A system to collect water from the dry air of the desert was born

Even in the most dry place on the earth, moisture is contained in the air, so that mankind can survive in a wider variety of environments as long as there is a method of extracting the moisture. Based on this idea, researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) are developing a system to extract moisture from the air.
In field tests, device harvests water from desert air | MIT News
http://news.mit.edu/2018/field-tests-device-harvests-water-desert-air-0322
Professor Evelyn Wang of Professor Mechanical Engineering Department and Professor Gale · E · Kendall, etc, who are developing "researchers of MIT" researchers are conducting research. In April 2017Proposed ideasResearch is underway on the basis of former graduate students of MIT and students of the University of California Berkeley. The system has already carried out on-site tests to extract moisture from the air of a very dry land in Tempe, Arizona, USA Achievement of more than a certain result.
Professor Wang said about the idea advocated in 2017, "We received a lot of criticism as being hype at first, but in the newly published paper, we answered a number of questions raised in the previous idea I am summarizing. "We insist that" a system that extracts moisture from the air "is a feasible system, not a fancy idea.
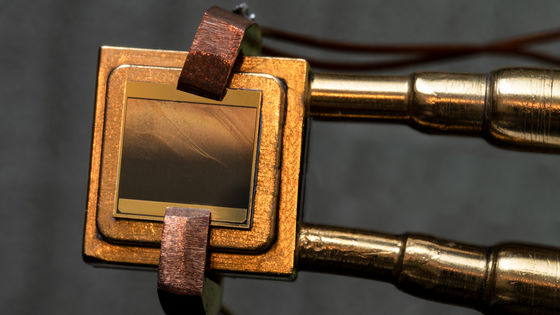
In the system developed by Professor Wang and othersOrganometallic skeletonExtract moisture from dry air using a high surface area substance with MOF. At present, the well-known "method of extracting moisture from the air" requires a high level of humidity in the air exceeding 50% and requires a large amount of energy for cooling to condense the moisture . However, according to Professor Wang et al. Using high surface area substances, it is possible to extract moisture from dry air with a humidity of about 10%. It is a system that can be used even in dry air, and is expected as a technology for stably supplying water to dry areas such as desert.
When I published a paper on "a system to extract moisture from the air" in 2017, the research team of Professor Wang was interviewed by Boston's local TV, WCVB Channel 5, with MOF among them We also introduce high surface area substances. It has a large surface area and can catch moisture in the air like a sponge.
MIT researchers making water out of air - YouTube
Professor Wang The research team is running test equipment at the roof of Arizona State University in Tempe, Arizona. Professor Wang commented, "It is confirmed that the field test is carried out on the dry land and it is actually possible to collect water even at the small dew point."
The test equipment installed at Arizona State University is operated only by sunlight, and although it was a device for demonstrating the concept, it is necessary to extract 4,5 liters of water per day with 1 kg of high surface area material I have succeeded. It seems that the research team estimates that if the optimum material is selected, the extraction efficiency can be increased to about three times that of the test equipment.
In addition, the method developed by the research team has the advantage that it can be used not only with low humidity but also with moving parts such as pumps and compressors, which can be worn out, rather than extracting moisture from mist etc. Especially, "It is a low humidity but it works perfectly passively in places with a lot of sunlight," says Hyunho Kim, one of the researchers. Furthermore, according to Sameer Rao, a member of the research team, "It is also possible to continuously operate the system using a wealth of low-grade heat sources such as biomass and waste heat."
The research team aims to expand and improve the efficiency of the system. The test equipment was designed to produce a few milliliters of water, and it was created to prove whether the system conceived in reality works. Therefore, developing the system to generate water in liter units is the next goal of the research team. And finally we aim to be able to extract sufficient amount to supply water to individual households.
It is also clear that impurities are not mixed in the water extracted by the system developed by the research team. In the test using the mass spectrometer, "There was nothing to leach into the water from the MOF," Professor Wang said. This means that the material is very stable, it means that you can get high quality water.
Yang Yang, professor of material science and engineering at the University of California, Los Angeles said, "This technology provides a new approach to solving the water shortage problem in dry climates, If possible, we can give a real impact to areas with poor water such as Southern California. "
Related Posts: