Research results show that tens of thousands of droplets are scattered when flushing water in a flush toilet

A computer-based
Aerosol generation in public restrooms: Physics of Fluids: Vol 33, No 3
https://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/5.0040310
FAU | Flushing a Public Toilet? Don't Linger, Since Aerosolized Droplets Do
https://www.fau.edu/newsdesk/articles/flushing-aerosols-study.php
The new coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) is known to spread through aerosols generated by coughing and sneezing of infected people. In addition, since SARS-CoV-2 was also detected in the stools of patients with new coronavirus infection (COVID-19), COVID-19 is a virus contained in the fecal-oral route of infected persons, which causes the oral cavity of other people. It has also been pointed out that the infection may spread through the fecal-oral route , which is transmitted through the virus.
Coronavirus found to be transmitted via feces-GIGAZINE

A research team at Florida Atlantic University (FAU) focused on the fact that 'public toilets are often closed with heavy traffic and poor ventilation,' said a research team at Florida Atlantic University (FAU) who actually installed aerosol measuring devices in public toilets. We conducted an experiment to install it.
You can see the experiment conducted by the research team by playing the following movie.
Research Video of Study Exploring Toilet Flushing Power to Test Risk of COVID-19 Transmission --YouTube
Research staff who install measuring equipment in front of the toilet bowl in a private room of a public toilet. The equipment was installed 5 feet above the floor.

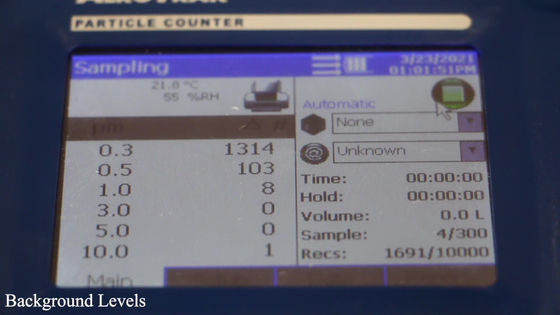
After starting the measurement and waiting for a few seconds, many particles with a particle size of 0.3 to 1 micrometer (µm) were detected even before flushing the toilet. Furthermore, when the staff flushes the toilet ...
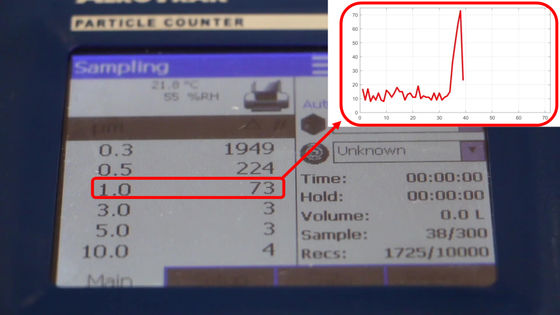
The number of particles has increased rapidly. The rate of increase was 69.5% for 0.3-0.5 µm particles, 209% for 0.5-1 µm particles, and 50% for 1-3 µm particles. Looking at the graph on the upper right, which shows the transition of the number of detected particles with a particle size of 1 µm, it can be seen that the number of particles of relatively large size increases rapidly immediately after running water.
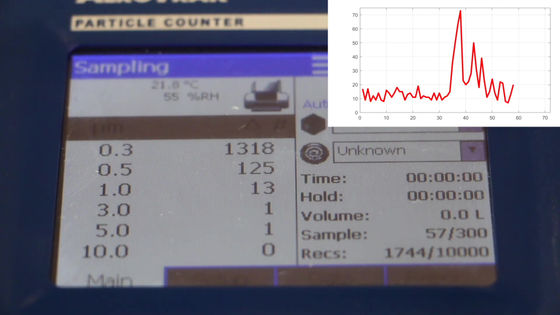
After that, the number of detected particles settled down over several tens of seconds.
Regarding the experimental results, FAU's assistant professor Siddhartha Verma said, 'When we conducted a test in which water was flowed 100 times or more in about 3 hours, the aerosol concentration around the urinal increased significantly, and the total amount of flying droplets generated in each test was several. It has reached 10,000, and even men's urinals have generated a large number of droplets of less than 3 µm. These droplets are so small that they float in the air for long periods of time. If it contains infectious microorganisms, there is a risk of developing an infectious disease. '
When flushing the toilet during the experiment, it was confirmed that the droplets flew up to a height of 5 feet (about 1.52 meters) for more than 20 seconds after the water began to flow. Also, although the number of droplets decreased when the lid of the toilet bowl was closed, there was not much difference from when the lid was opened, so it seems that it is possible that the droplets are popping out from the gap of the lid. ..
Manhar Dhanak, co-author of the paper, said, 'This study allows us to prevent aerosol retention in high-use areas such as public toilets by incorporating'proper ventilation'in the design and operation of public spaces. It was suggested, 'he reiterated the importance of ventilation.
You can understand the 'Ventilation method for COVID-19 measures' published by the Architectural Institute of Japan and the Society of Air Conditioning and Sanitary Engineering by reading the following article.
How should 'ventilation' be performed as a countermeasure against the new coronavirus? --GIGAZINE

Related Posts: