Five aerospace weapons secretly developed by the Soviet Union and Russia

by
In the Cold War of the United States and the Soviet Union, the two countries were engaged in a ' space race ' to compete for manned space flight and artificial satellite technology. Known for its secrecy with strict information control, the Soviet Union has developed various aerospace weapons so that the Western countries do not know, and its existence was revealed after the collapse of the Soviet Union. It was that. Russia's amateur UFO research site 'XissUFO today Space' summarizes some of the aerospace weapons developed by the Soviet Union and Russia.
Space track event's research Космический трэк событий: Declassified spacecrafts and orbital weapons of the USSR – Russia
https://www.xissufotoday.space/2018/04/declassified-spacecrafts-and-orbital.html
◆ 1: Polyus
·spec
Overall length: 37.00m
Maximum diameter: 4.10m
Weight: 80 tons
Launcher:
Input orbit: Altitude 280km, orbit inclination angle 64 °
Aiming device: optics, radar, low power laser
Armed: 1MW output carbon dioxide laser
Polyus is a space weapon designed to destroy US Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI) satellites with a carbon dioxide laser. The Polyus was actually launched in May 1987, but the Polyus separated from the launcher Energia was scheduled to rotate 180 degrees, but in production it rotated 360 degrees, resulting in the atmosphere of the South Pacific. It slowed down inside and burned out. It seems that this failure was caused by insufficient testing of the inertial guidance system due to the hasty production schedule.
In addition, Mikhail Gorbachev , the Supreme Leader of the Soviet Union at that time, decided that 'deployment is not desirable because tensions with the United States are already being eased,' and allowed it to be put into orbit after launch. The theory that it did not exist is also advocated.

by
·spec
Crew: 1 person
Overall length: 8.5m
Overall height: 3.5m
Wingspan: 6.4m
Launch weight: 4220kg
Thrust: 14700kN
The MiG-105 is a manned space flight test aircraft manufactured under the ' Spiral Project' aiming to develop a reusable spacecraft, and was launched into orbit from a launch vehicle navigating at supersonic speeds. The Spiral program had progressed until the actual navigation test was conducted, but in the 1980s, the ' Buran program ' was launched to counter the American Space Shuttle program, and the Spiral program was canceled.
◆ 3: BOR-4
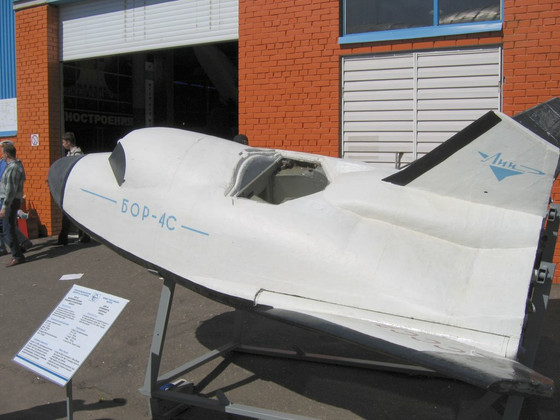

by Jno ~ commonswiki
·spec
Overall length: 3.86m
Overall height: 1.16m
Wingspan: 2.88m
Launch weight: 1450kg
The unmanned experimental aircraft used in the Spiral program are the BOR-4 and other BOR series. The BOR-4 was designed as a smaller version of the MiG-105, and because it had no propulsion device and was an unmanned aerial vehicle, its size was quite small.
Seven BOR-4s were manufactured, four of which have been confirmed to have been launched between 1980 and 1984. The Royal Australian Air Force witnessed the first BOR-4 landing in the Indian Ocean, and a part of the Soviet Union's Spiral program became known to Western countries.
◆ 4: Russian Aerospace Airplane (RAKS)

·spec
Overall length: 7.9m
Wingspan: 3.6m
Launch weight: 2200kg
Fuel (liquid oxygen) load capacity: 18 kg
RAKS was developed by the Russian Aeronautics and Space Administration in 1993 after the collapse of the Soviet Union. The basic concept of the development was 'a hypersonic aircraft using a scramjet engine ', and the Russian Aeronautics and Space Administration aimed to navigate at a speed of Mach 6-14. In addition, it was an experimental aircraft and was not supposed to carry people.
It is unclear what happened to RAKS in the end, but Russia continues to develop hypersonic aircraft even in the 21st century, and hypersonic gliding that can already be equipped with normal warheads or nuclear warheads. It is reported that the deployment of the body ' Avangard ' is in progress. Avangard is said to record a top speed of Mach 27, and President Putin said, 'Because it reaches the target like a meteorite or a fireball, the conventional missile defense system is no longer powerful .'
◆ 5: Kliper

·spec
Number of passengers: Up to 6 at launch, up to 7 at landing
Internal volume: 20 cubic meters
Launch weight: 1300 to 1450 kg
Maximum load capacity: 700 kg
Until then, Russia used the manned spacecraft ' Soyuz ' developed during the Soviet Union era to send crew members to the space stations ' Salyut ' and ' Mir '. As a next-generation manned spacecraft to replace Soyuz, the reusable spacecraft advocated by Russia is ' Kliper '. Kliper is designed on the premise that it has small wings on a plump body and 'enters the atmosphere at an angle that minimizes G on human occupants.'
Kliper was developed with funding from the Russian Aeronautics and Space Administration and the European Space Agency (ESA). The total budget estimated at the time of the announcement was 400 million dollars (about 46 billion yen at the rate at that time), but it is estimated that it actually cost 7 to 8 times that amount. As a result, the budget was constantly in short supply, and the Kliper development plan was decided to be 'indefinitely postponed' in 2006.
Related Posts:
in Vehicle, Posted by log1i_yk








