Research results indicate that the infectivity of the new coronavirus is twice the conventional expectation
The
Early Release-High Contagiousness and Rapid Spread of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2-Volume 26, Number 7—July 2020-Emerging Infectious Diseases journal-CDC
https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/26/7/20-0282_article?deliveryName=USCDC_333-DM25287
COVID-19 twice as contagious as previously thought – CDC study | ThinkPol
https://thinkpol.ca/2020/04/08/covid-19-twice-contagious-previously-thought/
In the field of epidemiology, an estimate of how much an individual with an infectious disease can spread the disease is expressed in terms of the number of basic reproductions (R0). It has been estimated to be 2.7. This means that people who have been infected with the new coronavirus have been thought to spread about two to three people.
However, the estimates of R0 so far were based solely on the initial infection data in Wuhan, and Los Alamos National Laboratory reviewed its model to determine the rate of increase in infection. R0 was recalculated by developing a new model by collating case reports reported outside Hubei Province, where Wuhan City is located, and data on human movement in China.
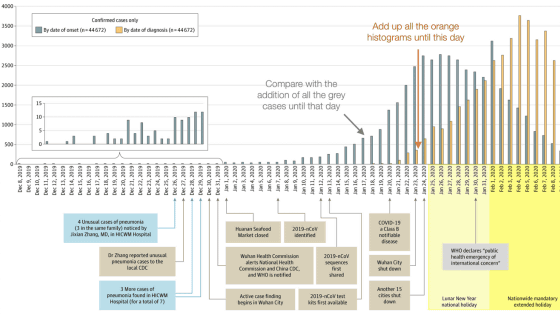
As a result, the time required for doubling the number of new coronavirus infections in earlier models was said to be '6-7 days', whereas it is actually '2.3-3.3 days' It turns out that. The median R0 was 5.7 when the interval between the onset of a new coronavirus infection and the onset of another person from that person to onset for 6 to 9 days was '5.7'. It was found that the rate of increase in the number of infected persons was significantly higher than that of '2.2 to 2.7'.
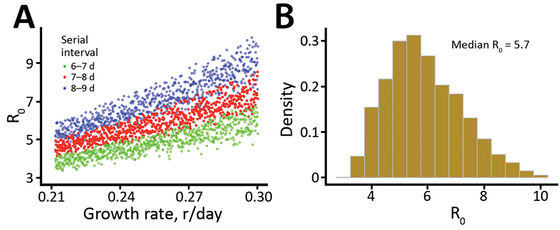
Figure A below shows the calculation results of R0 (vertical axis) when the onset interval is 6-7 days (green point), 7-8 days (red point), and 8-9 days (blue point) . Figure B on the left summarizes the results, and shows that the median R0 is 5.7.
One of the reasons why the value of R0 has been so greatly revised is that 'early data is old' is one of the causes, according to the research team at Los Alamos National Laboratory. The upper figure below shows the number of people who moved out of the city from Wuhan, China in January 2020 by the thickness of the line, and the lower figure is a time series graph. Earlier models used data from infected people before January 4, but the graph below shows that much more people are still moving after January 4.
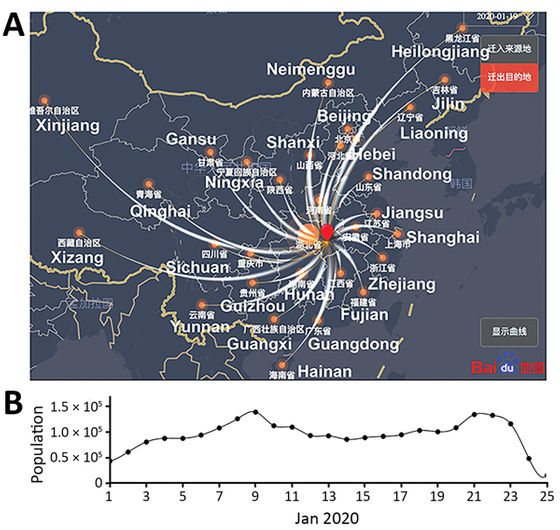
The research team said that `` the rally for the Lunar New Year's travel and celebrations in January 2020 may have contributed to the height of R0 '', and the lack of awareness of the problem is the infection rate of the new coronavirus Suggests that it may have caused an error in the guesswork.
Research results that the R0 of the new coronavirus is higher than estimated so far are not only `` difficult to stop the spread of infection '', but also when vaccines etc. appear in the future `` Efforts to eradicate new coronavirus also leap Will be more difficult '.
In addition to the new coronavirus, collective immunity, in which most people acquire immunity through vaccines, is important for eradication of infectious diseases. When R0 is 2.2, the required population immunization rate is 55%, but when R0 is 5.7, it is 82%, so more than 80% of the world's population needs vaccine to eradicate the new coronavirus. It is a calculation that has to acquire immunity by inoculation of etc.
On the other hand, there is some good news. Fortunately, the team said, `` Fortunately, the reduction in the number of cases confirmed in China and South Korea in March 2020 and the stable low incidence in Taiwan, Hong Kong, and Singapore are prompt It strongly suggests that this can reduce the spread of the new coronavirus, 'he emphasized again.
The following article details the plague control efforts in Singapore that the research team cited as an example.
What should Singapore learn from only two people killed by the new coronavirus? -GIGAZINE
In addition, a study focused on the structure of the new coronavirus, which was conducted separately from this study using a statistical model, stated that `` the new coronavirus is the coronavirus that caused SARS in 2003 (SARS-CoV ) Has a stronger ability to penetrate cells than ').
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1l_ks