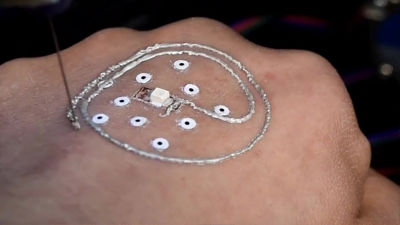
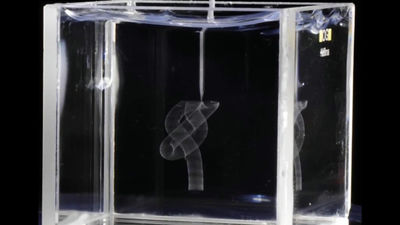
Succeeded in creating a 3D bioprinter that can three-dimensionally create human skin tissue using 'Lego'

Experiments using human body tissues are important in biomedical research, but it is not easy to obtain human body tissue samples. In recent years, 3D
Development and Evaluation of a Low‐Cost LEGO 3D Bioprinter: From Building‐Blocks to Building Blocks of Life - Moukachar - 2023 - Advanced Materials Technologies - Wiley Online Library
https://doi.org/10.1002/admt.202100868

We built a human-skin printer from Lego and we want every lab to use our blueprint
https://theconversation.com/we-built-a-human-skin-printer-from-lego-and-we-want-every-lab-to-use-our-blueprint-203170
Methods of obtaining human body tissue for biomedical research include obtaining body tissue from tissue removed by organ donation or surgery, but the amount of body tissue supplied by these means is Limited. Also, depending on the type of project, a specific size or type of body tissue is required, so it may be difficult to obtain the necessary body tissue.
The recent emergence of 3D bioprinting has provided a solution to the problem of procuring body tissue samples. In 3D bioprinting, a 3D structure that reproduces the complex shape of living tissue can be created by putting 'bioink' containing living cells into a cartridge and outputting it with a 3D bioprinter according to a program. Is possible.
However, 3D bioprinters are expensive, and many cost more than several million yen. Low-budget laboratories find it difficult to deploy such expensive 3D bioprinters. Therefore, a research team at Cardiff University succeeded in making its own 3D bioprinter using 'Lego', which is inexpensively available in a wide range of areas around the world and has a wealth of highly accurate replaceable parts.
The 3D bioprinter actually made by the research team can be seen in the following movie.
Printing synthetic human skin using a LEGO 3D printer - YouTube
``Commercial 3D bioprinters cost tens of thousands of pounds (millions of yen) or more,'' said Dr. Chris Thomas of Cardiff University. So Dr. Thomas and his colleagues decided to develop an inexpensive 3D bioprinter that could be used not only by themselves, but by researchers around the world.

Dr. Thomas and others noticed that it was Lego that can be easily obtained in a wide area around the world. Lego is not only inexpensive and can be used for a wide range of purposes, but each part is highly precise and standardized, so if you use the same type of block, you can make the same thing anywhere in the world. The research team incorporates microfluidic devices to accurately 3D print tissues and cells, using sub-brand
Dr Zion Coleman of the Cardiff University School of Pharmacy explains that the introduction of 3D bioprinting will allow us to experiment with 3D cell tissue rather than plates made from 2D cell culture. In the past, it was common to conduct biological experiments with cell tissue cultured on a flat plate, but since human body tissue is three-dimensional, using three-dimensional cell tissue allows more accurate experiments results can be obtained.

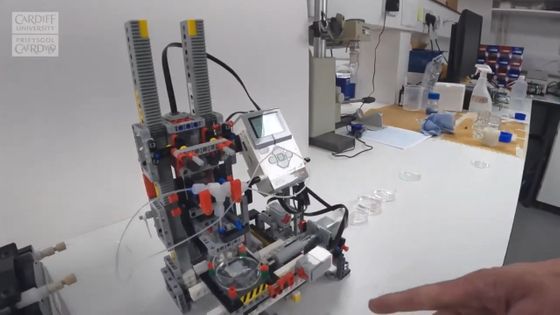
Next to Dr. Ahmed Moukachar, the lead author of the paper, is the Lego 3D bioprinter developed this time.

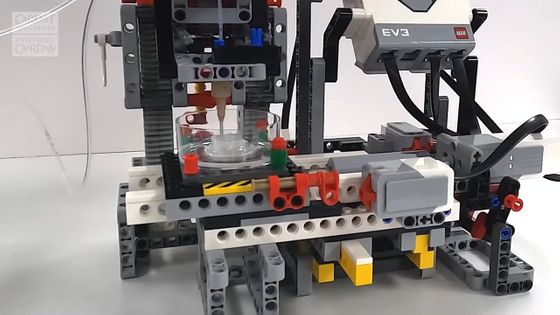
The Lego 3D bioprinter looks like this.
A small plastic Petri dish is layered with a gel-like substance containing cells.

The whole is made up of Lego blocks, and the construction cost is 500 pounds (about 83,000 yen).

MINDSTORMS minicomputers also control the movement of nozzles and Petri dishes, which are important in 3D printing.

With Lego 3D bioprinters, even non-engineering students can create exactly the same thing in a day if they have the parts. The research team explains the required parts list and manufacturing method in supplementary materials of the paper so that laboratories around the world can make the same Lego 3D bioprinter.

The research team said, ``Our 3D bioprinter is currently being used to create layers of skin cells, and we are working towards creating a full-fledged skin model. It is also possible to print different types of cells and incorporate different complexities into tissue samples, mimicking both healthy and diseased skin, referencing existing treatments, and developing new treatments for various skin diseases. It's an exciting opportunity to design therapeutics that are effective.'
Related Posts: