Even though there is no kelp, you can make a sustainable water purifier with 'SCOBY', the raw material for a mysterious fermented drink called 'Kombucha'.
by
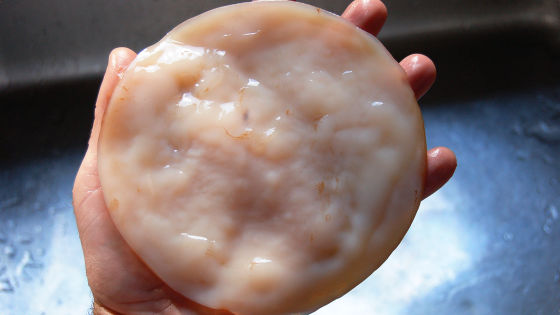
The popular drink 'Kombucha' in Europe and the United States is associated with kelp, but it is actually a drink that has nothing to do with kelp. Kombucha, known in Japan as ' black tea mushrooms, ' is a beverage fermented by adding sugar to black tea or green tea and soaking a mushroom-like gel-like mass cultivated in a medium. Research results have been announced that this mass called 'SCOBY (Symbiotic Culture of Bacteria and Yeast)' has been successfully made into a more effective biofilter than a commercially available water purification filter.
Kombucha cultures make excellent sustainable water filters, study finds | Ars Technica
https://arstechnica.com/science/2022/01/kombucha-cultures-make-excellent-sustainable-water-filters-study-finds/
Kombucha is not well known in Japan, but in 2020 it also appeared in Asahi Soft Drinks. You can read about the appearance, taste and aroma from the following articles.
Even though there is no kelp, the mysterious fermented drink 'KOMBUCHA' called 'Kombucha' has appeared in a limited quantity and limited to FamilyMart, so I tried it --GIGAZINE

In a new study, Montana Institute of Technology and Arizona State University have shown that this kombucha ingredient can be used to create filters that are more effective at filtering water than commercial filters.
Kombucha is usually made using 'SCOBY', a cellulosic fiber medium in which bacteria and yeast are cultivated.
Amazon | Organic JAS Organic Kombucha Starter Kit SCOBY 2 Pieces Set [Kombucha Culture Kit / SCOBY 2 Pieces and Japanese Instruction Set * No Tea Leaves] (243 grams x 2) | WORLD KOMBUCHA | Vegetable Juice Fruit juice mail order

SCOBY is also attracting attention as a new biomaterial. For example, in 2021, researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and Imperial College London developed bioconstituents that could be used as biosensors from SCOBY.
Researchers at MIT and Imperial College London used laboratory-grown brewer's yeast ' Saccharomyces cerevisiae ' instead of wild yeast to create biomaterials. It is said that SCOBY's 'parent' was created by culturing Saccharomyces cerevisiae with a bacterium called Komagata Ebacter Rhaeticus. Then, by manipulating yeast cells, we succeeded in detecting and decomposing estradiol , which is a pollutant, and luciferase, which is a bioluminescent protein. In addition, the research team showed that it is possible to have various functional characteristics by exchanging strains.
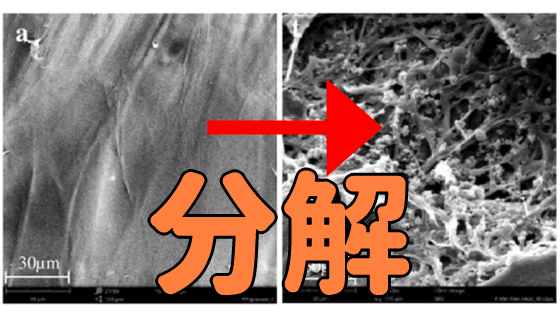
The new research results announced by Montana Institute of Technology and Arizona State University follow the above research. Contaminated drinking water kills many children around the world. Filters for removing bacteria, parasites, and viruses are commercially available, but these filters eventually become clogged, making it impossible to filter water. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop a filter that prevents the adhesion of oil, clay, minerals, and bacteria that cause clogging. And as a method to prevent the 'growth of bacteria' that causes clogging, a filter using SCOBY was devised.
Comparing SCOBY filters with commercially available filters, both filters became clogged over time. However, the SCOBY filter used in the experiment recorded 19-40% better performance than the commercially available filter. In addition, SCOBY's filter is resistant to dirt, and although it eventually clogged, the number of bacteria that propagated was less than that of commercially available filters.
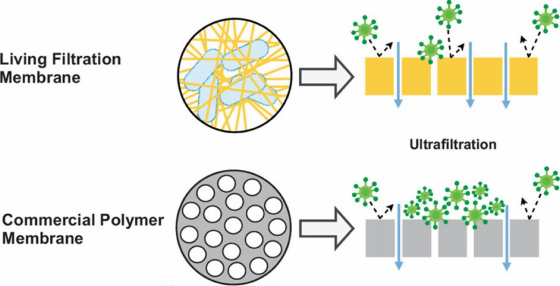
In the experiment, the genus Acetobacter , which is abundant in kombucha, was bred in SCOBY. The genus Acetobacter is used in the production of vinegar and is known for its antibacterial properties. The researchers believe that this property prevented the growth of bacteria in SCOBY's filters.
Related Posts: