What is 'JO-4.02' that was able to secretly perform voice communication across the borders of East and West Germany?

The 'JO-4.02 ' is an optoelectronic audio transceiver developed by the German optical equipment manufacturer '
JO-4.02
https://www.cryptomuseum.com/covert/opto/jo402/index.htm
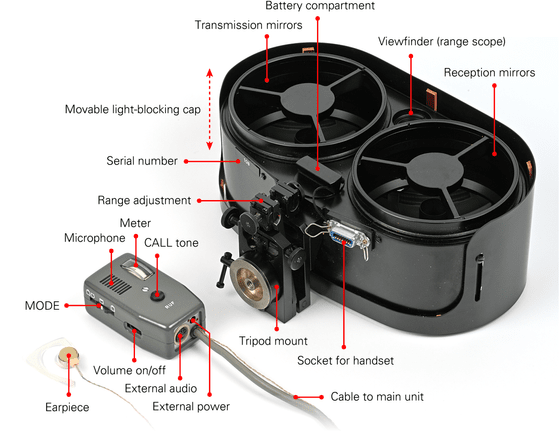
JO-4.02 is a transceiver with an oval housing measuring 315 mm in length x 340 mm in width x 120 mm in depth. It weighs 4346g and occupies most of its body with two large conical mirrors.

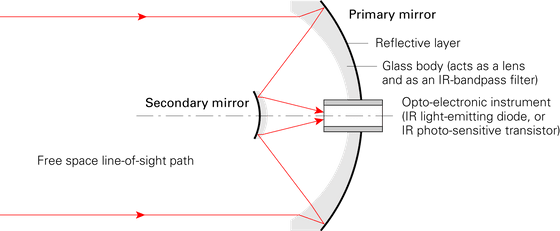
One of the two mirrors is for reception and the other is for transmission. Each mirror has two mirrors, a primary mirror and a secondary mirror, and the mirror surface has a glass finish that functions as a filter or lens. In the center of the primary mirror is a light source that emits infrared rays or a detector that receives infrared rays.
A 14-pin connector for connecting the handset and a mount for connecting to a tripod protrude from the bottom of the housing. The handset is equipped with a volume control knob and earpiece, and you can make a voice call by connecting it to the main unit via a cable. The recommended communication distance when communicating between JO-4.02 is about 5km.
In 2014, three German ham radio operators restored JO-4.02, and the audio of the test communication can be heard from this link. In addition, at this time, it is said that communication at 14 km (PDF file) was successful .
Related Posts:
in Hardware, Posted by log1p_kr