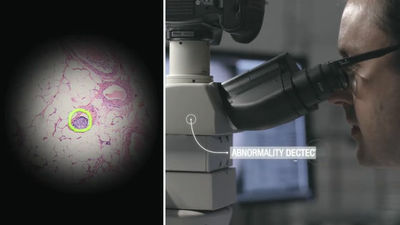
Google develops AI-powered protein crystal discovery system, promising breakthrough in drug development

Google's Brain Team, which researches artificial intelligence (AI), has announced that it has collaborated with researchers at
Google AI Blog: Automating Drug Discoveries Using Computer Vision
https://ai.googleblog.com/2018/07/automating-drug-discoveries-using.html
Teaching a Machine to Spot a Crystal – Duke Research Blog
https://researchblog.duke.edu/2018/06/20/teaching-a-machine-to-spot-a-crystal/
Because the biological functions of proteins are determined by their molecular structure, analyzing their molecular structure is important for developing effective new drugs. Furthermore, analyzing the molecular structure of proteins requires protein crystals. However, much about protein crystallization remains unknown, and even with modern technology, it remains difficult.
by
While most of the preparation and experimental processes for protein crystallization experiments have been automated, the results of crystallization experiments have traditionally been confirmed visually by humans using a microscope. In this case, the discovery of protein crystals relies solely on the observational skills and experience of the scientist conducting the experiment. If crystallization is overlooked or misjudged, the opportunity for an important discovery that could advance medical science could be lost.
The Machine Recognition of Crystallization Outcomes (MARCO) initiative at Duke University hopes to mitigate these risks by using AI to automatically recognize protein crystallization outcomes. The team approached Google with labeled data from over 500,000 protein crystallization experiments, and the Google Brain Team developed a system that uses deep convolutional neural networks to automatically classify crystallization outcomes.
By learning from the vast and diverse data collected by MARCO, AI can visually identify protein crystals with high accuracy. According to Professor Patrick Charbonneau of Duke University, the accuracy of identifying protein crystals by human beings is about 85%, while the latest AI developed by the Google Brain Team achieved 95% accuracy.
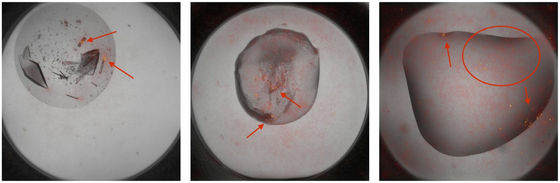
Professor Charbonneau said, 'By using AI to automatically discover and classify protein crystals, we will be able to almost completely automate the protein crystallization experiment itself. This will also make protein structural analysis easier, which is expected to significantly reduce the time and cost required for new drug research.'
The Google Brain Team has made this AI model publicly available on GitHub , and by using Google Cloud Machine Learning (ML) Engine , other researchers can use this AI in their own research.
Related Posts: