Google announces a method to teach a robot arm to do difficult tasks such as tying shoelaces and repairing another robot

Google DeepMind, the AI research division of Google, has announced a method for teaching a robot arm to perform complex tasks. The two methods announced are ' ALOHA Unleashed ,' which learns from human operation, and ' DemoStart ,' which is based on learning in a physical simulator. Each method allows a robot arm to learn a task using a different method.
Our latest advances in robot dexterity - Google DeepMind
◆ALOHA Unleashed
ALOHA Unleashed is a learning method developed for ALOHA 2, a two-armed, high-performance robotic arm jointly developed by Google DeepMind and Stanford University.

ALOHA Unleashed is based on
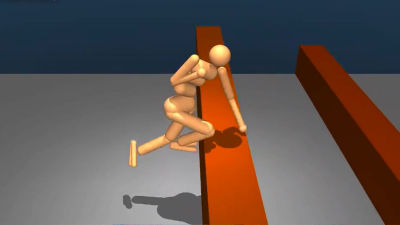
Below is a video of ALOHA 2 executing the operation 'tying shoelaces' learned using ALOHA Unleashed. Click on the image to see the video.

It is also possible to 'replace parts of other robots.'

The ALOHA Unleashed paper is available at the following link:
ALOHA Unleashed: A Simple Recipe for Robot Dexterity
(PDF file) https://aloha-unleashed.github.io/assets/aloha_unleashed.pdf

◆DemoStart
Robot arms are equipped with many moving parts and sensors, and the more powerful the robot arm, the more complex the operation. For this reason, it takes a long time and a lot of money to train a robot arm to perform automatic operations. DemoStart is a learning method that takes the approach of 'running the robot arm training in a physical simulator,' which saves time and money required for training.
DemoStart performs learning by recreating the parts and tasks of a robot arm within the physics engine ' MuJoCo '. Although there are some gaps between the physics simulation and the real world, DemoStart automatically generates a curriculum to fill the gap, allowing the results of learning in the physics simulation to be smoothly reflected in operations in the real world.
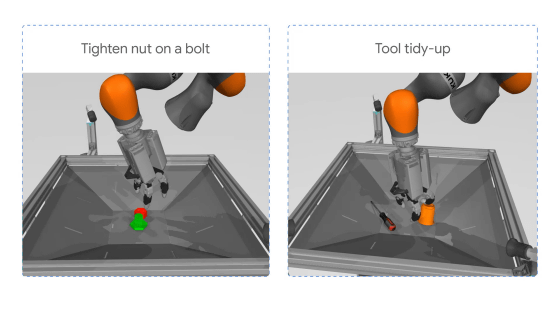
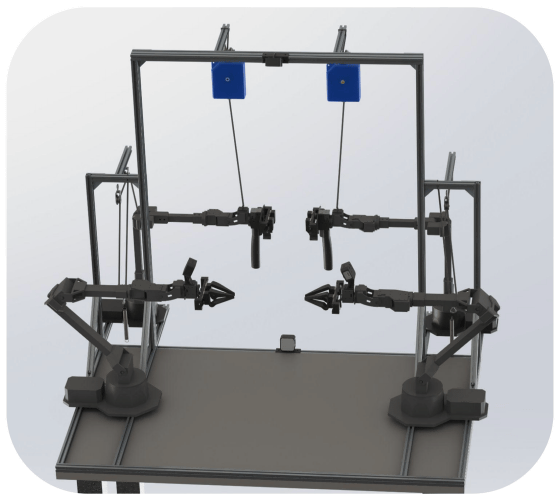
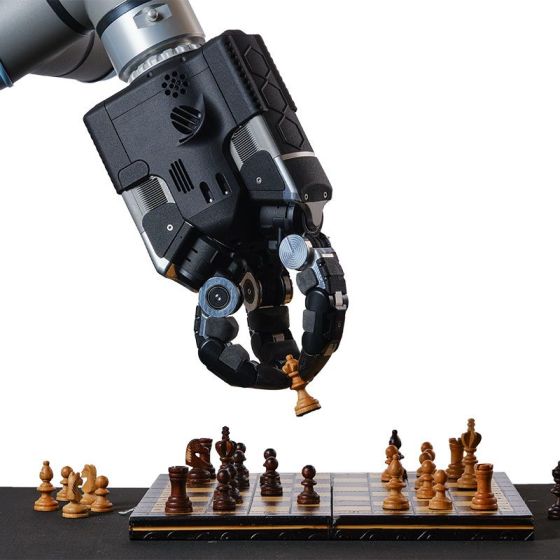
Google has already tested DemoStart using the robotic arm '
The DemoStart paper is available at the following link:
DemoStart: Demonstration-led auto-curriculum applied to sim-to-real with multi-fingered robots
(PDF file) https://arxiv.org/pdf/2409.06613
Related Posts: