Detailed summary of the next-generation Wi-Fi standard 'Wi-Fi 7', how much faster can it be than Wi-Fi 6?

The next generation
What is Wi-Fi 7?
https://www.androidpolice.com/what-is-wi-fi-7/
Wi-Fi 7 is also known as 'IEEE 802.11be'. Wi-Fi 7 is backward compatible with the previous standard Wi-Fi, so devices that support Wi-Fi 6 (IEEE 802.11ax) and Wi-Fi 6E (IEEE 802.11ax like Wi-Fi 6) can also use routers that support Wi-Fi 7. The same applies to client devices, which can connect to any Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 5 access point without issue.
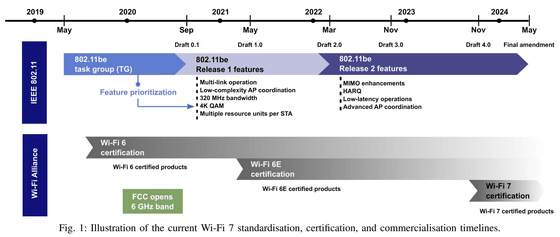
Wi-Fi 7 is in the draft stage, but certified and certified products are expected to appear in 2024, and based on the draft, Wi-Fi 7 compatible hardware may appear early in 2023 Android Police points out. The final specification will be decided by IEEE in 2024, and it is quite possible that some specifications may be deleted or added before publication, so if you want to purchase a complete Wi-Fi 7 product, Android Police recommends waiting until 2024.
The biggest feature of Wi-Fi 7 is that it extends the channel width to 320MHz at the frequency of 6GHz. In general, the wider the channel, the more bandwidth between the client device and the router, which means more data can be sent at once. With this channel width expansion, it is expected that the theoretical maximum communication speed will be at least doubled from Wi-Fi 6's 9.6 Gbps. In addition, at the draft stage, Wi-Fi 7 is said to be `` capable of achieving a communication speed of at least 30 Gbps '', and when MediaTek conducted the world's first demonstration of Wi-Fi 7, the current standard `` Wi-Fi 6 We have succeeded in recording 2.4 times the communication speed.

MediaTek estimates that Wi-Fi 7 communication speeds will rise to about 36 Gbps, but Intel says it may reach 46.1 Gbps. Please note that these figures are only 'theoretical maximum values', so it is thought that communication speeds up to this point will not be achieved in the actual environment due to various factors. Still, compared to the current Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E, Wi-Fi 7 is expected to have overwhelmingly faster communication speeds.
However, expanding the channel width to 320MHz, which is the key to increasing communication speeds, is only for frequencies in the 6GHz band. Therefore, it should be noted that the frequency of the 2.4 GHz band has a channel width of up to 40 MHz, and the frequency of the 5 GHz band has a channel width of up to 160 MHz.
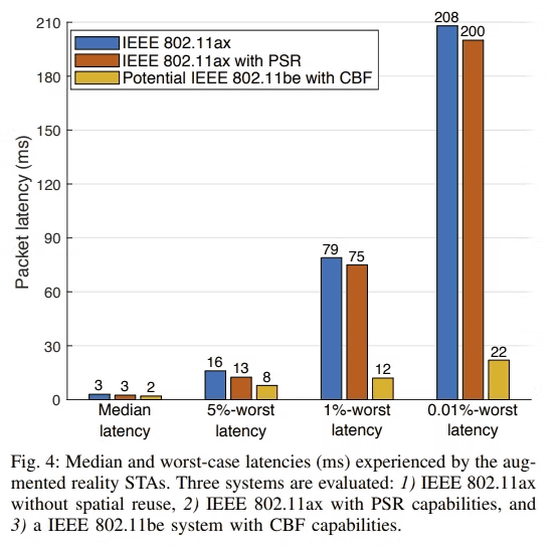
In addition, Wi-Fi 7 also provides significant latency (delay) reduction. Nowadays, content such as AR and VR is expected to become an important technology on the Internet in the future, and there are cases where even double-digit ms (millisecond) latency becomes a problem. In VR and AR, the lower the 'Motion to Photon latency (MTP latency)', which represents the lag until visual changes are reflected, the better. Wi-Fi 7 isn't meant to dramatically reduce typical latency, but it's designed to reduce lag under worst-case conditions.
In the graph below, the vertical axis represents latency (milliseconds: ms), and the horizontal axis represents median latency, lower 5% (5% -worst latency), lower 1% (1% -worst latency), lower 0.01% (0.01% -worst latency) latency). In the case of the previous standard, the lower the latency, the larger the latency occurred, but in the case of Wi-Fi 7 (yellow), the latency was significantly reduced in the client layer where the latency was particularly large.
In addition,
Additionally, a technology called MRU is introduced to reduce latency when multiple uploads occur. As a result, instead of queuing uploads in order so that devices do not overlap, they will operate on separate sub-frequencies. This was possible with Wi-Fi 6E, but Wi-Fi 7 is designed to work even better when uploading data of different sizes.
In addition, Wi-Fi 7 extends the MIMO data stream from Wi-Fi 6's maximum of 8 x 8 to a maximum of 16 x 16. This will improve throughput and increase the number of devices that can comfortably communicate with a single router. Specifically, Android Police cites advantages such as fewer problems when streaming video on multiple devices at the same time, and less lag when playing games with multiple people at the same time.
Although the IEEE did not mention it in the Wi-Fi 7 white paper, in the early drafts of Wi-Fi 7 they planned to make MIMO work well across multiple access points, called Coordinated Multiuser MIMO (CMU-MIMO). Regarding this, Android Police said, ``Although the benefits of CMU-MIMO are not clear, it seems that it can reduce interference in places where multiple access points are congested and improve the speed and reliability of individual devices.' However, it is unclear whether this CMU-MIMO will be implemented in the final specifications of Wi-Fi 7.
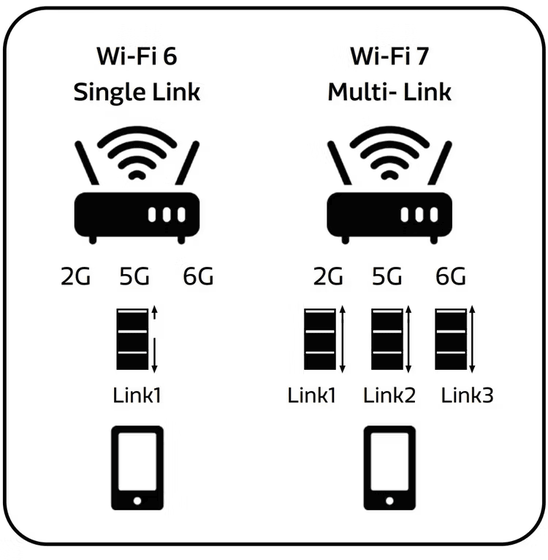
In addition, Wi-Fi 7 will also implement 'multi-link operation (MLO)' technology that combines multiple channels of different frequency bands. This does not just mean that the router acts as an access point for client devices and operates on the 2.4GHz, 5GHz and 6GHz frequency bands. It means that one client device will be able to access the access point simultaneously on each of the 2.4GHz, 5GHz and 6GHz frequency bands. According to Intel, by adopting MLO, the maximum data communication speed of Wi-Fi 7 may be 7.2 times that of Wi-Fi 6. In addition, MLO seems to have the advantage of reducing latency as well as other technologies.
In addition, the Automated Frequency Coordination (AFC) system, a technology for maximizing the use of the 6 GHz frequency band, has evolved and can be used on more devices than Wi-Fi 6E, and signal strength and connection reliability are also expected to improve.
Also, 4K QAM (4K Quadrature Amplitude Modulation), which is supported by Qualcomm's Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E compatible products, will be standard with Wi-Fi 7. QAM is a technique for packing more data into a single signal. Wi-Fi 6 was compatible with 1K QAM, but by supporting 4K QAM in Wi-Fi 7, the peak value of the data rate will increase by up to 20% and the maximum communication speed will also improve by 20%.
Considering these fine numbers, Android Police said, ``Wi-Fi 7 products should be about four times faster than Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E products, and if you use compatible devices, you will be able to communicate more reliably even in places where radio waves are congested or where Wi-Fi communication has been difficult.
Related Posts: