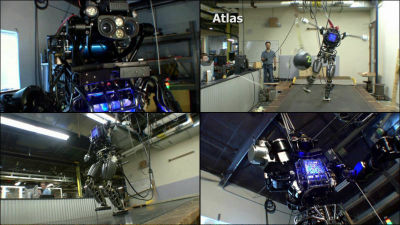
The U.S. Army was developing a '6-legged giant robot' in the 1980s

Speaking of multi-legged walking robots, the four-legged walking robot '
The US Army Spent Millions Developing Giant, Six-Legged Walking Trucks in the 1980s-The Drive
https://www.thedrive.com/news/36157/the-us-army-spent-millions-developing-giant-six-legged-walking-trucks-in-the-1980s
The U.S. Army embarked on the development of multipedal robots decades earlier than Boston Dynamics: ``More than half of the land on the earth passes through tracked vehicles such as trucks and tracked vehicles such as tanks. It was because he regarded it as a problem. In order to solve this problem, the Army, in cooperation with Ohio State University and others, has embarked on the development of a six-legged robot ' Adaptive Suspension Vehicle (ASV) ' operated by one operator.
The ASV project started in 1981 at Ohio State University with funding from the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) . Professor Robert McGhee and Professor Kenneth Waldron of Ohio State University were the center of the project, and it seems that millions of dollars (hundreds of millions of yen) were spent annually for about nine years. And in 1986, the research team developed 'a giant robot with six legs controlled by 17 computers' and succeeded in making it actually walk.
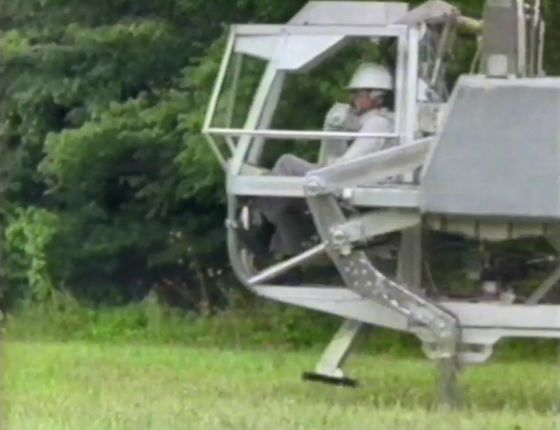
The photo below shows a six-legged robot developed by the research team. One operator rides in the driver's seat in the front and operates, and the rectangular box on the top of the leg is an Intel computer. Each leg is controlled by one computer, and the remaining 11 computers control the display in the cockpit and analyze the data of the pressure sensor of the leg and the distance measuring device attached to the upper part of the cockpit. It was The robot was equipped with an OS consisting of 150,000 lines of source code written in Pascal .

You can see how a 6-legged giant robot is actually walking from the following movie.
Walking on top of the camera...
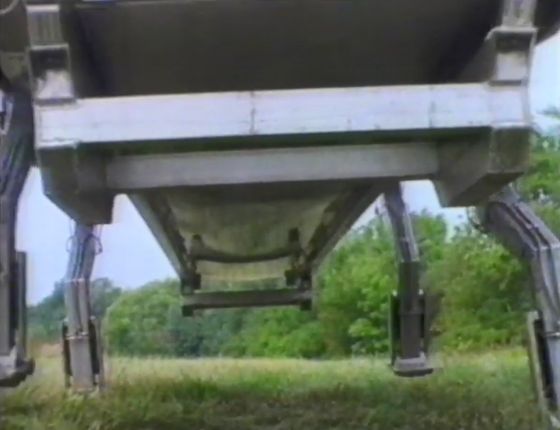

A 6-legged walking robot developed. The hydraulically controlled legs move slowly and walk on dirt on a stable foot.
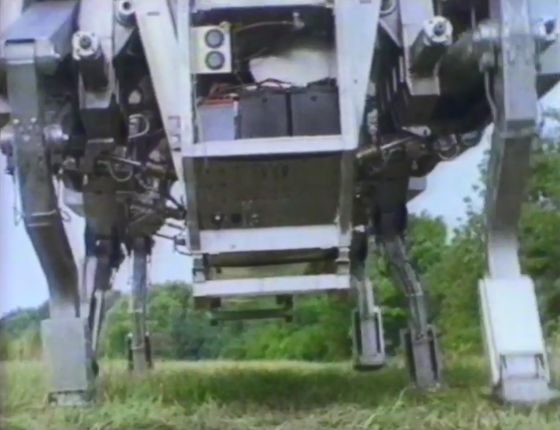

Seeing a person walking from a distance reveals the extraordinary nature of the computer protruding above the legs. The total length is 17 feet (about 5.2 meters), the width is 7.9 feet (about 2.4 meters), and the height is 9.8 feet (about 3 meters).
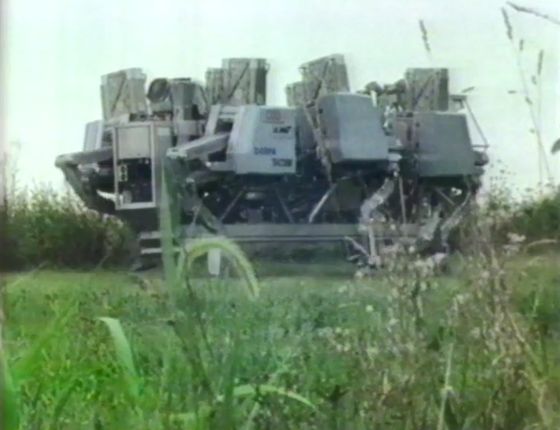

The center of the robot is equipped with a 900cc motorcycle engine, and the peak output is 91 horsepower. The power of this engine was sent to as many as 18 variable displacement pumps through the shaft, moving three legs at a time. The six-legged robot was controlled by a very complex mechanism, with a maximum speed of 8 miles per hour (12.8 kilometers per hour) and a cruising speed of about 4 miles per hour (6.4 kilometers per hour).
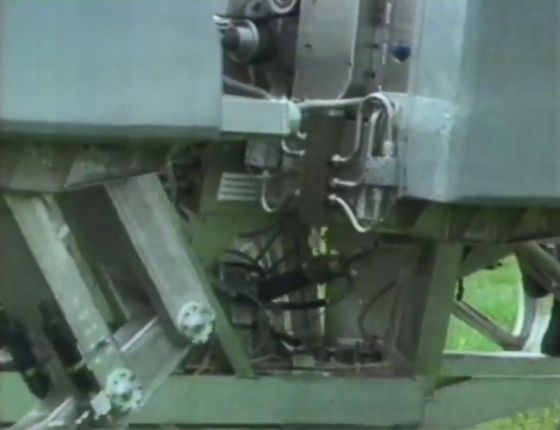

When the operator in the front cockpit instructs the direction to go with the keypad and joystick, the robot will start moving without complicated operations. According to some sources, the research team eventually aimed to develop an 'autonomous walking robot'.

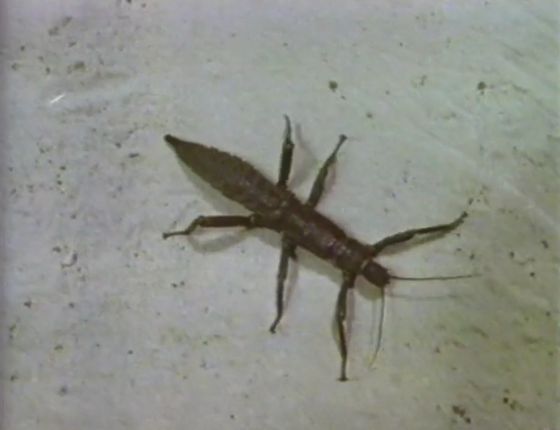
The walking system of the six-legged robot is based on how to walk a bug with a long torso.

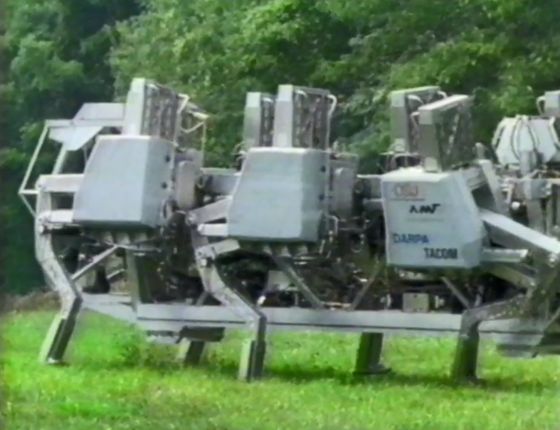
By tilting the base of the leg greatly, you can change the direction without moving back and forth.

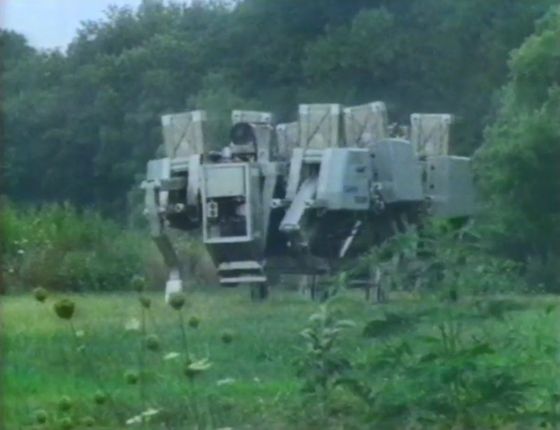
Although it looks high-tech at first glance, in addition to the slow cruising speed and the body weight of 5952 pounds (about 2700 kilograms), it can be loaded only 485 pounds (about 220 kilograms), so it is practical Was very limited. The six-legged robot was able to overcome vertical obstacles with a height of 6.9 feet (about 2.1 meters) and could cross a groove of 23 feet (about 7 meters) in width, but the Army gradually Losing interest, the program was discontinued in 1990.

At the time of writing the article, it is unknown where this six-legged robot is stored, and it is speculated that it may be stored somewhere at Ohio State University if it exists. The Drive reportedly contacted the engineering department at Ohio State University for clues.
Related Posts: