Attempt to protect astronauts from cosmic rays with 'radiation mold' found in Chernobyl

A research team at the University of North Carolina at Charlotte and Stanford University attempted to protect astronauts from radiation flying in space using mold found in the Chernobyl nuclear power plant that caused the worst
A Self-Replicating Radiation-Shield for Human Deep-Space Exploration: Radiotrophic Fungi can Attenuate Ionizing Radiation aboard the International Space Station | bioRxiv
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.07.16.205534v1
Testing Chernobyl fungi as a radiation shield for astronauts
https://phys.org/news/2020-07-chernobyl-fungi-shield-astronauts.html
Chernobyl Fungi To Protect Astronauts from Space Radiation
https://interestingengineering.com/fungi-from-chernobyl-reactor-could-save-astronauts-from-space-radiation
Fungus was discovered from the reactor ruins of the Chernobyl nuclear power plant in February 2020, Aspergillus niger is a kind of (Cladosporium sphaerospermum). This fungus is a large amount of melanin has been contained, not only can survive even in the fatal radiation level, that can be converted into chemical energy by absorbing the radiation report has been.
It was the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) that noticed this mold. High-energy radiation called ' cosmic rays ' is constantly flying in outer space, and it is said that astronauts are exposed to a dose of 0.5 to 1 millisievert per day during their stay at the ISS. Therefore, NASA is studying how to prevent astronauts from being exposed and thought that this mold could be applied.
In cooperation with NASA, a sample of mold found in Chernobyl was sent to the ISS. Then, the mold on one half of the Petri dish with the radiation detector was propagated, and the ISS was observed for 30 days, comparing with the other half that was not propagated.
In the images below, A to I are taken from Petri dishes at 6-hour intervals. It can be seen that the left side is the part coated with mold, and it covers one side in just 48 hours, even in a microgravity environment. The research team speculates that 'it uses ionizing radiation from the space environment for metabolism, and therefore shows a higher growth rate than on the ground.'
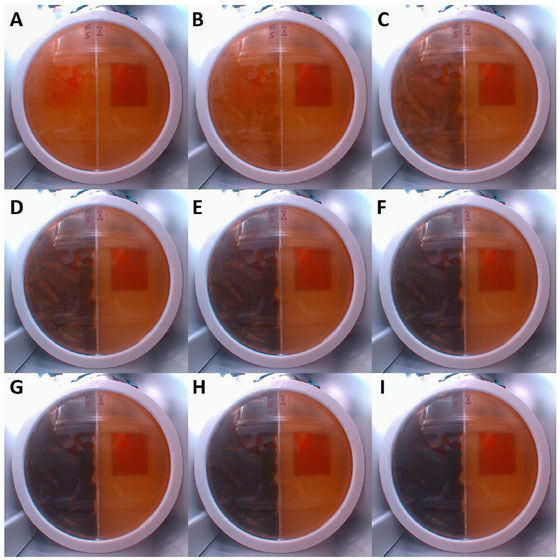
Experiments have also shown that the mold found in Chernobyl absorbs about 2% of the radiation that falls. NASA research scientist Kasthuri Venkateswaran, who led the experiment, suggested that the mold could be used as a 'sunscreen' against radiation.
In addition, the team said that the main advantage is that 'just by giving the mold a small amount of nutrients and exposing it to radiation, it propagates by self-replication from a microscopic amount', 'There is a 21 cm thick mold layer. Could significantly absorb the annual dose of exposure on the surface of Mars.'
NASA is promoting the ' Artemis Project ' aiming for manned lunar landing by 2024, and further manned exploration of Mars is planned. In the future, mold found in Chernobyl could be applied to protect space stations such as the ISS, lunar and Mars bases, and extraterrestrial astronauts from cosmic rays. You can expect enough.
Related Posts:







