What is the impact of space debris caused by Russia's 'satellite destruction with missiles'?

On November 15, 2021, it was reported that a large amount of
New images and analyzes reveal extent of Cosmos 1408 debris cloud | Ars Technica
https://arstechnica.com/science/2021/11/new-images-and-analyses-reveal-extent-of-cosmos-1408-debris-cloud/
Russian anti-satellite weapon test: What happened and what are the risks?
https://theconversation.com/russian-anti-satellite-weapon-test-what-happened-and-what-are-the-risks-172016
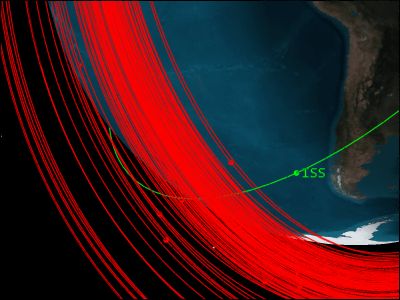
On November 15, 2021, US Secretary of State Antony Blinken issued a statement that 'Russia destroyed an artificial satellite with a missile, causing a large amount of space debris.' The destroyed artificial satellite is the communication interception satellite 'Cosmos 1408 ' launched during the Soviet era, and stayed at the ISS because there was a danger that space debris generated from this satellite would collide with the International Space Station (ISS). It was developing into a situation where the astronauts were evacuated.
'Russia shot down an artificial satellite with a missile,' the US State Department announced, astronauts are evacuating due to a large amount of space debris already occurring --GIGAZINE

Experts have reported on the effects of space debris caused by the destruction of Cosmos 1408 above. For example, Space Nav , a space-related analysis company, analyzed the distance between space debris and the surface of the earth. It became clear that Based on SpaceNav's analysis, tech news site Ars Technica said, 'Most of the space debris is concentrated on the 400-450km section. This is consistent with the altitude of the ISS, so astronauts staying on the ISS. It can be said that the evacuation was a proper decision. '
Updated orbital element distribution from the COSMOS 1408 ASAT event. Pic.twitter.com/E1VZKuSNn5
— SpaceNav (@ SpaceNav2) November 18, 2021
Professor Hugh Lewis , a physics researcher at the University of Southampton, also analyzes the time it takes for space debris from Cosmos 1408 to enter the atmosphere. If you look at the graphs posted on Twitter by Professor Lewis, you'll see that while many space debris plunge into the atmosphere in a few years, some continue to float in space for decades.
Also from the # Kosmos1408 simulation: re-entry predictions or, if you read the graph another way, prediction of the longevity of the debris cloud. Looks like several years before most of the fragments in the simulation re-entered & decades before they were all gone. pic.twitter.com/6zZtojkgJs
— Hugh Lewis (@ProfHughLewis) November 15, 2021
In addition, Professor Wendy Whitman Cobb, who studies strategy and security at the U.S. Air Force University , said, 'Space debris is a serious problem regardless of the cause.' The danger of this is increasing, and certain orbits can become completely unusable. It can take decades before this happens, but this time Russia's satellite destruction is a situation. Increased the likelihood of occurrence. '
Related Posts:
in Note, Posted by log1o_hf