A movie that explains how we detect the nuclear test performed secretly

ByNicolas Raymond
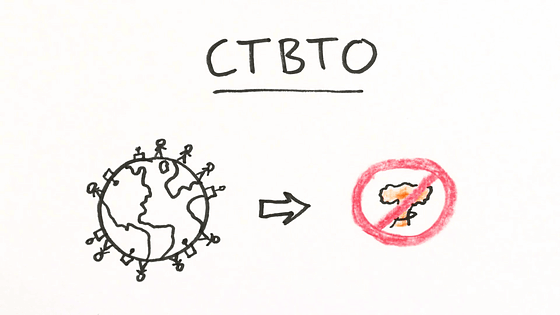
It was adopted in September 1996 and Japan ratified it in July 1997Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty(CTBT) prohibits experimental explosions and other nuclear explosions of nuclear weapons in any space including space, atmosphere, underwater, and underground. In order to verify compliance with the Convention, four kinds of monitoring observation stations, "seismological monitoring station", "radionuclide monitoring station", "underwater sound monitoring observation station" and "micropressure vibration monitoring station" Although it is installed, it is described in detail with illustration how how these stations can detect nuclear test.
How To Detect A Secret Nuclear Test - YouTube
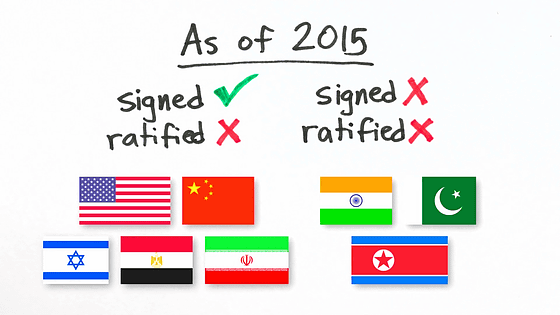
In February 2015, five countries, signed by the CTBT and yet to ratify, are "USA, China, Egypt, Iran, Israel". The three countries that have not yet signed or ratified are "North Korea, India, Pakistan".
As the Treaty continues to be effective, all countries requiring entry and signing are required to sign and ratify, but there is already a system called "International Monitoring System (IMS)" that monitors nuclear tests around the world 24 hours a day .
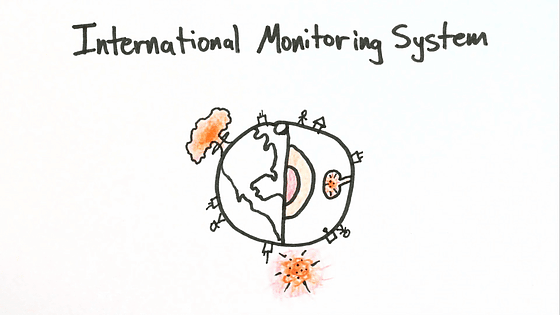
This movie explains how IMS works, and how it works. If a nuclear explosion occurs somewhere in the world, a huge amount of energy will be released.
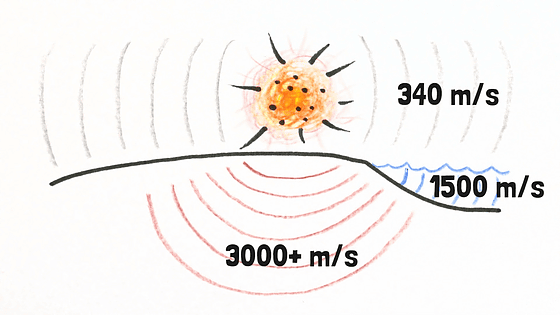
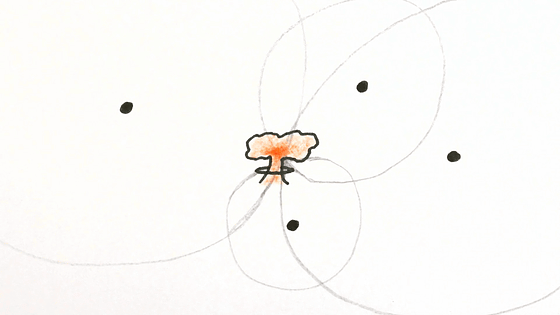
Since the released energy moves through the air, underwater, and underground with sound velocity, it is possible to determine the location of the nuclear explosion by triangulation from observation data of stations around the world.
In a very simple way, the observatory on the ground detects all extremely low frequency sounds caused by storms, glaciers, volcanic eruptions, volcanic eruptions, meteorite crashes, rocket launches, space shuttle accidents, and nuclear explosions on the earth It is.

Among these, the ultra low frequency emitted by the nuclear explosion is so big that it will not mistake other natural phenomena etc.

An underwater explosion can be detected by "underwater sonic sensor". It is like a very sensitive microphone floating on the ocean floor. As there are few other natural phenomena detected in the water, it is not confused with other detection data like the ground.

Nuclear tests carried out in the basement are mainly monitored by observation data of seismographs. The seismographs detect large earthquakes, small scale earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, mining, crashes of planes, ... ....

Scientists can easily distinguish which data is a nuclear explosion. As an example, a large shock was detected in the North Korean basement in 2006, 2009 and 2013, but both concluded that it was a nuclear explosion.

IMS monitors seismic waves, underwater sounds and micro-atmospheric vibrations all over the world for 24 hours ......

Radionuclide monitoring stations installed at 80 locations around the world monitor nuclear activity in the atmosphere.

The radionuclide monitoring stations not only detect the data that is the definitive proof that the nuclear test was conducted, but also it is possible to visualize how the radioactive fallouts disperse in the atmosphere.North Korea nuclear test in 2009The data showing that radioactive fallout has flown to Japan is also displayed.

Nuclear tests carried out secretly underground are more difficult to detect than others, but IMS can also send a team to the site if various sensors indicate suspicious data. However, because the treaty is not yet in effect, on-site investigation is considered illegal at this stage.

Thus, the IMS established by the Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty Organization (CTBTO) has already operated around the world, and the improvement and improvement of sensors are still being carried out. Also, the detected natural phenomena data is provided for scientific development, and it seems to be able to predict and monitor tsunamis, for example. Mechanisms capable of realizing "the world without nuclear weapons" are in place, signing and ratification of the country requiring entry into force is desired.
Related Posts: