A screw-type self-propelled microrobot with a total length of only 20 micrometers is developed, successful animal experiments to inject drugs by sticking to the desired place in the body
A research team at the University of Colorado Boulder has developed an ultra-compact microrobot with a total length of only 20 micrometers. This microrobot is self-propelled, and it has been reported that it actually succeeded in transporting drugs inside the body of mice.
Bubble‐Based Microrobots with Rapid Circular Motions for Epithelial Pinning and Drug Delivery - Lee - Small - Wiley Online Library
https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202300409

These tiny, medical robots could one day travel through your body | CU Boulder Today | University of Colorado Boulder
https://www.colorado.edu/today/2023/05/24/these-tiny-medical-robots-could-one-day-travel-through-your-body
You can see how the microrobot developed by the research team moves in one shot by watching the following movie.
A robotic Fantastic Voyage-YouTube
This microrobot is made of a material called biocompatible polymer and is manufactured with technology similar to 3D printers.
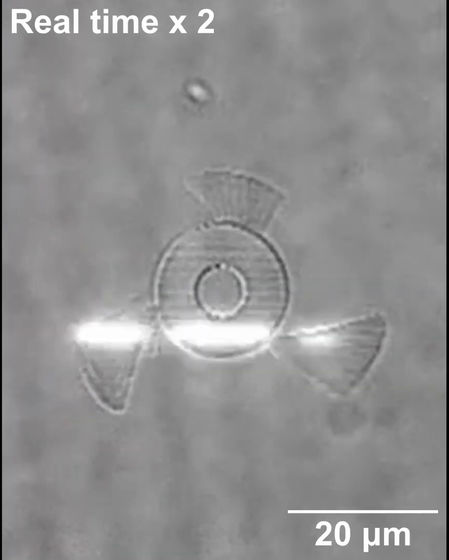
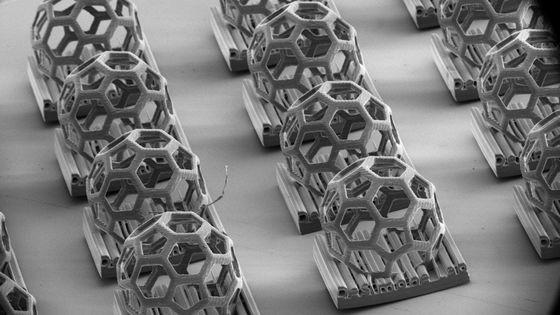
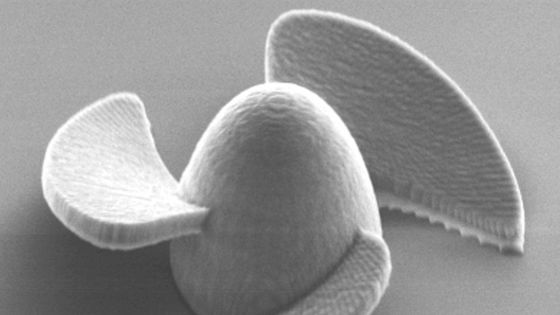
The total length of the microrobot is only 20 micrometers, a fraction of the diameter of a single hair. It has a small rocket-like body with three small wings and is shaped like a ship's propeller.
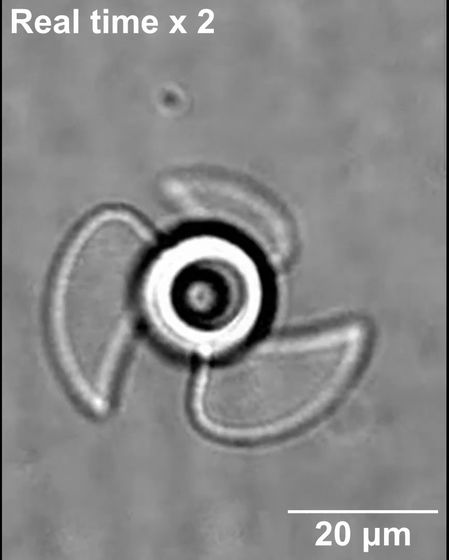
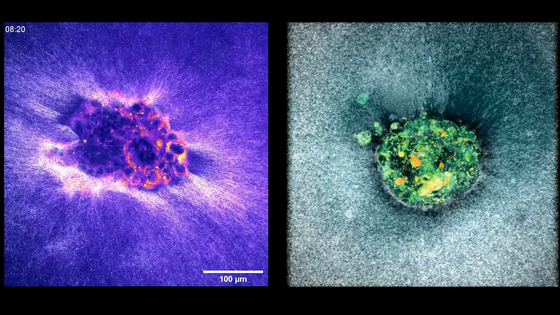
This microrobot has small air bubbles in the center of the screw, like an upside-down cup submerged in water. Then, when ultrasonic waves hit this microrobot, the bubbles vibrate violently, propelling the robot forward.
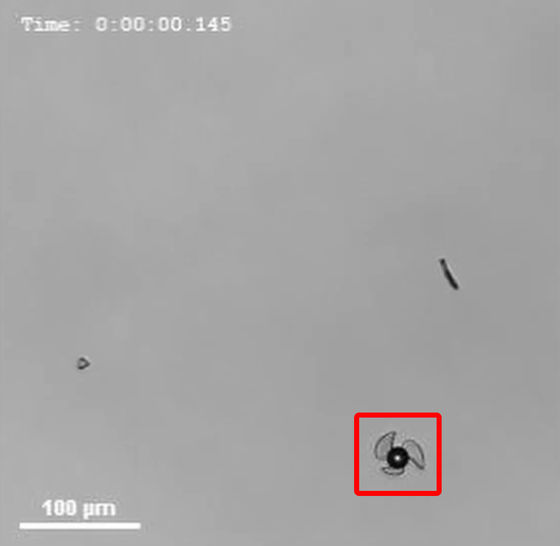

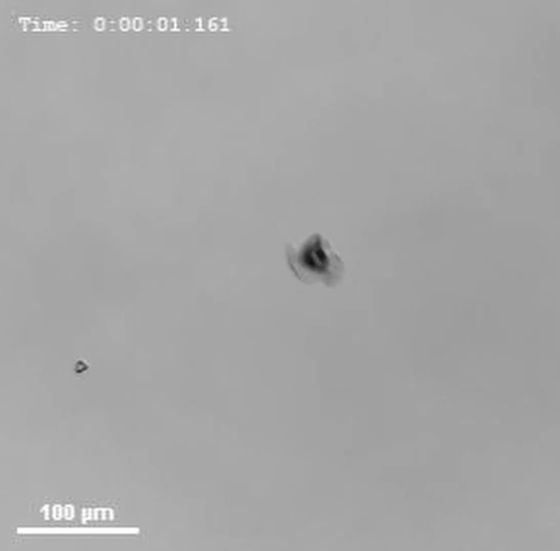
The movie's microrobot is designed to have only one of the three wings short, so it moves like spinning.

Below is a picture of the microrobot taken with a scanning electron microscope.
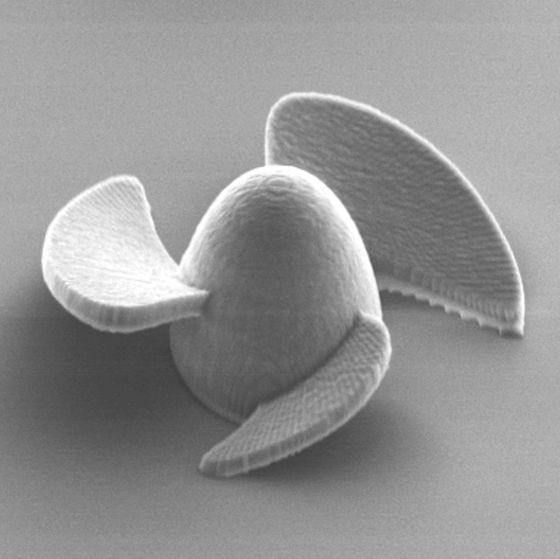
The research team believes that this microrobot can be applied to treat interstitial cystitis, a designated intractable disease. Patients with interstitial cystitis need to regularly inject an anti-inflammatory drug called `` dexamethasone '' into the bladder using a catheter at the hospital, but the research team is an experiment to inject this dexamethasone with a micro robot The we.
The research team manufactured thousands of microrobots containing high concentrations of dexamethasone and injected them into the bladders of experimental mice. After going around the body, the microrobot finally reached the bladder and succeeded in sticking to its inner wall. At this time, it is said that pee will be a little difficult to come out.
A microrobot attached to the bladder wall slowly released dexamethasone over a period of about two days. By using microrobots to inject drugs slowly over a long period of time, it is expected that frequent visits to the hospital will be eliminated.
The research team states that there are still many challenges to making microrobots move freely within the human body. The goal is to
Related Posts: