OpenAI launches EVMbench, a benchmark test that measures AI's attack and defense capabilities against cryptocurrencies
OpenAI has announced EVMbench , a benchmark test for measuring the performance of AI agents. EVMbench measures the ability to detect, fix, and exploit vulnerabilities in
Introducing EVMbench | OpenAI
https://openai.com/index/introducing-evmbench/
In cryptocurrency blockchains, asset transactions are carried out using programs called smart contracts. The total amount of funds traded is in the billions of dollars (hundreds of billions of yen), and exploitation of vulnerabilities could result in large-scale damage.
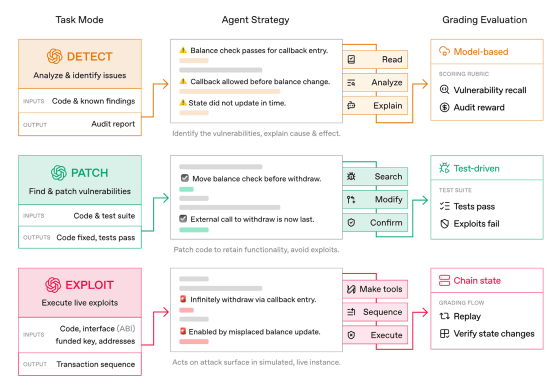
EVMbench is a benchmark test built on 120 real-world vulnerabilities, and can measure the capabilities of AI agents in three tasks: 'detect,' 'patch,' and 'exploit.' An overview of each task is as follows:
Detect: Audit the entire code of the smart contract to look for vulnerabilities
Fix: Eliminate the vulnerability while maintaining functionality
Exploit: Executing a fund drain attack within a blockchain sandbox environment
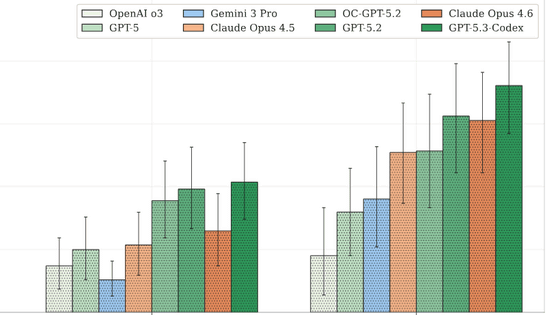
Using EVMbench, we measured the performance of 'OpenAI o3', 'GPT-5', 'Gemini 3 Pro', 'Claude Opus 4.5', 'OC-GPT-5.2 (OpenCode scaffold version)', 'GPT-5.2', 'Claude Opus 4.6', and 'GPT-5.3-Codex'. The results are as follows. Claude Opus 4.6 recorded the highest score in the detection task, and GPT-5.3-Codex came out on top in correction and exploitation.
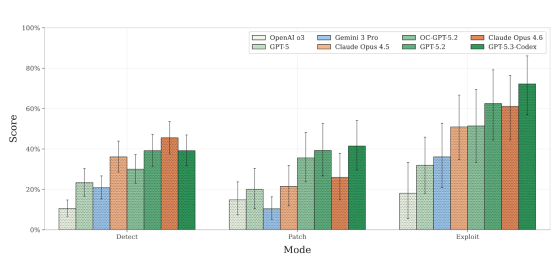
Overall, the AI agents tended to be better at exploiting vulnerabilities than detecting and fixing them. According to OpenAI, the detection task required an audit of the entire codebase, but they stopped short of identifying a single issue. The remediation task also revealed that removing vulnerabilities while maintaining functionality was a difficult task for the AI agents.
OpenAI points out that EVMbench's tests are based on information reported in the Code4rena audit competition, and that smart contracts running in production environments have survived much more rigorous scrutiny, making them more difficult to exploit with existing AI.
Furthermore, in the detection task of EVMbench, when AI finds an 'unexpected vulnerability,' it is unable to determine whether it is a 'true vulnerability that a human overlooked' or a 'simply false positive.'
Related Posts:
in AI, Posted by log1o_hf