What exactly is 'UEFI' that replaces the BIOS that runs when the PC boots?
by
One of the system requirements for Windows 11 released on October 5, 2021 is 'UEFI, Secure Boot Support'. UEFI is a program that is executed before the OS boots on the PC like the conventional BIOS, but as the PC equipped with the conventional BIOS is out of the operation target of Windows 11, UEFI and the conventional BIOS What you are doing in is completely different.
Differences Between UEFI and BIOS, and Which One You Should Use?
https://www.maketecheasier.com/differences-between-uefi-and-bios/
What's The Deal With UEFI? | Hackaday
https://hackaday.com/2021/11/30/whats-the-deal-with-uefi/
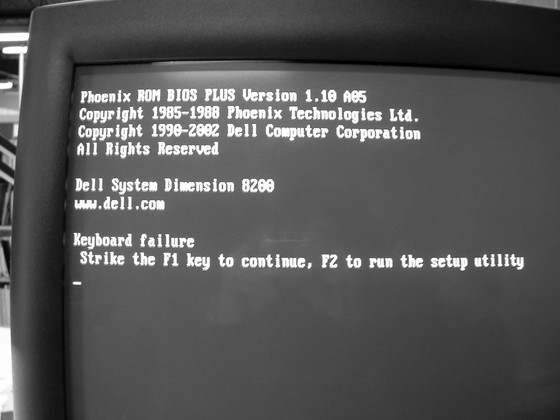
BIOS is an abbreviation of 'Basic Input / Output System' and is the firmware stored in the ROM on the motherboard of the PC. When you boot your PC, the BIOS program written to the ROM boots, initializes the hardware, controls hardware devices such as the keyboard, mouse, CPU, and storage device, and calls the OS boot loader. increase. In other words, the BIOS acts as a bridge between the hardware boot and the OS boot. The BIOS manages partitions with a special storage area called the Master Boot Record (MBR), but the MBR can manage up to 4 partitions and has a maximum disk capacity of 2TB.
by
UEFI is an abbreviation of 'Unified Extensible Firmware Interface', which is a specification set by an organization called 'United EFI Forum ' and is based on EFI (Extensible Firmware Interface) developed by Intel and Hewlett-Packard (HP). .. Both UEFI and BIOS are seemingly 'programs that run before the OS boots', but the actual tasks they are performing are different.
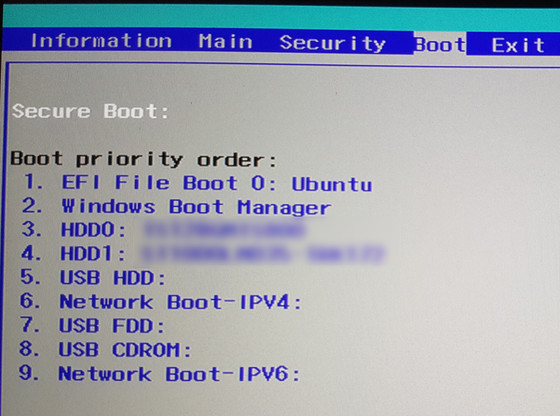
UEFI supports a partition format called GUID Partition Table (GPT). GPT can manage up to 8 zettabytes (8 billion TB) according to the specifications, and the maximum number of partitions is 128. In addition, UEFI is a mechanism that stores all information related to initialization and booting in a special area called the EFI system partition provided on the HDD or SSD. This EFI system partition also contains the boot loader for the OS installed on your computer. UEFI is platform independent, which has the advantage of slightly faster boot times for your PC in some cases.
by
EFI and UEFI were developed by Intel and are designed for x86 processors. The x86 is an instruction set architecture developed for the Intel 8086 , a 16-bit microprocessor, and because the Intel 8086 was given a 20-bit memory address space, there was a 1MB memory limit. After that, the processor evolved steadily, such as IA-32 which expanded the x86 architecture to 32 bit and x64 which expanded to 64 bit, but all x86 processors are compatible with Intel 8086 at startup to emphasize compatibility. It works in real mode .
The BIOS works by reading the address of the next device to initialize and the first sector of the hard disk that contains the code to execute. Also, select and initialize the boot device for booting the OS. However, since the BIOS operates in a 16-bit environment in real mode, the amount of code that can be read and executed from ROM is subject to a memory limit of 1MB. Also, since the BIOS basically operates only in a 16-bit environment, there is a restriction that a low-level language such as an assembler must be used for its development, even though the program becomes complicated due to the progress of hardware for each motherboard. It was also a matter of concern that the difficulty was high.
Intel tried to develop EFI in 2000 because it thought that this BIOS should be abolished and replaced with new firmware. UEFI can operate in 64-bit mode from the beginning, so memory restrictions have been removed, secure boot to prevent malicious code from being executed before the OS loads, and drives with built-in encryption. You will be able to use the security function. Another big advantage is that the firmware can be coded in high-level languages such as C ++ and Rust.
by Cathy
However, at that time, the problem of compatibility between 64bit and 32bit was not solved, and the 64bit machine itself was not widely available in the market, so EFI was not attracting attention. Therefore, Intel launched the United EFI Forum in 2005 to publish the EFI specifications and renamed it UEFI. Various manufacturers such as AMD, IBM, and Microsoft also participated in the United EFI Forum, and UEFI specifications were developed. Microsoft released Windows XP Professional x64 Edition in 2005 when it announced UEFI.
UEFI received a lot of attention from the market in 2011, when Intel's second-generation Core processor, Sandy Bridge, was introduced, and motherboards compatible with the Sandy Bridge generation introduced UEFI instead of the legacy BIOS. As a result, the recognition of UEFI has increased. It's also affected by the fact that more than 2TB of storage began to be sold at affordable prices around the same time.
In addition, in 2017 Intel announced a policy to remove the BIOS compatible module Compatibility Support Module (CSM) from UEFI. This CSM was for executing 16-bit code written for legacy BIOS on UEFI, and it was possible to emulate the BIOS with CSM. However, leaving compatibility with legacy BIOS not only curbs the spread of UEFI, but also continues to carry security risks.
However, Hackaday, a tech news site, said, 'The biggest complaint about UEFI is that it's a closed black box. UEFI is accessing your computer unknowingly and after the OS boots. Is also resident in the HDD. ' In addition, although updating UEFI is easier than BIOS, if the system does not start up due to an update mistake, it is physically impossible to repair, so the risk is also high.
Related Posts: