Introducing data storage that can pack up to 500TB in CD size

Blu-ray discs, which have emerged as the successor to DVDs, are large-capacity storage media that can store 25GB of single-layer discs and 50GB of dual-layer discs. Furthermore, by applying nanoscale processing to glass with a laser, data can be written at a density 10,000 times higher than that of Blu-ray discs, and a technology that can be stored for a long time has been announced.
High speed ultrafast laser anisotropic nanostructuring by energy deposition control via near-field enhancement
High-speed laser writing method could pack 50 | EurekAlert!
https://www.eurekalert.org/news-releases/932605
With the spread of convenient clouds, the amount of data generated around the world is exploding, but HDDs, which consume a lot of energy and have a short life, are mainly used for storage in data centers that process such data. In addition, conventional optical discs such as CDs and DVDs have a small capacity, and advanced DNA storage that can write 100 TB or more per gram has a problem of difficulty in durability.
In the past, '5-dimensional data storage ' that writes data to glass with a laser was developed to solve the problems of life and durability, but it is not very practical because the data writing speed is slow and the capacity is not so large. It wasn't.
Introducing '5-dimensional data storage', a data storage that can be used forever without a lifetime --GIGAZINE

A research team led by Yuhao Lei, a postdoctoral fellow at the University of Southampton in the United Kingdom, who set out to improve this problem, used a 'high-repetition femtosecond laser ' to form small nanostructures of 500 x 50 nanometers on glass. I did. At this time, the research team used an optical phenomenon called 'near-field enhancement' instead of writing directly on the glass with a femtosecond laser. This method of forming nanostructures using weak light pulses has made it possible to minimize thermal damage, which has been a problem when using high-repetition lasers.
Birefringence occurs due to the anisotropy of nanostructures, which allows you to control the 'orientation' and 'size' of nanostructures written on glass. By combining this optical 2D and spatial 3D writing, the research team has succeeded in creating a writable 5D data storage that is faster than before.
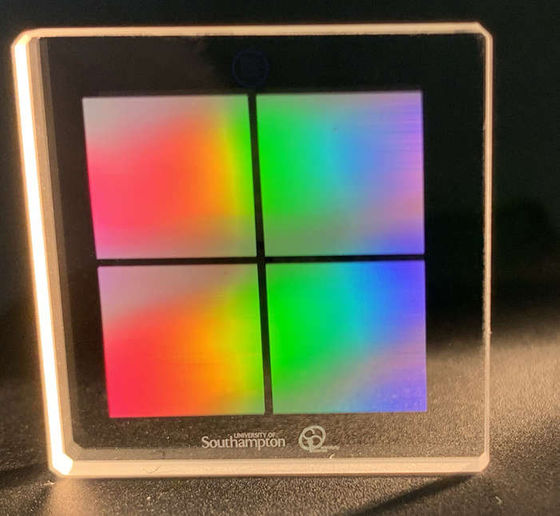

by Yuhao Lei and Peter G. Kazansky, University of Southampton
'This new approach has brought data write speeds to practical levels, allowing large data to be written in a reasonable amount of time. This technology is superior to highly localized nanostructures. Not only can we achieve data capacity, but we can also reduce energy consumption by adopting pulsed light that can be written with relatively low energy. '
Using this technology, the research team was able to write 5GB of text data to a glass disc the same size as a regular CD with almost 100% accuracy. If the system is further improved in the future, it will be possible to write 500 TB of data to a CD-sized glass disc in about 60 days. Since 5D data storage has the advantage of being able to store data semi-permanently, Lei said, 'The cloud is supposed to store data temporarily, but 5D data storage using glass. We believe it will be useful as long-term data storage for national libraries and museums. '
Related Posts:
in Hardware, Posted by log1l_ks