Research shows that the quality of rice in Japan and China is declining due to global warming

A Chinese research team analyzed data from China and Japan spanning more than 35 years and found that rising nighttime temperatures are having a significant impact on rice quality. This deterioration in rice quality due to rising temperatures is likely to become even more severe in the future, and is emerging as a new challenge for food security.
Warming Leads to Lower Rice Quality in East Asia - Liu - 2024 - Geophysical Research Letters - Wiley Online Library
Climate warming is reducing rice quality in East Asia, research reveals
https://phys.org/news/2024-11-climate-rice-quality-east-asia.html
This study analyzed the effects of climate change on rice quality in East Asia. A research team led by Xianfeng Liu of Shaanxi Normal University in China analyzed data from China and Japan over the past 35 years and found that rice quality has been declining.

by
The study used the 'High Quality Rice Rate (HRR)' as an indicator of rice quality, which is the percentage of rice grains that retain more than three-quarters of their original length after milling. In China, the overall average was about 62%, declining by 1.45% per decade, while in Japan the average was about 66%, declining by 7.6% per decade from 1996 to 2010.
It was found that the main cause of quality deterioration is an increase in nighttime temperature. Quality begins to decline at nighttime temperatures of 18°C or higher in China and 12°C or higher in Japan. This is believed to be due to a decrease in photosynthesis and starch accumulation caused by high temperatures. It was also found that the amount of sunlight, precipitation, and lack of water vapor pressure during the day also have a significant effect on quality.
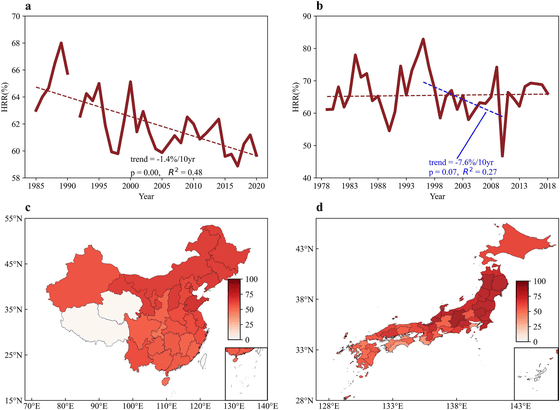
Geographically, both countries show a tendency for quality to be higher in the north than in the south, which may be related to the south experiencing higher night-time temperatures closer to the equator.
Future projections predict that quality declines will continue depending on greenhouse gas emission scenarios. In low-emission scenarios, declines of 0.5% in Japan and 1.5% in China are expected between 2020 and 2100. In high-emission scenarios, a steeper decline is expected, especially after 2050, with concerns of a decline of more than 5% in China by 2100.
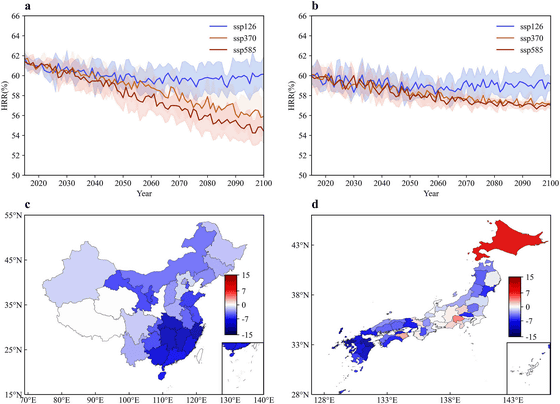
The findings suggest that climate change could have significant impacts on food security, population nutrition and economic stability, highlighting the importance of developing new varieties that can adapt to climate change.
Related Posts: