Salmonella may have infected human to pig, not pig to human

Pork meat and internal organs are
Emergence of human-adapted Salmonella enterica is linked to the Neolithization process | Nature Ecology & Evolution
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41559-020-1106-9
Oldest reconstructed bacterial genomes link farming, herding with emergence of new disease
https://phys.org/news/2020-02-oldest-reconstructed-bacterial-genomes-link.html
Farming gave us salmonella, ancient DNA suggests | Science | AAAS
A group studying the origins of Salmonella from Neolithic remains was conducted by a group of researchers such as archaeologist Felix M. Kee at the Max Planck Institute for the Anthropology of Human History in Germany. He used a method called HOPS (Heuristic Operations for Pathogen Screening) that can extract DNA of ancient bacteria from archaeological relics such as fossils, excavated more than 6,500 years ago in Europe, Russia and Turkey. The genomes of Salmonella typhi, a species of Salmonella, were extracted from the teeth of 2739 humans. We have succeeded in obtaining the oldest bacterial genome so far.
by
The discovery of Salmonella DNA from the teeth of Neolithic humans means that the owner of the tooth was suffering from a systemic Salmonella infection at the time. Alexander Herbig, co-author of the dissertation, said of the finding: `` A wide range of analyzes across time, geography, and culture have enabled the first attempt to link pathogen evolution to the development of human life using molecular genetics. I did. '
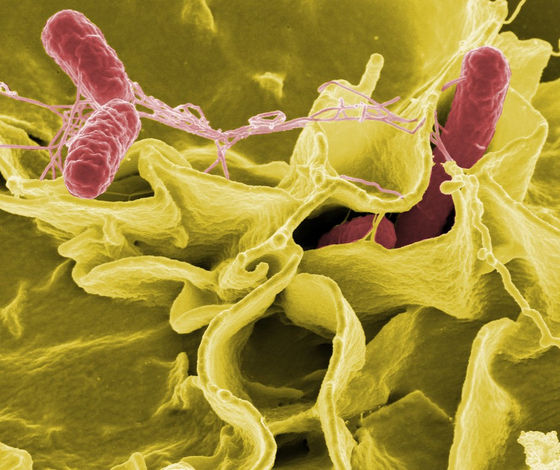
In addition, the research group classified the genomes of eight Salmonella strains into about 2500 Salmonella groups, and found that two of the eight species were those that triggered abortion of horses and sheep. And the remaining six were all the ancestors of Paratyphi C , which cause very serious infections when transmitted to humans.
A study published in 2018 found that this type of Salmonella was also found in remains from about 4000 years ago. 4,000 years ago coincided with the time when pigs began to be domesticated, so at the time of discovery, it was considered that 'Salmonella was most likely introduced from pigs to humans.'
However, the discovery of the ancestors of R. typhi C from bones from an earlier age than previous research has raised the possibility that it has infected 'human to pig' contrary to the previous theory. On the other hand, the research group said in a paper that `` It is possible that both human and pig Salmonella have evolved separately in an environment where humans and animals are in close contact, not pigs or humans. '' I support the theory.

Genome analysis also shows that unlike modern Paratyphi C, which only infects humans, ancient ancestors of Paratyphi C lack `` genes that can infect humans and cause severe infections '' It turns out that. From this, the research group speculated that 'Salmonella bacteria, which had been infected by ancient humans, had mild symptoms instead of infecting both humans and animals.'
'This discovery may give us an idea of how pathogens change hosts, because the new coronavirus has recently become a pandemic,' said Anne Stone, a human geneticist at Arizona State University Tempe. That's a very timely lesson given what we do. '
Related Posts: