The National Institute of Infectious Diseases' 'Influenza Epidemic Level Map' shows at a glance how critical the influenza epidemic is

In the winter of 2024 to 2025, influenza is expected to spread explosively, with reports that the number of influenza patients in Tokyo
Trend Level Map
https://www.niid.go.jp/niid/ja/flu-map.html
National Institute of Infectious Diseases Infectious Disease Information Center Influenza Epidemic Level Map
https://kansen-levelmap.mhlw.go.jp/Hasseidoko/Levelmap/flu/new_jmap.html
In Japan, influenza is expected to become widespread in the 2024-2025 season, and each prefecture is calling for people to take preventive measures against infection, such as washing their hands frequently, wearing masks, and getting enough rest. In Tokyo, the number of patients reported for two consecutive weeks, from December 9th to 15th and from December 16th to 22nd, was more than double the number of the previous week, and there are concerns that the infection will spread further as more people gather during the New Year holidays.
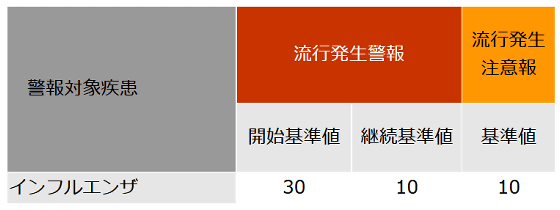
The Infectious Disease Epidemiology Center of the National Institute of Infectious Diseases operates an influenza warning and advisory system based on the number of patients who visit approximately 5,000 designated medical institutions nationwide. Warnings and advisories are issued by tallying the number of patients reported by designated medical institutions by health center, and determining whether the number of patients per week exceeds a certain line. At the time of writing, the warning line is 30 people per designated medical institution, and the advisory line is 10 people. In addition, if a warning was issued in the previous week, the warning will continue if the number of new patients reported is equal to or exceeds 10 people, which is the threshold for continuing the warning.
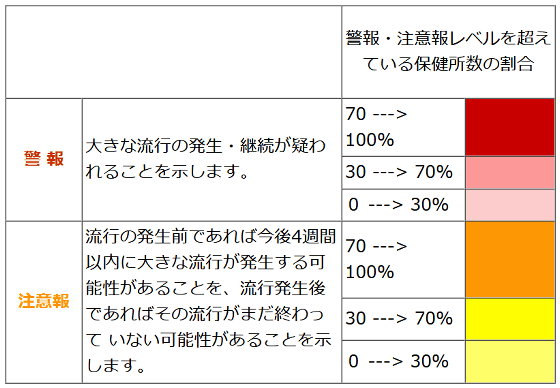
The Infectious Disease Surveillance Center updates the 'Influenza Epidemic Level Map' every week based on the warning and advisory system so that the influenza epidemic situation can be seen at a glance. On this map, if there are public health centers in each prefecture that have exceeded the warning level, they are shown in three levels of red, and if there are public health centers that have exceeded the advisory level, they are shown in three levels of orange.
Each color indicates the percentage of public health centers in the prefecture that issued warnings or advisories. The percentage of public health centers that exceeded the warning level is dark red (70-100%), slightly lighter red (30-70%), and light red (0-30%). The percentage of public health centers that exceeded the advisory level is dark orange (70-100%), dark yellow (30-70%), and light yellow (0-30%).
And here is the influenza epidemic level map for the 51st week of 2024 (December 16th to 22nd), updated on Friday, December 27th, 2024. The total number of reported patients was 211,049, and the average number of patients per fixed point was 42.66, more than double the number of reports per fixed point from the previous week, which was 19.06. Almost all prefectures are at alert level, and only Akita, Yamagata, and Toyama are at warning level.

Broken down by prefecture, the scores were 82.64 in Oita Prefecture, 65.57 in Kagoshima Prefecture, 61.62 in Saga Prefecture, 60.03 in Chiba Prefecture, 59.86 in Fukuoka Prefecture, 56.76 in Aichi Prefecture, 55.63 in Yamanashi Prefecture, 52.68 in Ehime Prefecture, 51.06 in Saitama Prefecture, 50.64 in Miyazaki Prefecture, and 50.03 in Yamaguchi Prefecture, indicating that the disease is particularly prevalent in Kyushu and the Kanto region.
Based on reports from designated medical institutions, the total number of patients nationwide, including those diagnosed at medical institutions other than designated medical institutions, was estimated to be approximately 1.674 million. By age, there were approximately 128,000 patients aged 0-4, 254,000 patients aged 5-9, 260,000 patients aged 10-14, 155,000 patients aged 15-19, 132,000 patients in their 20s, 145,000 patients in their 30s, 208,000 patients in their 40s, 196,000 patients in their 50s, 98,000 patients in their 60s, and 97,000 patients aged 70 or older.
By clicking on the 'Influenza Epidemic Level Map,' you can see more detailed information such as warnings and alerts for each public health center. For example, the warning and alert levels for each public health center in Tokyo are as follows:
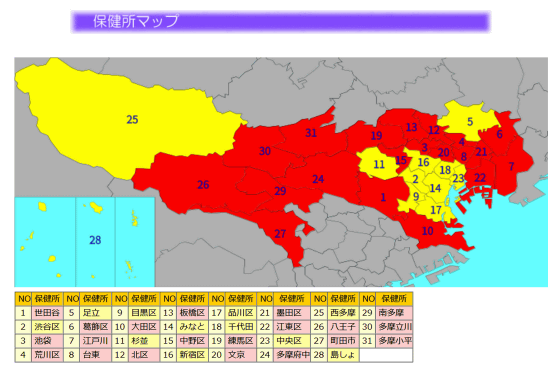
This is a graph showing the trend of public health centers in Tokyo that issued warnings or alerts. The number of influenza patients began to increase from the 49th week (December 2nd to 8th), and by the 51st week, the majority of public health centers had suddenly reached the warning level.

Due to the increased movement of people during the New Year holidays, influenza infections may spread more than ever before, and it has been reported that there is a shortage of medicine to deal with the sudden increase in patients. In addition, some medical institutions are closed during the New Year holidays, so holiday clinics are expected to be more crowded than usual .
Doctors and local governments are urging people to boost their immune systems by getting enough nutrition and rest, as well as to take thorough measures to prevent infection, such as frequently washing and disinfecting their hands, and wearing masks in crowded places.
Related Posts:
in Web Service, Review, Posted by log1h_ik