Research results show that rattlesnakes 'fool the other person's ears into misunderstanding the sense of distance' by changing the sound they make.

Frequency modulation of rattlesnake acoustic display affects acoustic distance perception in humans: Current Biology
https://www.cell.com/current-biology/fulltext/S0960-9822(21)00973-8
Rattlesnake rattles trick human ears
https://phys.org/news/2021-08-rattlesnake-rattles-human-ears.html
Rattlesnake rattles use auditory illusion to trick human brains | Live Science
https://www.livescience.com/rattlesnakes-trick-brains-auditory-illusion.html
One day, when Professor Boris Chagnaud, a neurobiologist at Ludwig Maximilian University , approached the rattlesnake in the laboratory, he noticed that the rattlesnake's sound changed along the way. When I was curious and checked, I found that the sound that was small and low frequency when I was relatively far from the rattlesnake suddenly became louder and the frequency became higher as it approached a certain range. It was said that. When he left the rattlesnake again, the sound and frequency gradually returned to normal.
Intrigued by the changes in rattlesnake sound, the research team of Chanaud and colleagues actually conducted experiments with rattlesnakes. You can see the state of the experiment and the change in the sound of the rattlesnake by watching the following movie.
Adaptive rattling fools distance perception / Curr. Biol., Aug. 19, 2021 (Vol. 31, Issue 19) --YouTube
At the tip of the rattlesnake's tail, there are a number of hard knots made of keratin, and by shaking the tail, the knots rub against each other, making a sound that sounds like 'sharp' or 'rattle'. This sound is believed to have the purpose of informing other animals of their existence and avoiding danger.

If you play the rattlesnake making a sound at a speed 12.5 times slower than usual, you can clearly see that the tip of the tail is shaking.

In addition, the rattlesnake can change the loudness and frequency of the sound by changing the speed at which the tail trembles. At first, it was a sound that showed the timing of shaking the tail with 'rattle' ...

As you increase the speed of shaking, it will change to a 'jerking' sound.

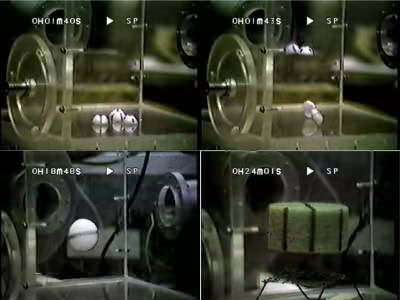
The research team of Chagnaud et al. Conducted an experiment to investigate how various objects approach the rattlesnake in order to investigate whether the sound of the rattlesnake changes with the approach of the object.

In the experiment, the approaching object was reproduced with 'shadow projected on the wall by a projector'. The shadow that was small at first ...

It will get bigger and bigger.

Eventually, the rattlesnake shook its tail and began to make noises ...

At some point I suddenly changed the volume and frequency of the sound. According to the research team, the frequency of the sound was 40Hz at the maximum until the middle, but when the object approached to some extent, it suddenly jumped to the magnitude of 60 to 100Hz. In additional experiments, it was also found that it was not the size of the object that affected the change in the rattlesnake sound, but the 'speed at which the object approached.'

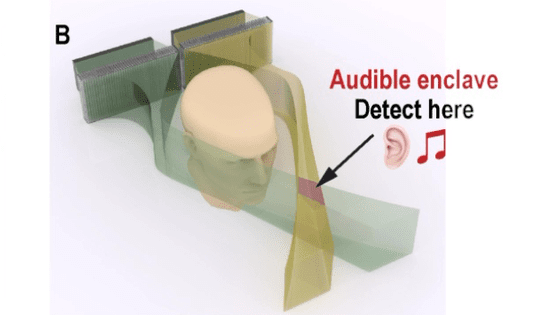
To find out why the rattle snake changes its sound in response to the approach of an object, the research team virtually constructed a 'grassland where the rattle snake is hiding' in the VR space, and asked 11 subjects to walk in the VR space. I conducted an experiment. In the experiment, subjects were instructed to approach the rattlesnake and stop at the point where they thought they were one meter away from the rattlesnake.

The 'virtual rattlesnake' prepared by the research team is programmed to make a sound at 5 to 20 Hz when the subject is in the range of 8 to 4 meters, and to raise the frequency to 70 Hz at once when approaching within 4 meters. rice field. As a result of the experiment, all the subjects misunderstood the sense of distance due to the change in the rattlesnake sound, and stopped at a place more than 1 meter away. On the other hand, if the subject did not change the frequency when approaching the virtual rattlesnake, the subject was able to recognize the distance between the rattlesnake and himself with much higher accuracy.

From this result, Chagnaud believes that rattlesnakes misunderstand the sense of distance by changing the sound that sounds according to the approach of the other party, creating a 'safe distance margin'. 'Rattlesnakes have not only made noises to appeal their presence, but have also evolved an innovative solution, similar to a distance alarm when driving a car in the back,' said Mammals. He argued that rattlesnakes may have evolved ways to deceive mammals as a result of repeated encounters with large mammals.

Related Posts: