A machine learning method that discovered two extrasolar planets is made public
Google engineer Chris Shallue uses machine learningKepler Space TelescopeWe analyzed the data and discovered two extrasolar planets. The code used for that analysis appeared in GitHub, and it is made available to anyone.
Research Blog: Open Sourcing the Hunt for Exoplanets
https://research.googleblog.com/2018/03/open-sourcing-hunt-for-exoplanets.html
models / research / astronet at master · tensorflow / models · GitHub
https://github.com/tensorflow/models/tree/master/research/astronet
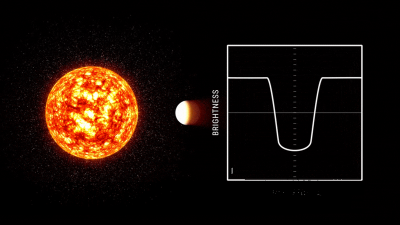
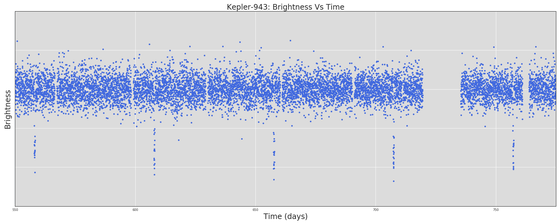
There are several kinds of ways to find outstanding planets, but what Chris Shallue used wasTransit methodWhat is called. The transit method is a method to capture the decrease in the light quantity of a star when the planet traverses in front of a fixed star. When light intensity data of a star obtained from the Kepler Space Telescope is plotted on the ordinate with the amount of light on the horizontal axis and time is taken on the horizontal axis, it appears as a valley of the U shape in the graph and the existence of the planet becomes clear.
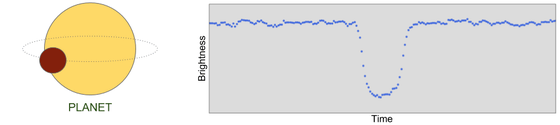
However, the phenomenon that the amount of light temporarily falls like this occurs not only when the planet crosses the star, but also when the dark stars cross the front of a bright star, etc. It also occurs due to various causes. Therefore, we use a neural network to judge whether the cause of decrease in light intensity is a planet or something else.
This time it was releasedPage on GitHubIt is described in detail how to locate the extrasolar planet, and anyone can rediscover the planet by the same procedure as Chris Shallue. A capacity of about 100 GB is necessary to use a large amount of data, but those who are interested in application of machine learning and discovery of extra solar system are worth seeing at first glance.
Related Posts: