Why are Chinese companies driving the development of digital infrastructure in African countries?

by
In recent years, Chinese companies have shown a willingness to strengthen their ties with African countries and are investing heavily in building digital infrastructure. He is the editor of the Rest of World, an international non-profit journalism organization, on why Chinese companies are driving the development of Africa and the problems of African countries wanting to promote 'digital sovereignty' to deepen their ties with China. Yinka Adegoke explains.
The real reason China is pushing “digital sovereignty” in Africa
https://restofworld.org/2021/the-real-reason-china-is-pushing-digital-sovereignty-in-africa/
Senegal Macky Sall President 2021 June, the capital of Dakar along with the establishment of the National Data Center, which was built in the suburbs, and to move the government data and digital platform from the foreign server to the National Data Center was mentioned . The move aims to strengthen Senegal's 'digital sovereignty,' but construction costs of 46 billion CFA francs (about 9 billion yen) are covered by Chinese loans, and equipment and technical support are provided by Chinese companies. It was provided by Huawei.
Adegoke points out that some may find contradictions about Senegal's declaration of 'digital sovereignty' made possible by China's technology offerings and lending. However, in the last 20 years, China has deepened relations in the field of communication technology in almost all African countries, and Senegal's national data center is only one aspect of a broader problem.
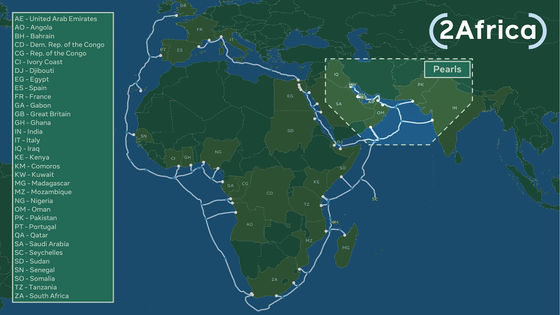
China and African countries hold an official forum called the Forum on China-Africa Cooperation (FOCAC) every three years from 2000, and at the 2018 FOCAC, China will support major infrastructure projects throughout Africa. I made a promise. Under the Belt and Road Initiative, a wide-area economic zone initiative promoted by China, this will total $ 60 billion in loans and grants from Chinese financial institutions, including the China Export-Import Bank , which provides policy lending. Approximately 6.8 trillion yen) is expected to be provided.
In 2015, as part of the Belt and Road Initiative, China launched the 'Digital Silk Road Initiative, ' which promotes the digitization of overseas countries under the leadership of China. The Digital Silk Road Initiative includes all digital-related fields such as international electronic commerce, smart cities, fintech apps, big data, IoT, smartphones, and submarine cables. It is aiming to introduce Chinese technology as standard.

Motolani Agbebi, a researcher at the University of Tampere, Finland, points out that China's involvement in the African telecommunications sector has been in place since before 2015. As early as 1999-2001, Huawei and ZTE started their activities in African countries with the support of China's foreign policy. In recent years, with the pandemic of the new coronavirus, the importance of remote work and distance education has increased in Africa as well, and as a result, the importance of the Digital Silk Road concept for China has also increased.
In recent years, as more and more countries are concerned about China's growing international influence, we will build huge physical infrastructure in developing countries, such as railroads and airports, which can be done by investing huge amounts of government funds. The project is under close scrutiny. Agbebi could appear to be more politically neutral because digital infrastructure is somewhat more costly than physical infrastructure, which African countries often cannot afford on their own. I pointed out that there is.
Analysts say that by playing an essential role in digital transformation in African countries, China will be able to build a solid foothold in global affairs and create new economic opportunities for Chinese companies. I think it can be done.
Africa accounts for nearly 17% of the world's population, while it accounts for less than 1% of the world's data center capacity, making it a market that is expected to grow with future digital transformation. In addition, the situation that Huawei and ZTE are subject to various restrictions from Western countries such as the United States is also one of the factors that increase the importance of African countries as economic zones for these companies. In fact, many digital projects in African countries are led by Chinese companies and entrepreneurs, and the Chinese government often supports them later in the form of loans, said policy analyst Ovigwe Eguegu. I am.
The China-related companies with a strong influence in African countries, to sell more than half of the smartphone in Africa conductive hearing Technology (Trang Sion) and, like entrepreneurs in the circumferential shed Nigeria electronic payment company, of which Mr. involved OPay is Can be mentioned.
Chinese IT companies are revolutionizing FinTech in Africa-GIGAZINE

'It's up to African policy makers and governments to keep Chinese companies out of full control of the digital ecosystem. This caution applies to all foreign partners, but China. The depth of relations between high-tech companies on the African continent means that China is in a very strong position to harness the government's geopolitical influence. ' Hannah Wanjie Ryder, an analyst who has been closely watching the relationship between China and Africa for many years, said that African companies are not just inviting Chinese technical experts, but are launching joint ventures with Chinese companies. He argued that it was necessary to guarantee the transfer of knowledge, the maintenance of corporate control, and the sharing of intellectual property.
Related Posts:
in Note, Posted by log1h_ik