It turns out that glaciers in the sea 'melt much faster than previously expected'

by
One of the major effects of global warming is the melting of glaciers in high mountains and polar regions. Researchers had estimated the melting speed of the glacier from the temperature, temperature, and ocean current etc. However, researchers at the University of Oregon and the University of Alaska have actually measured the glacial melting rate below the sea surface. The glacier melting model was found to be 'very imprecise' and melting the glacier at a much faster rate than expected.
Direct observations of submarine melt and subsurface geometry at a tidewater glacier | Science
https://science.sciencemag.org/content/365/6451/369
Underwater glacial melting up to 100 times faster than thought, study finds | The Independent
https://www.independent.co.uk/environment/glacial-melting-climate-breakdown-sea-level-rise-study-a9021266.html
Oceans Are Melting Glaciers from Below Much Faster than Predicted, Study Finds | InsideClimate News
https://insideclimatenews.org/news/25072019/glacier-melting-warming-oceans-climate-change-arctic-antarctica-study
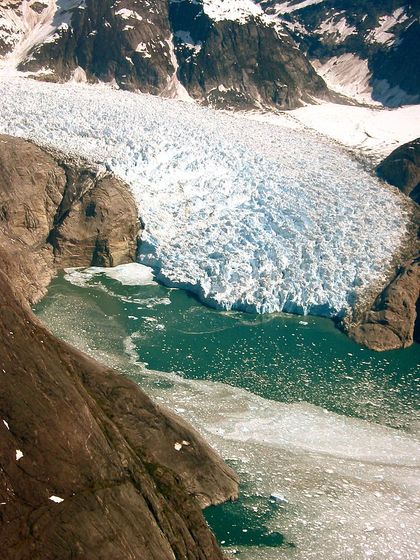
Water temperature, air temperature, and ocean current have been considered as the main factors for melting glaciers below sea level, and glacier melting models were created based on these data. The research team not only relied on the model, but also directly observed the melting of the
A research team consisting of glaciologists, oceanographers, engineers, etc. used sonar to measure what the contour of the glacier under water is, and also the flow, temperature, salinity, etc. of the water melted from the glacier Also about. In addition to these data, he observed melting of glaciers using time-lapse photography, and also measured melting of glacier surfaces using meteorological station data.
As a result of two years of observation, it was found that glacier melting in seawater is progressing much faster than previous glacier melting models. 'We found that glacier melting below the surface was much faster than expected, and in some cases glaciers melted at 100 times faster than expected,' said Rebecca Jackson , coauthor of the paper. It is said that 'it comes out.'

Researchers have pointed out that in previous models glacier melting was too simplified, for example, what shape is the glacier below the water surface, or the salt concentration of seawater also affects the melting rate It is said that The melting rate of glaciers under seawater seems to be a complex entanglement of several factors.
Glacier melting due to global warming has become a serious problem, and research results are also published every year that the glacier, which is three times the ice of the entire Alps, is melting.

In addition, because the lower part of the glacier protruding toward the sea is immersed in the seawater, the glacier below the water melts and the overall balance collapses, and the part above the seawater collapses and the sea May fall on the Therefore, the fact that the conventional model of the glacier melting rate under water changes is very significant in considering glacier melting.
The effect of melting of glaciers is often described as 'rise of sea level' etc., but the research team said, 'The flowing of the melt water will stir the seawater by flowing in the melt water, changing the balance of nutrients and increasing plankton' He points out the impact on ecosystems such as “more fresh water flows into seawater and salinity changes”.
Glacier melting due to global warming not only is a symbolic event brought about by global warming, but also has a great impact on people's lives. The research team stated that creating a more accurate glacier melting model is important for people preparing for glacier melting.

by Tim Rawle
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1h_ik







