below shows the yield of foreign bonds compared to Japanese Government Bonds (JGB). In the second half of 2022, it can be confirmed that the US government bonds (UST) shown in blue and the British government bonds (Gilt) in light blue have lower yields than JGB.
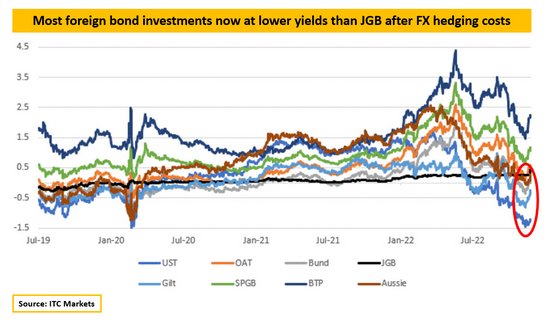
'There is a possibility of a new monetary policy approach to inflation by the Bank of Japan,' Peccatiello said of the Bank of Japan's decision. In addition, Mr. Pecatiello, who predicts a global recession in 2023, will tend to appreciate the yen in an environment where the yield gap with overseas narrows and Japanese investors are conscious of domestic demand . suggests a possibility.
'We are concerned that the value of European and American bonds seen by Japanese investors will decline due to the Bank of Japan's decision, and that future decisions will further reduce the value,' said Pecatiello. .
Related Posts:
in Note, Posted by log1r_ut







