Clearly that the oldest ``13.4 billion year old galaxy'' in observation history could be photographed with the James Webb Space Telescope

It became clear that the James Webb Space Telescope succeeded in photographing the oldest galaxy 13.4 billion years ago in observation history.
Astronomers Just Confirmed the Most Ancient Galaxies Ever Observed
In July 2022, NASA photographed the universe for the first time with the James Webb Space Telescope, an infrared observation space telescope launched as a successor to the Hubble Space Telescope. NASA said of the color photographs taken by the James Webb Space Telescope, ``The deepest and sharpest images of space ever taken.'' Thousands of galaxies are shown, including ', and it was suggested that celestial bodies that could not be photographed with conventional technology may also be reflected.
Finally the first color photograph taken by the James Webb Space Telescope is released, the amazing performance of thousands of galaxies - GIGAZINE

The pictures taken by the James Webb Space Telescope at this time are as follows.
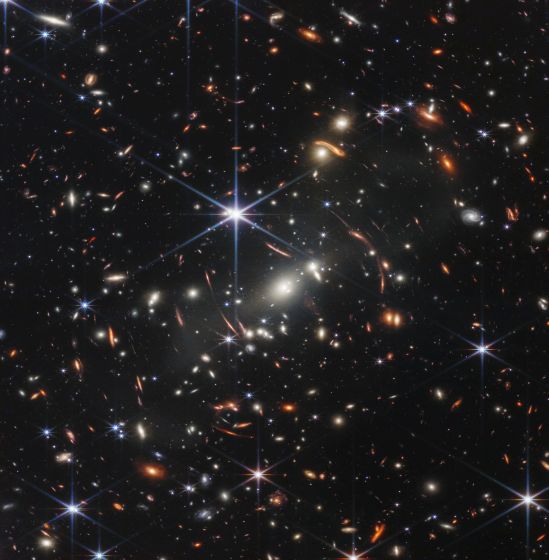

Among astronomers, it is said that this photo may be the oldest
Astronomers use a measure called redshift to describe exactly how far apart galaxies are. The higher the redshift, the farther the celestial body is from the earth, and the pictures taken by the James Webb Space Telescope found galaxies with redshifts of '10.5' and '12.5' . A galaxy with a redshift of 12.5 is said to be the most distant galaxy ever observed.

In addition,
Brant Robertson, a member of the NIRCam science team and a professor of astronomy and astrophysics at the University of California, Santa Cruz, said: I succeeded in observing it. I have absolute confidence in that wonderful distance, ”he said, expressing joy about this discovery.
The research team first analyzed the data of NIRcam, a very sensitive infrared camera. As a result, it has become possible to point out the existence of the ``light of the galaxy emitted 13.4 billion years ago'' and ``the farthest galaxy in observation history'' as mentioned above. But to confirm whether these are indeed 13.4 billion-year-old galaxies or the most distant galaxies ever observed, it has become the gold standard for accurately analyzing the distance and age of early galaxies. It seems that it is necessary to perform a spectroscopic analysis. Emma Curtis-Lake, an astronomer at the University of Hertfordshire in England, explains why spectroscopic analysis is necessary because ``closer galaxies can pretend to be very distant galaxies.'' I'm explaining.
NIRspec was the key to performing spectroscopic analysis, Robertson said, which allowed him to publish two studies . However, both of these studies are in the pre-peer-review stage.
Renske Smit of Liverpool John Moores University, who participated in the study, told the BBC in an interview, 'The observed galactic light is the size of Her Majesty's eyes on a pound coin held outstretched. It's small,' he says . In addition, it seems that it is estimated that about 100,000 galaxies are included in this small light.

To estimate the age of young galaxies, scientists measure their redshifts. This is a phenomenon in which the wavelengths of electromagnetic waves coming from distant celestial bodies become longer (redder in terms of visible light) due to the Doppler effect . Therefore, distant old galaxies are not only observed in the infrared, but also have the characteristic that electromagnetic waves are interrupted at specific points due to intergalactic hydrogen scattering.
The research team used NIRspec to analyze in more detail ``those with redshift discontinuities'' among the light observed by NIRcam. After observing 250 galaxies for 28 hours, it turned out that 4 galaxies have a redshift exceeding '10', that is, they are quite old galaxies. According to the research team, these four galaxies are quite small, having only about 100 million times the mass of the sun, and the stars in the galaxies are all less than 100 million years old. There are at least 100 billion stars in the Milky Way galaxy where the earth exists, and the sun is thought to be about 4.6 billion years old.
The research team says that this young galaxy is 'generating stars at an amazing speed, growing nearly 10 times faster than existing galaxies of similar size.' Below are four galaxies with redshifts exceeding '10' announced by the research team this time. Redshift is ``13.20'' (JADES-GS-z13-0), ``12.63'' (JADES-GS-z12-0), ``11.58'' (GS-z11-0), ``10.38'' (JADES-GS- z10-0). JADES-GS-z13-0 is a galaxy observed only 325 million years after the Big Bang, and is the galaxy that exists at the farthest position from the earth.
These galaxies are said to be the oldest spectroscopically confirmed galaxies, but the research team notes that older galaxies may soon be observed. The James Webb Space Telescope is designed to observe galaxies as early as 100 million years after the Big Bang.
The James Webb Space Telescope aims to deepen our understanding of galaxy formation by studying young stars and galaxies. Astronomers aim to detect ' cosmic reionization, ' in which the strong light of stars strips electrons from hydrogen and helium, ionizing the surrounding gas. The timing of galaxy formation may also be subtly different.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by logu_ii