AI-based breast cancer screening will increase the detection rate by 20% and reduce the workload of radiologists by 44%

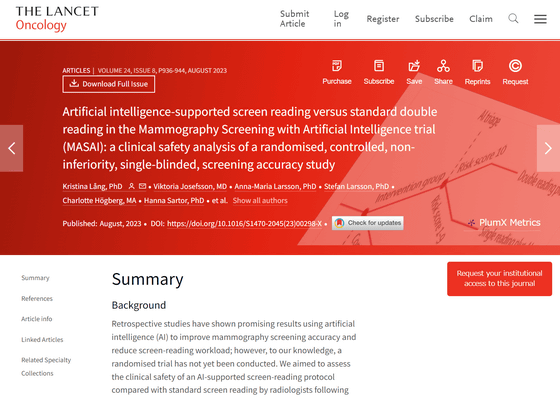
Artificial intelligence-supported screen reading versus standard double reading in the Mammography Screening with Artificial Intelligence trial (MASAI): a clinical safety analysis of a randomized, controlled, non-inferiority, single-blinded, screening accuracy study - The Lancet Oncology
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanonc/article/PIIS1470-2045(23)00298-X/fulltext
AI use in breast cancer screening as good as two radiologists, study finds | Breast cancer |
https://www.theguardian.com/society/2023/aug/02/ai-use-breast-cancer-screening-study-preliminary-results
AI-assisted cancer screening could cut radiologist workloads in half | Engadget
https://www.engadget.com/ai-assisted-cancer-screening-could-cut-radiologist-workloads-in-half-193427969.html
AI can conduct breast cancer screenings in less time than humans but just as well, study finds | ZDNET
https://www.zdnet.com/article/ai-can-conduct-breast-cancer-screenings-in-less-time-than-humans-but-just-as-well-study-finds/
According to statistical data released by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) in December 2020, breast cancer has surpassed lung cancer to become the ``most common cancer in the world''. According to data, more than 2.3 million women develop breast cancer each year.
A large-scale randomized controlled trial involving more than 80,000 women was conducted to verify the usefulness of AI in breast cancer screening, which is an effective method for early detection of breast cancer. It was published in The Lancet Oncology, a medical journal dedicated to treating cancer.
The study reveals that AI-based breast cancer screening can perform as well as two radiologists working together to perform breast cancer screening.
Most of the existing research on 'analyzing the results of
However, the current study directly compared breast cancer screening using AI with breast cancer screening by radiologists in only Swedish women with an average age of 54 years. In the experiment, half of the radiographs taken by mammography were double- read (double-checked) by a radiologist, and the other half were read by AI and a radiologist (one person).
Breast cancer screening with AI resulted in 244 (28%) diagnoses of breast cancer, compared with 203 (25%) breast cancer screening with only human radiologists has been diagnosed as In other words, breast cancer screening by AI succeeded in detecting 41 more breast cancers. Of the 41 breast cancers detected by breast cancer screening using AI, 19 were invasive and 22 were carcinoma in situ. In addition, it seems that AI breast cancer screening did not falsely detect breast cancer.
Furthermore, compared to breast cancer screening by human radiologists, breast cancer screening by AI has been shown to read 36,886 times less. As a result, it became clear that implementing AI breast cancer screening could reduce the screen reading workload for radiologists by as much as 44%.
Furthermore, whether breast cancer screening using AI can reduce the number of
However, research has shown that “AI-based mammography screening can significantly reduce the reading workload while providing the same cancer detection rate as standard double reading. It also shows that the use of AI is safe, ”he emphasizes the usefulness of AI-based breast cancer screening. In addition, the research team said, ``The greatest potential for using AI for breast cancer screening at this time is that it can reduce the burden of excessive interpretation on radiologists.'' He argued for the utility of using AI to reduce workload.
In addition, the research team said, ``Our AI-assisted screening system requires at least one radiologist in charge of detection, which may eliminate the need for double reading of most mammograms. Doctors' workload is greatly reduced, allowing them to concentrate on more advanced diagnoses.'
'These promising safety analyzes will inform new trials and programs to address the acute shortage of radiologists in many countries,' said lead author Dr. Christina Long of Lund University. It should be used to do so, but it's not enough.'

Professor Stephen Duffy, a cancer screening researcher at Queen Mary University, praises the study for its high quality, but says about AI-based breast cancer screening: 'For example, the results of this paper The number of carcinoma in situ, which is thought to be overdiagnosed, is increasing,' he said, raising concerns about the possibility of overdetecting breast cancer.
On the other hand, a spokesperson for the UK's National Health Service (NHS) praised the findings as 'very encouraging'. Dr Catherine Halliday, Chancellor of the Royal College of Radiology, also said, 'AI has enormous potential to maximize efficiency, support decision-making and identify and prioritize the most urgent cases. This could potentially save clinicians time,” he said, adding that he hopes AI will play even more roles in areas other than breast cancer screening.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by logu_ii