A fossil of a mammal that weighs six times as much as an elephant and is taller than a giraffe is found

Many interesting fossils have been discovered, such as
An Oligocene giant rhino provides insights into Paraceratherium evolution | Communications Biology
https://www.nature.com/articles/s42003-021-02170-6
New Discovery Shows Tibet as Crossroads for Giant Rhino Dispersal ---- Chinese Academy of Sciences
https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/life/202106/t20210617_272231.shtml
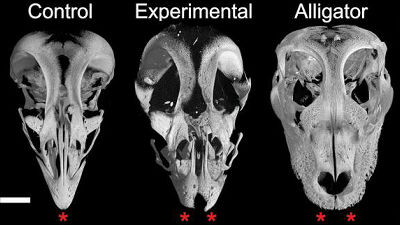
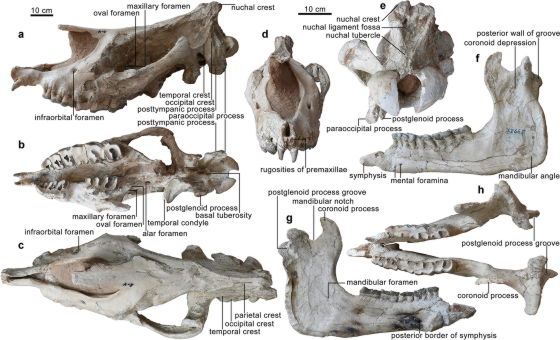
The fossil discovered in Linxia, China this time is one of the ancient rhino family 'Near horn beast ' due to its huge skull with a length of 1.1 meters and characteristic teeth like two fangs. It became clear that it was named 'Paraceratherium linxiaense '. It is also known that the Near Horn Beast inhabited the earth about 26.5 million years ago and had a huge figure with a body length of 8 meters, a height of 7 meters, and a weight of 21.7 tons.
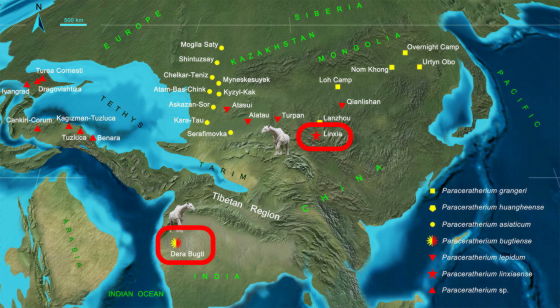
According to the research team, the genus Parakeraterium includes 'P. grangeri,' 'P. huangheense,' 'P. asiaticum,' 'P. lepidum,' which lived in Central Asia (currently around Mongolia and Kazakhstan), and present-day Pakistan. 'P. bugtiense' (red frame in the lower left) that inhabited the western part has been confirmed, and the process and phylogenetic relationship of these species spreading to distant areas have not been clarified. However, the discovery of Parakeraterium linciaense in Linxia City (red frame in the upper right) has clarified the diffusion process and phylogenetic relationship of the genus Parakeraterium.

'The results of this study show that 26.5 million years ago, when the genus Near horn beast was thought to have crossed Tibet, the Tibetan Plateau was lower than it is today and did not become a barrier to the movement of mammals. '.
Related Posts: