Proteins associated with Alzheimer's disease found to be regulated by circadian rhythms

It has been pointed out that
Chi3l1 / YKL-40 is controlled by the astrocyte circadian clock and regulates neuroinflammation and Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis | Science Translational Medicine
https://stm.sciencemag.org/content/12/574/eaax3519
Protein involved in removing Alzheimer's buildup linked to circadian rhythm – Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
https://medicine.wustl.edu/news/protein-involved-in-removing-alzheimers-buildup-linked-to-circadian-rhythm/
Biomarker of Alzheimer's found to be regulated by sleep cycles
https://newatlas.com/medical/biomarker-alzheimers-protein-sleep-cycles-rhythm/
The human body is greatly influenced by the circadian rhythm in the body, and various biological processes such as sugar absorption, thermoregulation, immune response, and inflammatory response are controlled by the circadian rhythm. Therefore, it is said that the disorder of the circadian rhythm causes various health problems and illnesses.
Regarding Alzheimer's disease, sleep habits and circadian rhythm disturbances are related to Alzheimer's disease because patients often have sleep problems and patients with sleep disorders are more likely to develop Alzheimer's disease. Many researchers think. A 2019 study showed that 'quality sleep may help increase cerebrospinal fluid flow, wash away waste products associated with Alzheimer's disease, and reduce the risk of Alzheimer's disease.'
Good sleep may help reduce the risk of Alzheimer's disease-GIGAZINE

A research team at the University of Washington, who has previously investigated the link between Alzheimer's disease and sleep habits, pointed out in a 2018 study that disruption of the sleep cycle may be an early sign of Alzheimer's disease. The research team reports that disturbed circadian rhythms accelerate the accumulation of a protein called amyloid β, which is often found in the brains of Alzheimer's disease patients.
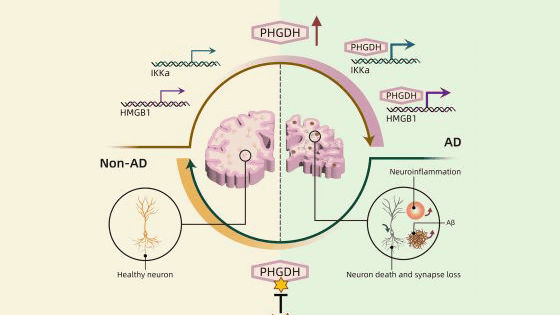
In a new study, we focused on a protein called YKL-40 to understand the mechanism by which circadian rhythm disturbances accelerate the accumulation of amyloid β. YKL-40 is contained in the cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer's disease patients at a high level, and the amount contained increases as the disease progresses, so it is known as a biomarker for Alzheimer's disease.
'YKL-40 was highly regulated by the clock gene that controls circadian rhythms,' said research team associate professor Erik Musiek. I paid attention to it.
After investigating the relationship between YKL-40 and circadian rhythm, it was found that the amount of YKL-40 produced was regulated by circadian rhythm. 'Inflammation in the morning can increase the amount of YKL-40. If the time changes and inflammation occurs in the evening, the amount of YKL-40 can decrease,' Musiek said. ..

Next, the research team used mice with Alzheimer's disease, which tend to accumulate amyloid β, and manipulated the genes in some mice to eliminate the gene that produces YKL-40. A study of the brains of 8-month-old mice revealed that mice that did not produce YKL-40 had about half the amount of amyloid β accumulated compared to mice that normally produce YKL-40. is.
Immune cells called microglia are involved in the removal of amyloid β, and the amount of microglia was large in mice that did not produce YKL-40. In this regard, Musiek said, 'The YKL-40 protein probably acts as a regulator of microglial activation in the brain,' arguing that when YKL-40 is removed, microglia appear to be more activated. doing.
In addition, the research team analyzed data from 778 patients with Alzheimer's disease to determine the association between YKL-40 and Alzheimer's disease. Twenty-six percent of the patients had a gene mutation that reduced the amount of YKL-40 protein, and those with this gene mutation reportedly had a 16% slower decline in cognitive ability than those who did not.
'People have been measuring YKL-40 in cerebrospinal fluid for several years, but I wasn't sure if it worked well or badly,' Musiek said. YKL-40 has bad consequences for Alzheimer's disease, suggesting that people with less YKL-40 have milder symptoms, 'said a future-designed treatment targeting YKL-40. Insisted that there was a possibility.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1h_ik