Research showed that cognitive ability will decrease in a room without air conditioner, how much performance will change?

Students who lived in dormitories without air conditioners reported that the performance was lower than the students who live in dormitories with air conditioners. The fact that the higher the indoor temperature is adversely affecting the cognitive ability of young people is again proved, and the research team insists that it is necessary to design a building that mitigates the influence of extreme fever on health.
Reduced cognitive function during a thermal wave of residents of non-air-conditioned buildings: An observational study of young adults in the summer of 2016
http://journals.plos.org/plosmedicine/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmed.1002605
Extreme heat linked with reduced cognitive performance among young adults in non-air-conditioned buildings | News | Harvard TH Chan School of Public Health
https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/news/press-releases/extreme-heat-linked-with-reduced-cognitive-performance-among-young-adults-in-non-air-conditioned-buildings/
The research team led by Mr. Joseph Allen, associate professor at the Climate, Health and Global Environment Center (C - CHANGE) in Harvard Public Health Graduate School in Boston, targeted to 44 students at Harvard University, We investigated the impact in 2016.
Twenty-four out of 44 people lived in an air-conditioned dormitory built in the 1990's and the remaining 20 people lived in an air-conditioned dormitory for over 80 years. Subjects' students receive two kinds of cognitive tests, "answering the character color of the displayed word" and "simple calculation problem" on the smartphone immediately after getting up every morning, the student's cognitive ability is measured from the score It was.

by Creative Commons
As a result, students who lived in a dormitory without air conditioning found that the reaction time was 13.4% slower than the students who live in the dormitory with air conditioning, and the score of the calculated test had decreased by 13.3%. The difference in cognitive function between these two groups was also seen at the time of a cold after passing by not only when a fierce heat wave with a maximum temperature exceeding 30 degrees came.
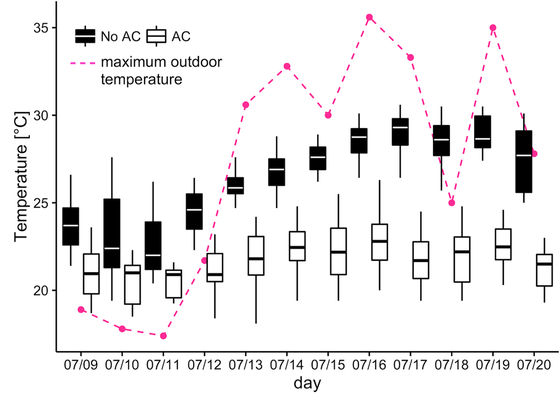
In the graph below, the black box plot shows the room temperature of the dormitory without the air conditioner, the white box plot shows the room temperature of the dormitory with the air conditioner, the red dotted line shows the maximum temperature in the outdoors. From 13th July, the maximum temperature has risen sharply and you can see that thermal waves are arriving. The room temperature of the dormitory with the air conditioner is keeping 25 degrees or less although the change of room temperature is getting bigger. On the other hand, the room temperature of the dormitory without the air conditioner rises at a stretch due to the arrival of heat waves. In addition, there is no indication that the room temperature will go down little.
As a result of the survey, it was clear that the higher the indoor temperature, the lower the cognitive ability of the student, and the place where the air conditioner was not able to adjust the room temperature continued to affect the performance. The climate of Boston is the same subarctic humid climate as Hokkaido, and it is known that coldness in winter is very strict. According to Allen, the building is designed to keep the heat in the cold climate, so it is difficult to release the heat accumulated by the summer day, the heat wave continues indoors, the indoor human beings It has an adverse effect on cognitive ability. The research team argues that sustainable adaptation measures for changing climates should be incorporated into the design of the building to maintain educational achievement, productivity and safety.
Related Posts:
in Note, Posted by log1i_yk