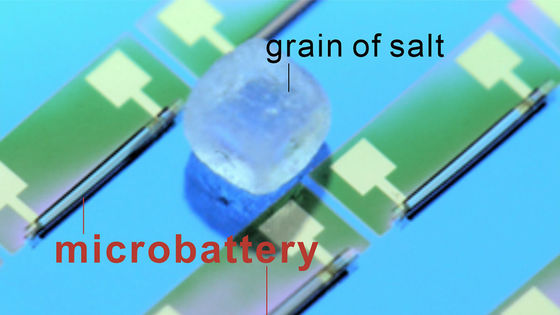
Introducing a glucose battery that gets power from glucose in the body

An ultra-thin battery was devised that absorbs glucose from the human body and converts it directly into electricity. It is expected to effectively power implant devices to be implanted in the body.
A Ceramic-Electrolyte Glucose Fuel Cell for Implantable Electronics --Simons ---- Advanced Materials --Wiley Online Library

Ultrathin Fuel Cell Generates Electricity From Your Body's Own Sugar
https://scitechdaily.com/ultrathin-fuel-cell-generates-electricity-from-your-bodys-own-sugar/
It is well known that glucose taken directly by humans and glucose decomposed from carbohydrates are used as energy. The battery designed by Philip Simmons and colleagues at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology is a mechanism that decomposes glucose using an electrolyte and converts it into electrical energy.
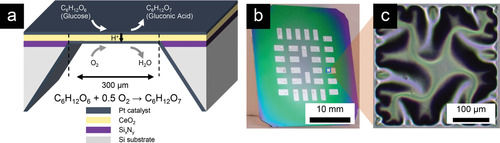
The width of the battery is about 300 micrometers for 30 hairs, the thickness is 400 nanometers, and it is said to generate about 43 microwatts of electricity per square centimeter.
The technology to convert glucose into electrical energy was already devised in the 1960s, but existing batteries were difficult to miniaturize and were made of materials that could not withstand heat sterilization when implanted in the body.
Therefore, Simmons et al. Used cerium (IV) oxide , which has excellent heat resistance, ionic conductivity, and electron conductivity, as a material to solve the problem. The newly designed ceramic-based glucose fuel cell can withstand up to 1112 degrees Celsius and is thought to be able to coat implant devices and other devices to effectively power it.
Related Posts: