Why is it difficult to make 'skin' look real with computer graphics?

In recent years,
Why it's so hard to make CGI skin look real --YouTube
The following is a list of scenes where the main characters awaken in 'Final Fantasy Movie ' released in 2001 and 'Alita: Battle Angel ' released in 2019. There is a gap of about 20 years between the two films, and the footage shows that there was a big breakthrough in CG.
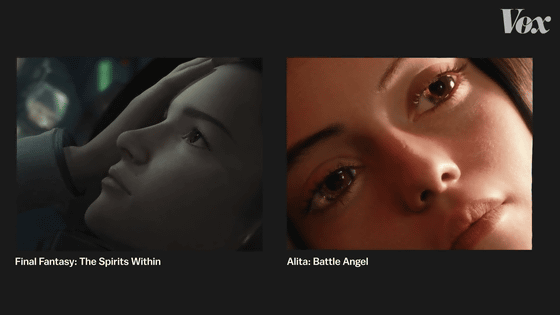
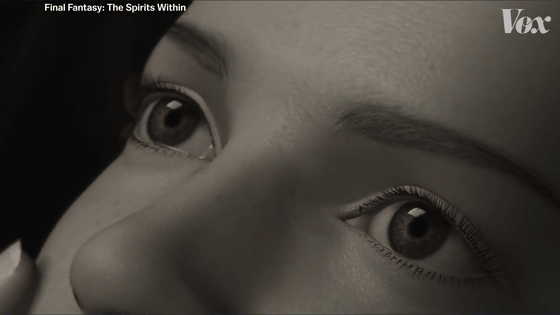
The movie version of FINAL FANTASY is one of the oldest movies in which CG-drawn realistic humans appear.

Even though they are 'real humans,' for us in 2021, the characters in the movie FINAL FANTASY have no life, frankly, like the characters in the game, because of their movements and textures. Vox points out that it looks like.
Arita: Battle Angel characters, on the other hand, have eyes and mechanical bodies that are far from real, but are closer to real humans in terms of skin.

Nick Epstein ofNew Zealand's VFX specialist Weta Digital answers the question, 'How did you get the skin to look more realistic?' Epstein was the supervisor of the visual effects division of Arita: Battle Angel and the lead technical director of Avatar.
Arita: Battle Angel is

The reality is the difference between heaven and earth from the 2001 'The

Compared to The Mummy 2, Arita: Battle Angel is a CG that is much closer to the performer.


'That's why we decided to create a full-body digital version of Rosa Salazar and apply realist elements and barometers later.'
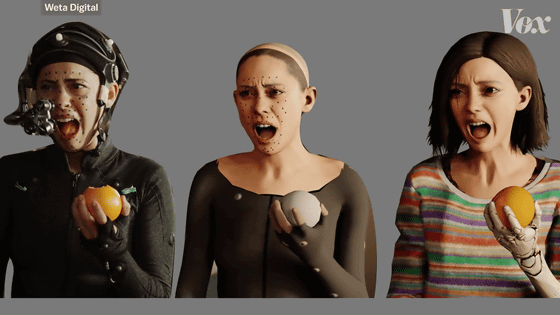
According to Epstein, there are four types of realist elements that he applied later: '

Albedo refers to the

Epstein and his colleagues created a skin color map from the actual Rosa Salazar, and made adjustments to modify the color tone based on Alita's mood and physical condition. For example, in the scene where Arita is angry, the cheeks and forehead are redder and the appearance of blood on the head is reproduced.

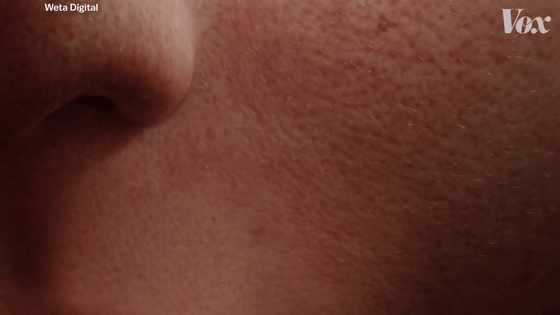
Displacement is a technique that gives the skin a realistic feel such as greasiness by adding pore-level drawings. If you zoom in on Arita's skin, you'll see countless wrinkles.
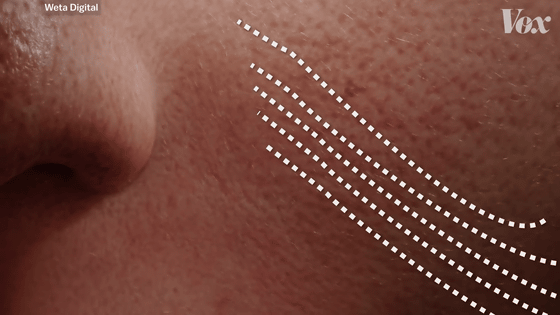
'I'm not happy to see me in the camera, but my forehead is shining strongly, my nose is shining a little, but my cheeks aren't shining very much.'

'Each part of the face has a'line of the same glow'. Along these lines, the effect is actually applied.'
Next, 'Subsurface' will be explained by Henrik Wang Jansen, chief scientist of Luxion, who creates

Mr. Jansen specialized in the angle of reflection when light passes through the surface of an object. Janssen proved that every CG looks real when this reflection angle is simulated quickly, which has greatly contributed to the breakthrough of the entire video industry.

For example, when irradiated with laser light, the spoon reflects all the light, but human skin transmits part of the light. Mr. Jansen conducted basic research to apply this concept to CG.


For example, the full CG animation movie '

'In Shrek, there is a

For this reason, Jensen wrote a treatise on simulating subsurface scattering in milk. This treatise was passed on to Shrek's creators, and the sequel '
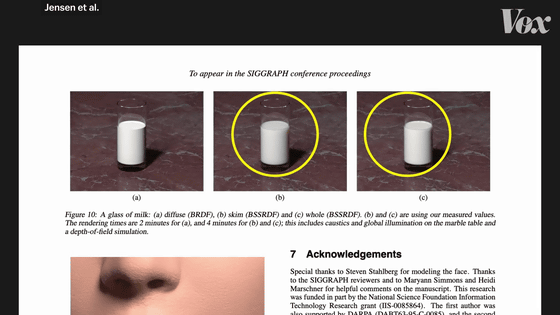
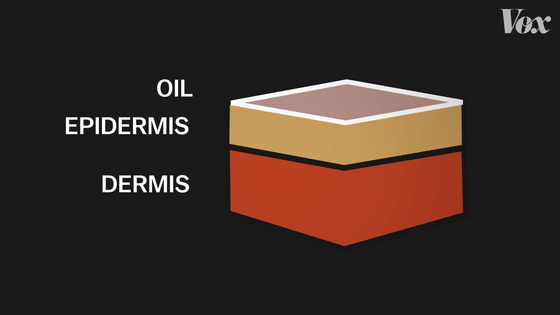
Subsurface scattering occurs on the skin as well as milk, but very early algorithms were designed to produce the same surface scattering on and inside the skin. Therefore, Mr. Jensen applied the idea that human skin has three layers: 'fat', 'epidermis', and 'dermis'.
In addition, we created an algorithm that causes different surface scattering depending on the color depth of the skin.

'This study has made it more compelling to render human skin.'
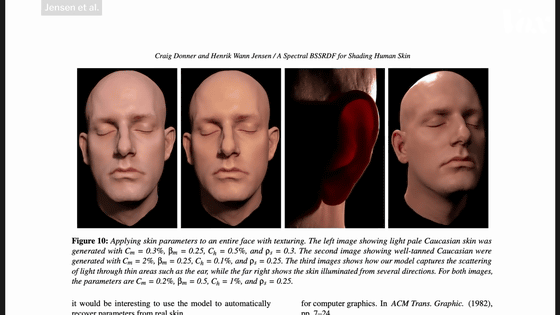
Epstein again talks about the final Dynamic Changes. Dynamic Changes is about facial movements, with Epstein and colleagues scanning Rosa Salazar's face reading aloud a voice-balanced collection of texts called

In the 2001 movie version of FINAL FANTASY, attention was focused on the character's 'eye movement', but in 2019 Alita: Battle Angel, the texture of the skin and the expression of light became a hot topic. 'The only question left is how real it will be,' Vox concludes the movie about this technological advance.

Related Posts:
in Video, Posted by darkhorse_log