It turned out that the minerals exhibited at the museum for 140 years were actually dinosaur eggs

A mineral discovered in central India and stored in
The first known dinosaur egg? A new discovery from the Museum's collection | Natural History Museum
https://www.nhm.ac.uk/discover/titanosaur-dinosaur-egg-agate-museum-discovery.html
Centuries-old rock turned out to be ancient dinosaur egg | Miami Herald
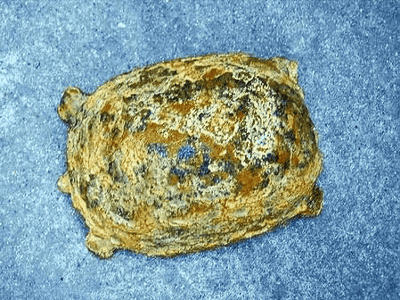
Agate specimens collected in central India were registered in
However, at a mineral exhibition held in France in 2018, curator Robin Hansen saw a dinosaur egg that looked similar to minerals housed in the Natural History Museum in London. The situation changes from According to Hansen, the dinosaur egg was spherical, had a thin skin, and had a dark agate in the center.
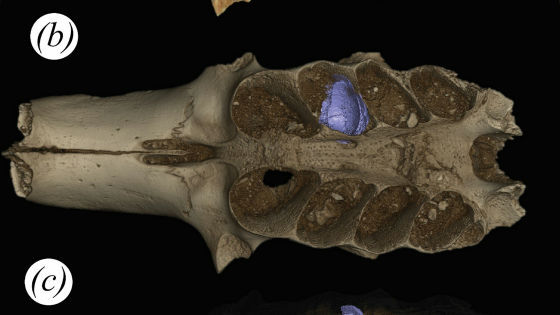
Mr. Hansen asked paleontologists Paul Barrett and Susanna Madement to investigate mineral specimens held by the Natural History Museum in London. Upon examination, the mineral specimen was found to be similar in size and shape to a dinosaur egg, with a thin layer around the agate that looked like an egg shell. It also turns out that two large spherical objects were once gathered around this mineral.
Barrett and colleagues used a CT scanner to further investigate the minerals, but the agate was so dense that it was not possible to observe the details of the minerals. However, the location from which this specimen was collected, as well as its size, shape, and surface features, make it almost certain that the mineral is a dinosaur egg. Furthermore, this egg matches the characteristics of Titanosaurus eggs that once lived in China, India, Argentina, etc., and this mineral is definitely said to be Titanosaurus eggs.

This egg was discovered by Charles Fraser in central India between 1817 and 1843. At that time, the word 'dinosaur' did not even exist. Also, it wasn't known until 1923 when dinosaur nests were first discovered in Mongolia that dinosaurs laid eggs. 'That means dinosaur eggs were being collected at least 80 years ago, when they were first scientifically recognized,' Barrett said.
The titanosaurus that laid this egg is 37 meters long and weighs 57 tons, making it one of the largest land animals ever to exist on Earth, but the size of the egg is quite small, about 15 cm in diameter. is. ``To survive on land, titanosaurs are thought to have laid a large number of eggs in a single spawning cycle, about 30 to 40, like sea turtles and crocodiles,'' Barrett said. increase.

by Garrett Ziegler
'Titanosaurus laid many eggs, and it seems that some of them hoped to grow into adults,' Barrett added.
Central India, where Titanosaurus lived, was once located in a supercontinent called Gondwana . In addition, there is an active volcano group called ' Decan Traps ' in central India, and since Titanosaurus with a huge body cannot sit on eggs and warm them, the warm ground of Deccan Traps is a spawning place. was said to be best suited for
However, shortly after the Titanosaurus laid its eggs in warm sandy soil, a nearby volcano erupted, erupting debris and lava that covered the eggs and nests, leaving the eggs stranded in the cooled, solidified lava, which could have affected the internal structures and structures. rotten embryo . After that, silica -rich water permeated rocks and eggshells, eventually becoming a pink agate, which was dug up in central India 60 million years later and was to be housed in the Natural History Museum in London. It is guessed.
Related Posts: