How many digits does NASA use for pi?
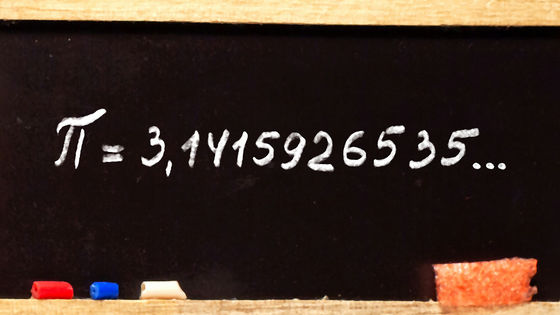
How Many Decimals of Pi Do We Really Need? --Edu News | NASA / JPL Edu
https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/edu/news/2016/3/16/how-many-decimals-of-pi-do-we-really-need/
'Does NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) use' 3.14 'when using pi for calculations, or does it use a value that is about 300 digits after the decimal point?' Is the question that actually arrived at NASA's Facebook.
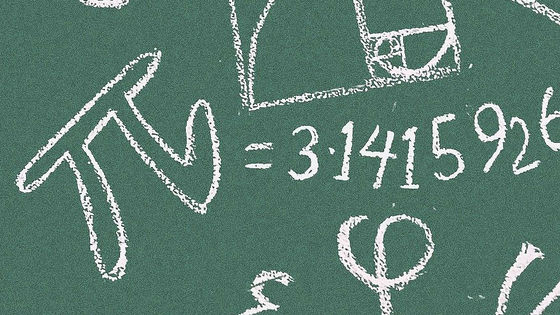
Mark Rayman, NASA's Head of
According to Mr. Rayman, when using pi, decimals are rounded down after considering the error within the allowable range. 'Scientists often don't have to include a lot of numbers after the decimal point in their physical real-world calculations,' Rayman said, using the pi that is actually done at NASA. Explains pi and error with three examples of calculations.
◆ 1: Earth
Considering the circumference of the earth, the diameter is about 7926 miles (about 12,742 km) based on the position of the equator. Using the pi rounded to the 15th decimal place, the circumference of the earth is about 24,900 miles (about 40,000 km). The error that occurs at this time is in nanometer units, which is about the size of one molecule. 'Of course, there are various types of molecules and their sizes, but I hope this case will give you a hint. The error due to the pi that does not increase the number of digits too much is about 1 / 10,000 of a hair. It's just that thin, 'said Rayman.

◆ 2: Voyager 1
Rayman also explained
'If you have a circle with a radius of 12.5 billion miles, and you round the pi to the 15th decimal place, the circumference will be a little over 78 billion miles (about 125,528,830,000 km). The point to be careful is not 'whether the value is accurate' but 'how much error was caused by reducing the number of digits of the pi'. For the pi up to the 15th decimal place There is a slight error in the circumference, but when you calculate the circumference of a circle with a radius of 12.5 billion miles, the error is only about 1.5 inches (about 3.81 cm). Think about it. A circle of 78 billion miles or more. For the circumference, the error is about the length of a human decimal, 'says Rayman.
◆ 3: Space
'Think of the largest possible size, the size of the universe. The radius of the universe is about 46 billion light-years . If the circumference of a circle with a radius of 46 billion light-years is the simplest atom, hydrogen. How many orders of magnitude do we need to have a circumference to accurately calculate an atom diameter of only 0.1 nanometers, ”Layman asks.

According to Rayman, the answer is 'need 39 or 40 decimal places.' 'Think about how fantastically vast the universe is. You can see the darkest, most beautiful, star-filled nights, but the universe is far beyond what we can imagine. And think about the fact that one atom is incredibly small, knowing that you don't have to use tens of digits of pi to cover the entire range, from the atom to the universe. Let's do it, 'says Rayman.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by darkhorse_log