GitHub is rampant in the practice of artificially inflating stars, and a survey has found that about 70% of inflated repositories are related to malware

GitHub, the world's largest software development platform, has a feature called '
4.5 Million (Suspected) Fake ⋆ Stars in GitHub: A Growing Spiral of Popularity Contests, Scams, and Malware
(PDF file) https://arxiv.org/pdf/2412.13459
The Rise of Fake GitHub Stars: A Growing Security Threat
https://cyberinsider.com/github-plagued-by-4-5-million-fake-stars-problem-misleading-users/
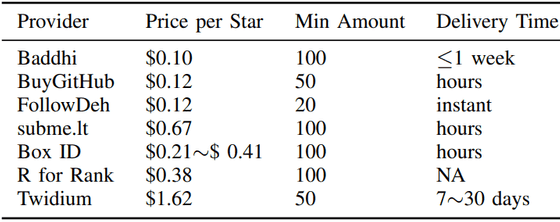
GitHub stars are an important factor that act as a primary signal of a repository's popularity and quality. However, some users have made a business out of artificially boosting the stars of certain repositories, at a cost of $0.10 (about 15 yen) per star, according to the research team. The table below shows the prices of star-inflating services on GitHub. You can see that the 'price per star,' 'minimum order quantity,' and 'number of days until a star is awarded' vary depending on the service.
These repositories appear to have many stars, misleading developers and organizations into thinking the project is trustworthy when in fact it is a low-quality project that may be hiding malicious code or lacking community support.
Many of these fraudulently inflated repositories pose as repositories for tools such as game cheats or cryptocurrency bots, and contain obfuscated malware that can compromise systems or steal data.
The research team developed
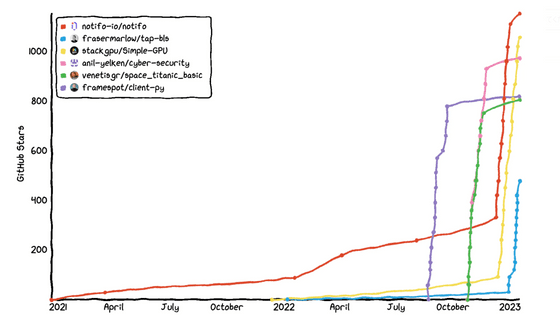
In addition, these star padding campaigns have been on the rise since the beginning of 2024, and it has been revealed that approximately 16% of repositories that received 50 or more stars in July 2024 were involved in star padding campaigns. Furthermore, more than 70% of repositories with inflated stars were either phishing scams or disguised malware, highlighting the direct security risk to the software supply chain.
'Many developers and organizations rely on the number of stars given to a repository as an indication of its quality. Fake stars can encourage the adoption of insecure repositories, put organizational security at risk, distort the software ecosystem, and obscure truly high-quality projects,' Cyber Insider points out.
He also suggested that 'when assessing the quality of a repository, look not only at the number of stars, but also at the activity of pull requests and discussions. GitHub also has a responsibility to proactively address this issue. GitHub should strengthen its moderation system to associate fake star activity with malicious repositories and actively remove them.'

Related Posts:
in Software, Posted by log1r_ut