What is the grand distributed system 'IPFS' that breaks away from central sovereign HTTP and creates a new Internet world?

The world of the Internet is made up of " HTTP " of the communication protocol, but due to the system design where there is a server which manages information (data), it has the disadvantage that information is lost from the web when the server goes offline. Unlike centralized HTTP, which has such structural drawbacks, the distributed file system " Interplanetary File System (IPFS) " has been devised, and projects are starting to build a new Internet world.
The InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) | Simply Explained & Illustrated
https://achainofblocks.com/2018/10/05/ipfs-interplanetary-file-system-simply-explained/
◆ Internet by HTTP <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> <br> The Internet is an indispensable part of our life by communicating with family and friends through the Internet , browsing news, However, there is a structural flaw in the current Internet "There is information in a concentrated form". Specifically, since information existing on the Internet is stored in a server of a company that manages all information, if the server is separated from the network due to some circumstances, the information will be lost from the Internet I will.
Due to such structural shortcomings, communication problems due to server problems also result in blocking information for those who do not want access to information. The Turkish government seems to be a threat to national security and it is easy to see that it robbed access to Turkish citizens' information by blocking certain sites such as Wikipedia.
A situation in which social media is blocked on a large scale in Turkey, and view as regulation by the authorities - GIGAZINE

Although it is still used as a communication protocol because there is a big merit of being able to transmit information at a high speed to HTTP, it is pointed out that the big reason to keep using HTTP is "There is no really good choice other than HTTP". In that case, computer engineer Juan Bennett invented the distributed Internet file system which replaces HTTP called "Interplanetary File System (IPFS)". Briefly, IPFS is to switch the Internet from HTTP to P2P method.
◆ What is Interplanetary File System (IPFS)?
Originally Bennett, who was studying computer science at Stanford University, was developing a system to quickly send large files via the Internet. It seems that the data transmission system was constructed in a way that incorporates the " Git " mechanism that allows data version management to " BitTorrent " which is a protocol that efficiently and dispersively transmits a large amount of data. Mr. Bennett who created the data transmission system realized that this system functions not only as a data transfer tool but also as a system that changes the structure of the Internet. IPFS is conceived in that way.
· Difference between IPFS and HTTP
To understand IPFS, Bennett says that understanding and comparing the mechanism of HTTP making up the existing Internet is easy to understand.
In the case of downloading images from the Internet, in the HTTP system, you usually specify the file you want to download with the notation URL containing the domain name of the company saving the photo. For example, as for the image file of GIGAZINE, an image file format (Graphics file format) such as "https://i.gzn.jp/img/2018/12/10/anker-eufy-robovac-30c/00_m.jpg" is added to the URL of GIGAZINE It is specified in a form that includes .jpg). In HTTP, it is done by the method of "Location Based Addressing" which allows the computer to access the location where information is obtained by URL, and if the specified place (server) is in the offline state, You will not be able to retrieve the necessary information.
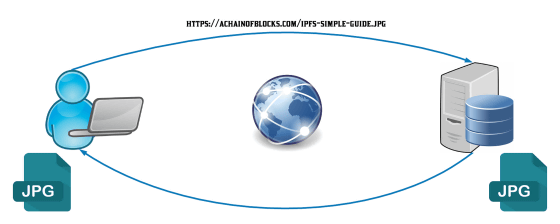
In Location Based Addressing, if a server is down, all information contained in the server will be inaccessible from the Internet. However, even if a computer that holds downloaded data or cached data exists while somewhere in the world when the server is operating normally, other users can not access that information, There will be a state where information disappears from the Internet.
In order to solve this problem, IPFS introduces the concept of "Content-Based Addressing (content-based access)". That is, with IPFS, files on the network are distributed "shared" over the network with "hash" values that serve as "fingerprints" that can identify individual files. A person who gets a specific file by specifying a hash will be able to specify the hash and provide the file to the person trying to access the file. In such a distributed system, the more requested files are placed in a larger group of nodes and shared, so it will be in a more accessible state.
Furthermore, it is possible to check that the file has not been altered from the user or the node by comparing the hash value when receiving the file. Specifically, when requesting a specific hash to receive a file, reception is refused if the received hash does not match. "This is the same as checking items purchased at Amazon.If you ordered green socks but red socks arrive, it's like you can refuse to pick up and wait for green socks," Bennett I am in a similar situation.
In addition, IPFS adopts a mechanism of deduplication, so even if there are shares of the same file from multiple users, files are created on the network only once, efficient use of the network I will.
· How IPFS works <br> Bennett explains about how to build distributed IPFS.
First, IPFS stores files in "IPFS objects". Each object can store only 256 KB of data and can include a link to another IPFS object. By linking, we can store more than 256 KB of data.
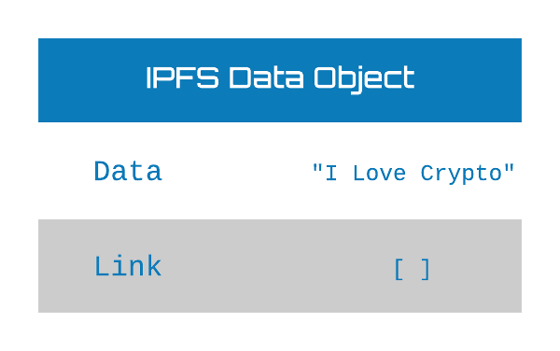
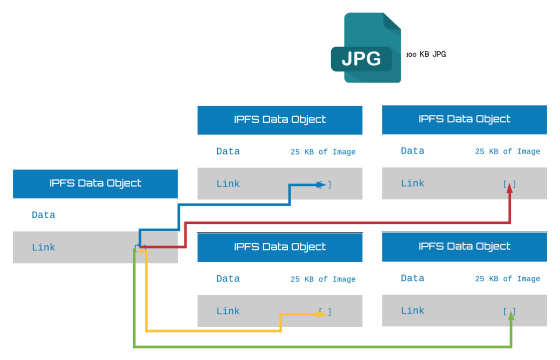
For example, when saving an image file, the file is divided into multiple objects up to 256 KB. IPFS creates "empty objects" that link to all the objects that make up the image. By doing so, Bennett says that the architecture can use IPFS as a true file system.
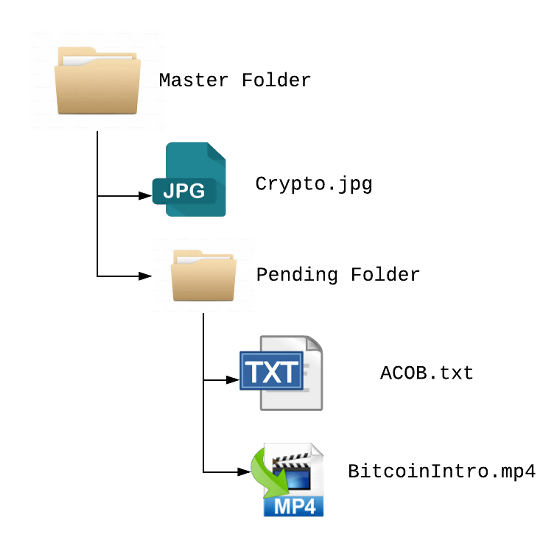
For example, the following data (folder) having a directory structure is ...
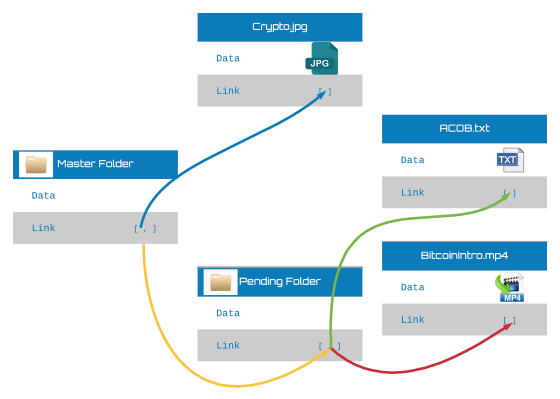
In IPFS, it is constructed as the following objects. Since IPFS adopts Content-Based Addressing, it is guaranteed that each file is immutable, and the point that can prevent tampering is similar to " block chain ".
It is IPFS that can prevent tampering, but of course it is also possible to update the data. All of the data update information is recorded by the mechanism of Git, and IPFS is a great advantage of being able to confirm the change contents.
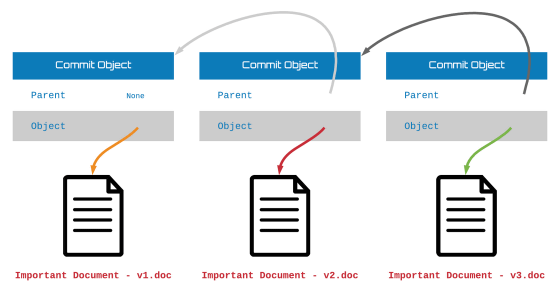
For example, consider creating a text file called "Important Document - v1.doc" and sharing it on an IPFS network. In this case, a new object called "Commit object" is created, and Important Document - v1.doc is stored.

If time passes, Important Document - v1.doc requires critical updates, IPFS simply adds a new file "Important Document - v2.doc". A new Commit object of the file updated by the software is created, a link with the previous version is created and it is automatically linked. The linking work is repeated for each update, so that the entire management history can be accessed from all nodes.
· Issues of IPFS network operation
Nodes on the IPFS network are required to hold the cache of downloaded files and make them available when needed by other users. If a document is hosted on four nodes, if all of that node goes offline, the same problem as HTTP occurs that the document can not be accessed. So, there is a problem of how to maintain nodes.
One solution is to give incentives to provide nodes to the network. Specifically, it is considered to construct a mechanism that can obtain rewards by providing free space of computer storage to the network. The compensation will be paid in virtual currency called " Filecoin ". About this mechanism, Mr. Bennett expresses "It is like Airbnb, a mechanism that profits by lending out a vacant house (storage)". Thanks to Filecoin, there are incentives to keep nodes online as much as possible.

Addressing using "content hash" is widely used, such as block chains of virtual currency and commit of code backup, but still can not interoperate these underlying data structures It is said that. Therefore, a data model " InterPlanetary Linked Data (IPDL) " common to all protocols derived from hash has been invented. By providing a library that IPDL makes data interoperable between tools and protocols, it seems to be important for realizing IPFS because all data models using hash can be unified.
Bennett says that Filecoin and IPDL will be more detailed on the blog in the future.
◆ Future aimed at IPFS The creator of J-C · R · Rick Rider of "Arpanet", the predecessor of the Internet (Internet), has a grand goal of "to build a network between galaxies" It was. In other words, the designation "Internet" was actually an abbreviation for "Intergalactic Network". Based on the formation of such Internet, Mr. Bennett said that he called the new network to switch the Internet over HTTP to the P2P network " Interplanetary File System".

IPFS to create a new decentralized Internet for the centralized current Internet is a very ambitious project. Regarding the creation of a decentralized mechanism, it has already been adopted in virtual currency and finance, but we will try new decentralized thought on the Internet as well.
Mr. Bennett said that HTTP will not fade out immediately with the advent of IPFS, but HTTP will still remain a very useful protocol. However, it is certain that HTTP is a relatively old technology over 25 years since its birth, and IPFS will continue to expand due to technology evolution, ultimately replacing HTTP, Bennett expects It is.
Related Posts:
in Software, Web Service, Posted by darkhorse_log