A beautiful picture of the Orion Nebula taken by the James Webb Space Telescope
byNASA
A photo of the
Western News - Western researchers among first to capture James Webb Space Telescope images
https://news.westernu.ca/2022/09/jwst-pdrs4all-orion-nebula/
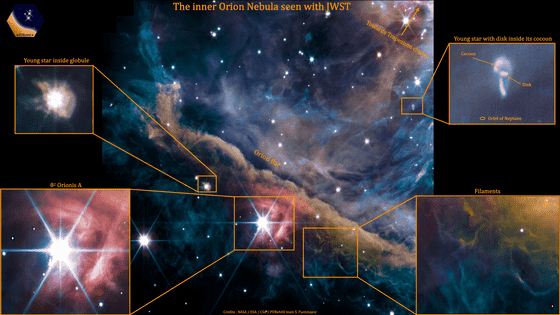
The inner Orion Nebula seen with JWST – PDRs4All
https://pdrs4all.org/pdrs4all-first-images-release/
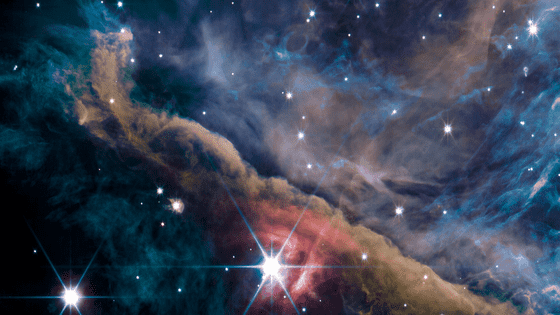
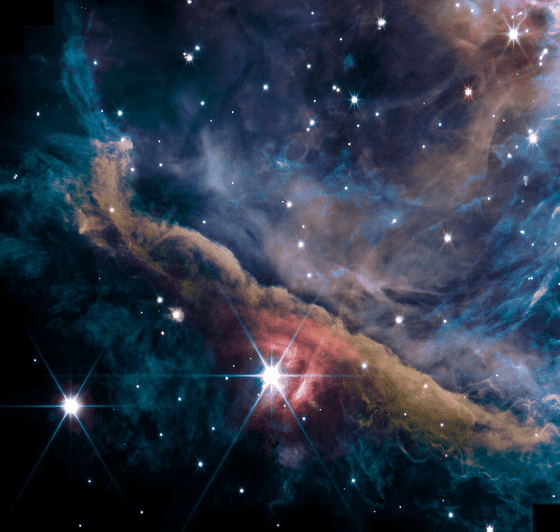
The James Webb Space Telescope captured the inner region of the Great Orion Nebula located in the constellation Orion, 1,350 light years away from Earth. The images are composites of emissions from hydrocarbons, molecular gases, dust, scattered starlight, etc., using multiple filters.

byNASA
The most conspicuous is a band of high-density gas from the upper left to the lower right of the image, and the brightest star in the center is a young star called 'θ2 Orionis A'. The blurred light located in the upper left of θ2 Orionis A is the ``baby'' of the star. Clouds with dense gas and dust collapse when gravity becomes unstable and become like this, gradually increasing mass, causing nuclear fusion, and starting to shine.
byNASA
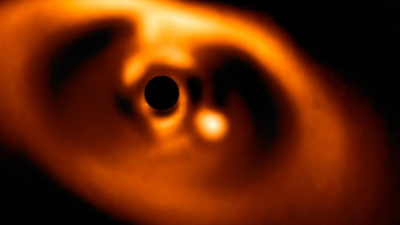
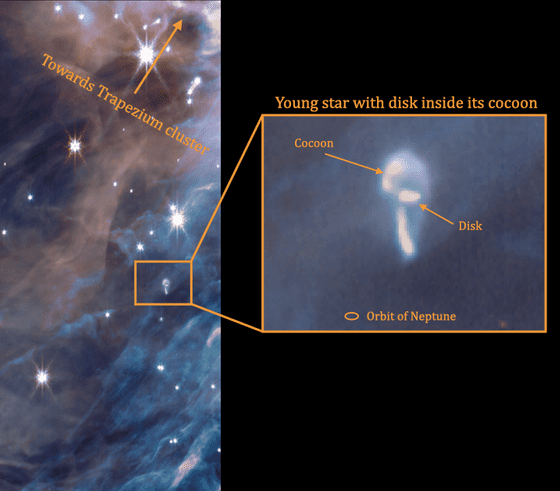
The cocoon-like object in the upper right is a planet surrounded by a disk of gas and dust. These disks are annihilated or
by NASA
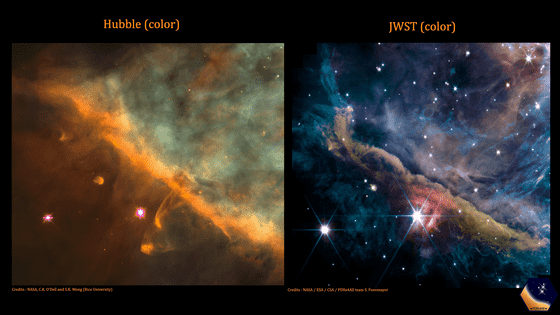
By the way, an image comparing the same area with a photo (left) taken by the Hubble Space Telescope has also been released. The James Webb Space Telescope has more precise infrared vision, so it seems that it is possible to find faint stars in thick dust layers.
by NASA
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1p_kr