How was the anti-piracy measure for Sega's last game console 'Dreamcast' broken?

by
The game hardware ' Dreamcast ', known for its orange swirl and unique controller, was Sega's last home-use game console released in 1998. Mr. Fabien Sanglard, a former Google engineer who studies game programs, explains 'why the dreamcast copy protection technology that should have been strong was broken'.
How the Dreamcast copy protection was defeated
http://fabiensanglard.net/dreamcast_hacking/
Sanglard said he took a vacation and traveled to Japan after publishing a book about DOOM game engines. At that time, he stopped by the game center ' HEY ' in Akihabara and played the popular masterpiece shooting game ' Ikaruga ' overseas. 'Ikaruga' was 'interested in Sega's ultimate game console, Dreamcast,' as the full arcade-versioned title was released in Dreamcast, said Sanglard.
The Dreamcast released by Sega on November 27, 1998 had a graphic performance specialized for 3D processing, and was designed for easy porting of arcade games. In addition, since it comes standard with a modem that can connect to a telephone line, it was an epoch-making game machine at that time, allowing you to surf the web without using a PC or play games online. However, due to a lack of production lines, the initial movement was delayed, and the PlayStation 2 that was released when the supply was stable could not compete, and in 2001 SEGA announced withdrawal from the home game hardware business. Even so, there are still many games that can only be played with Dreamcast, and even now, 20 years after its release in 2018, it is still a game hardware with many fans.

by
Dreamcast's soft media is a proprietary optical media disc called ' GD-ROM '. The GD-ROM jointly developed by Sega and Yamaha has a recording capacity of approximately 1GB, which exceeds the 700MB of the CD-ROM used in the previous generation Sega Saturn and rival PlayStation . In addition, due to its original development, GD-ROM is said to have stronger copy protection than the popular CD-ROM.
The size and appearance of the GD-ROM are almost the same as the CD-ROM, but the reading area on the back is divided into two areas, a dark area and a light area. The dark area is a 35MB CD-ROM compatible area, and included a voice warning that 'This is a game disc for dreamcast' when put in the CD player on the disc. On the other hand, the bright area is a high-density area that can store up to 984MB, and all game contents were stored. Since GD-ROM drives for PCs are rarely available, it was considered virtually impossible to extract game data from Dreamcast game discs.

Dreamcast had no operating system (OS). Although the
When loading a game disc with Dreamcast, the bootstrap is first loaded from the last track of the GD-ROM into the RAM of Dreamcast itself. The bootstrap contains a file called 'IP.BIN' that displays the SEGA license screen . Also, this IP.BIN contained the name of the game executable, '1ST_READ.BIN'.
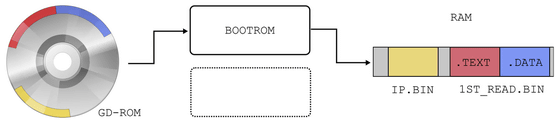
Dreamcast had a MIL-CD playback function. MIL-CD means 'Watching CD', which is a medium that can be played as a music CD on a normal CD player, while allowing you to watch original content on compatible devices. SEGA's development engineers knew that this MIL-CD playback function would be the entry point of hacking, so they designed to scramble 1ST_READ.BIN when the game body detects a CD-ROM. This scrambler made it impossible to use Dreamcast to read the illegally copied CD-ROM of the game contents.
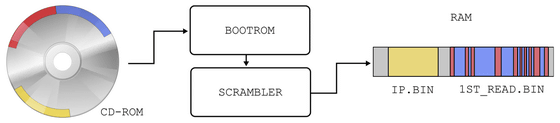
However, the Katana SDK , Dreamcast's official SEGA development system, was stolen and the security of this scramble was broken . Since this SDK includes a descrambler that restores the scrambled 1ST_READ.BIN, it seems that it is possible to start the game from the CD-ROM with Dreamcast.

After that, there remains the problem of how to store 1 GB of game content in 700 MB CD-ROM, but the file format used in GD-ROM is the same as CD
Sega has since removed the MIL-CD playback feature from Dreamcast version 2. However, it was late at that time, tools for playing pirated versions had already spread, and in 2000, PlayStation 2 which adopted a DVD-ROM boasting a large capacity of 4.7 GB per layer as media was also introduced. And profits plummeted. Sega has a dreamcast inventory of 2 million units, and the list price of 29,800 yen was finally reduced to 9900 yen, and it was almost sold out. SEGA, which has announced that it will withdraw from the development of home-use game consoles since the end of Dreamcast sales, is dedicated to developing game software.
Related Posts:







