Engineer considered 'Why was it so late when the bicycle was invented'

by
In the history of vehicles modern bicycles were born in the late 1800's after the invention of steam cars. Engineer Jason Crawford examines the question, 'Are bikes that work as simple as cars would have been born earlier?'
Why did we wait so long for the bicycle?
https://rootsofprogress.org/why-did-we-wait-so-long-for-the-bicycle
Crawford muttered the above questions on Twitter, and received various hypotheses from the people around him.
Why wasn't the bicycle invented until like the late 1800s?
— Jason Crawford (@jasoncrawford) June 25, 2019
The hypotheses received by Crawford are broadly divided into:
-Parts such as chains, gears and ball bearings require advanced technology and cost to produce, and technology has not kept pace.
The first bike made is one without pedals, and there are designs with widely different wheel sizes. It took a try and an error to get the bike to the final design.
-Before the 1800's, the road was full of trash and droppings from a horse-drawn carriage, and when it rained it became muddy and far from paved roads, so it was not suitable for bicycles.
• A bicycle was not needed, as a “horse” capable of carrying heavy loads was a common means of transportation. The food crisis arose, and not only humans but also horses were starved, creating a demand for bicycles.
・ It is the 'middle class' who needs bicycles, so to speak, the rich aristocrats and poor farmers alone can hardly create a bicycle market. With the growth of the economy, people who needed bicycles were born and used as entertainment, and their needs were further increased.
・ There was not much interest in 'helping invention' itself until a certain point in history.
Crawford delved into the history of bicycles to find out why bicycle inventions were delayed.
According to Crawford's research, the idea of a 'human powered vehicle' was presented by Giovanni Fontana, a Venetian engineer, in the 1400s. This was a four-wheel drive vehicle that used ropes to move gears and rotate the tires to move forward.
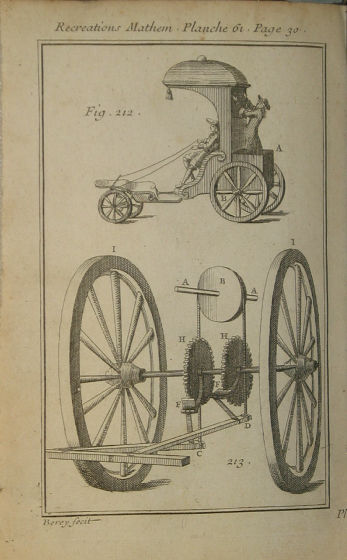
Also, Jacques Ozana, a mathematician who has been active in the 17th century, continues that 'horse-powered, man-powered vehicles' can go anywhere, exercise and be healthy without the need for resources such as wind or steam. You There are also people who actually tried to make a man-powered vehicle modeled on a carriage, and in the 1774 London Journal there was a record that a 6-mile-per-hour (about 10 km) vehicle was made, and French inventor Jean -Pierre Blanchard has also recorded vehicles that run tens of kilometers from Paris to Versailles.
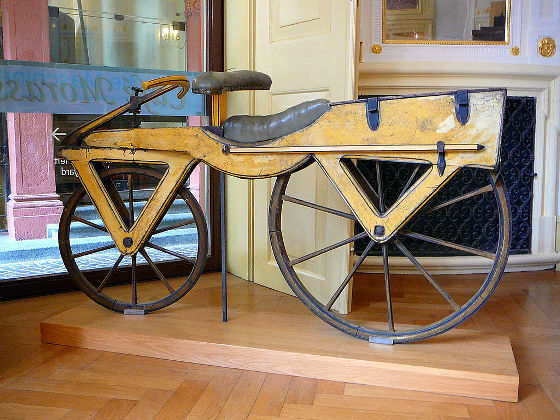
The history of the invention of bicycles has largely moved when

by
Dryzine does not have the pedals and gears, so it can not achieve the speed and efficiency of a modern bicycle. People felt that it was possible to get up to 20 km / h in a way that used a modern scooter-like feeling, and it became a rage in Europe in 1818-1819. However, it quickly disappeared because it caused many injuries and it was in the way of pedestrians.
By having several inventors pedal the bicycle by the 1860s, the bicycle is greatly efficient. However, because there were no gears or chains at this point, it was necessary to move many feet to move forward. A bicycle with an unusually large front wheel was developed in the 1870s to solve this problem, but it was difficult to balance and it was prone to injury when it was stopped.
Later, in 1885, John Kemp Starley invented a bicycle with a wheel and pedals separated and a chain and cranked design. Also, Dunlop founder John Boyd Dunlop invented a pneumatic tube tire, and in 1888 he finally completed the modern bicycle.

From this history, Crawford first concludes that one of the reasons for the delay in the invention of bicycles was that 'the goal was not to know the correct design of the bicycle itself'. In the history of the invention of bicycles, the original people were trying to make a 'four-wheel drive vehicle' and progress has stopped.
Crawford said, “The people at the time had no experience in mathematical engineering, and did not notice the unrealisticity of the“ human-powered four-wheeled vehicle ”concept, as to why only the carriage was the model of the vehicle. It will be said that the idea. In addition, it is also one of the reasons that the invention of the bicycle was delayed that Drais had to try and error for decades to realize efficiency, comfort and safety after producing bicycles. .
Furthermore, the development of new materials and technologies was essential to realize the final bicycle design. Advances in manufacturing technology were needed to create pneumatic tires, small lightweight chains and high quality gears at low cost.

by Markus Spiske
And one more thing, Crawford emphasizes the fact, 'Why nobody thought about rickshaws until the 1400s?' There were already watchmakers in the 1300's, and the Romans produced watermills and harvesters. The ancient Greeks made gear machines called Antiquitira machines, and even if there were no tires or chains, why did not anyone even go to the bicycle experiment? That's Crawford's question.
In this regard, Crawford talks about 'economic and cultural factors in invention.' In other words, to create an invention requires the support of the whole culture for research and development to create an invention. Karl von Drais, who created the prototype of the bicycle, was a baron with leisure time. Also, many of the researchers at that time were noble or wealthy people who were not nobles. Inventions were born when people with financial and time affordability were passionate about leisure time.
In addition, Crawford cites the phrase 'Innovation is essentially not possessed by human beings, and innovation will not occur unless people try to innovate,' said economic historyologist Anton Howes. In a culture that does not demand for, there is no innovation and talks about 'cultural factors'.
Related Posts:
in Vehicle, Posted by darkhorse_log