How is the accuracy of 'NTP', which keeps the date and time of PCs and smartphones correct, guaranteed?

Nowadays, many devices such as computers and smartphones display accurate time. Regarding where such 'accurate time' is obtained, Unix system developer Tony Finch gave a lightning talk 'Where does' at ' RIPE 86 ' held from May 22nd to 26th, 2023. My computer get the time from?'' is posted on my blog.
Where does my computer get the time from? – Tony Finch
https://dotat.at/@/2023-05-26-whence-time.html
Where does the computer get its time?

NTP .

NTP has a hierarchy called stratum. An NTP server in stratum 3 obtains time from an NTP server in stratum 2, an NTP server in stratum 2 obtains time from an NTP server in stratum 1, and so on. Masu.
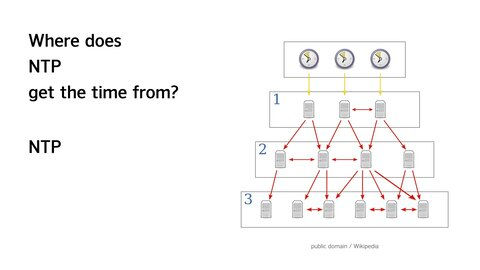
And stratum 1 NTP servers often set their time based on GPS.

So where does GPS get the time?

Schriever Space Force Base, Colorado, United States. It used to be Air Force Base, but in 2021 it was renamed Space Force Base.

Where does Schriever Space Force Base get its accurate time?

This is an alternative master clock for the United States Naval Observatory ( USNO ). This alternate master clock is located at Schriever Space Force Base.

And the alternate master clock gets its time from USNO in Washington, DC.

USNO uses a combination of three elements to determine time. The first element is an atomic clock .

There are numerous atomic clocks installed on the USNO grounds.

The second element is the International Earth Rotation and Reference System Project (IERS), based at the Paris Observatory. IERS observes the Earth's rotation and appropriately uses leap seconds to synchronize its time with the Earth's rotation.

Regarding IERS time determination, the necessary data is collected from institutions around the world. For example, the exact heading parameters are obtained from USNO.

The third element is the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM) , which manages Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) .

BIPM sets UTC based on data from atomic clocks around the world.
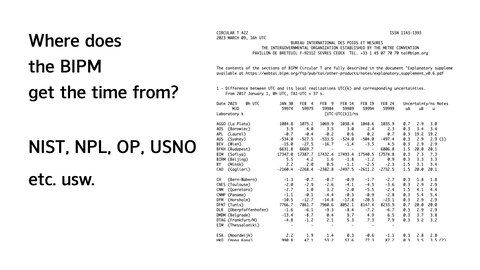
BIPM is responsible for maintaining the International System of Units (SI), and the definition of the system of units is decided by the General Assembly of Weights and Measures (CGPM), which is the superior organization of BIPM.

The International System of Units defines ``1 second'' as ``the duration of 9,192,631,770 times the period of radiation corresponding to the transition of the two hyperfine structure levels of the ground state of a cesium-133 atom.''

Where did CGPM get the magic number 'approximately 9.2GHz'?

In 1955, Louis Essen and Jack Parry built the first cesium atomic clock, which defined the modern second.

The definition of the second at the time was based on astronomy, so Essen and Parry enlisted the help of the USNO to determine the frequency at which a cesium atomic clock would beat one second.

William Markowitz of the USNO measured time based on celestial bodies, while Essen measured time with a cesium atomic clock, and both were able to correlate measurements even at distant locations by listening to WWV time signals. .

Markowitz was measuring the calendar time established by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 1952.
Regarding the astronomical ephemeris, in the late 1800s Simon Newcombe compiled a huge amount of astronomical data and created a mathematical model.

And Simon Newcombe worked for USNO.

It seems that it is possible to go back further, but Mr. Finch ended the slide saying, ``The layer is gone.''

Related Posts:







