Why are the construction costs of nuclear power plants so high?

Nuclear power generation has the advantage that the power generation cost is very low compared to other power generation, and there are expectations for the realization of a carbon-free society, but the high construction cost hinders the expansion of its use. In the United States, there were plans to build multiple nuclear power plants in Washington State in the 1980s, but construction has been postponed because construction costs have increased to six times the initial estimate. Brian Potter, the author of many columns on architecture, summarizes why construction costs have risen so much.
Why are nuclear power construction costs so high? Part I

Why are nuclear power construction costs so high? Part II
There are three types of costs involved in operating a power plant: 'fuel costs,' 'operation and maintenance costs,' and 'capital costs (depreciation of construction costs).' In the case of a nuclear power plant, the capital cost will rise from 60% to 80% due to the high construction cost.
Power plants change over time, so power plants operate and shut down as demand changes, but nuclear power plants cost money with or without power, and are so easy to shut down and restart. Most of the time, they are running continuously because they are often not designed to be able to.
Nuclear power generation uses a heat source to convert water into steam, and the steam turns a turbine to generate electricity, so it is almost the same as thermal power generation except for fuel. Reactors include light water reactors that use light water as moderators, heavy waterreactors that use heavy water, and graphite furnaces that use graphite. Light water reactors are the most orthodox reactors in the world.
Many experts said that other methods were more suitable for power plants, but the reason why light water reactors became mainstream in the United States seems to be that they were adopted by the U.S. Navy. increase. The US Navy has also considered a method that uses liquid sodium as a coolant, but it has been determined that sodium is not suitable for a nuclear reactor used by the Navy because it reacts violently with water. After that, the existing light water reactor technology was to be used for the early development of civilian nuclear power generation technology.
Construction of commercial nuclear power plants began in the United States in the 1960s. In the graph below, the horizontal axis shows the construction start time, and the vertical axis shows the construction cost per kilowatt at the overnight cost assuming that the construction can be done overnight without considering interest etc., for verification. Excluding the furnace, it was initially made at 1000 dollars per kilowatt (360,000 yen at the rate at that time (360 yen per dollar)), but in 10 years it will be 9000 dollars (1.8 million yen when converted to 200 yen per dollar). Is up to.
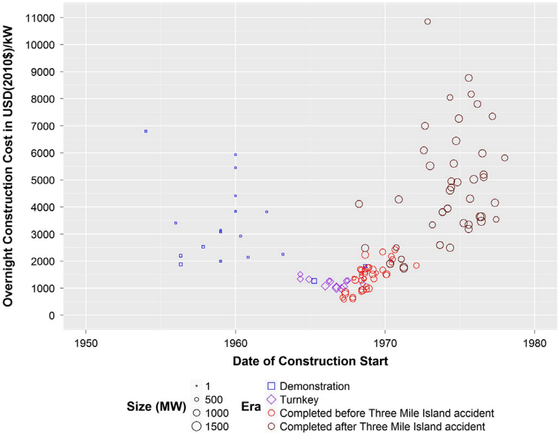
It is said that the tendency of price increases is the same in France, Germany, and Japan, but in the United States, the rate of increase in construction costs is particularly large, and it is said to 'show negative learning' because it 'worse over time'. increase.
According to past estimates, the overall inflation rate between 1976 and 1988 was 5.5%, material costs rose 7.7% a year, and labor costs rose 18.7% a year. In the first place, the construction time was more than 5 years in the 1960s, but it has increased to 12 years in 1980, and the cost of financing and labor is increasing. One of the factors behind this increase in costs was the result of a lawsuit between the Coordinating Committee and the Nuclear Commission on the construction of the
The increase in labor costs is partly due to the increased burden of power plant construction due to the tightening of regulations. As a group of professional engineers developed new nuclear-related standards and the manufacturing, testing, and performance standards for basic structural parts became stricter, the prices of parts became higher. In the latter half of the 1970s, the design engineering effort required for each nuclear power plant tripled.
These standards changes can lead to design changes at power plants under construction, sometimes requiring the removal of parts that have already been worked on, with the intervention and monitoring of high-paying people such as design engineers, managers, and field inspectors. Will be required. As of 1978, there was an opinion that 'achieving stable licensing requirements is a clear goal of every effort to obtain a shorter and predictable project period.'
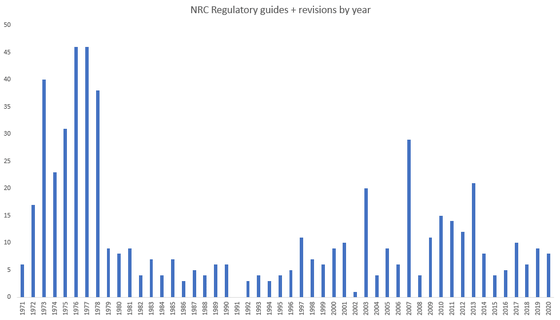
A graph showing the NRA regulatory guide and the number of revisions from the 1970s to 2020. You can see that the number of revisions was very large in the 1970s, then decreased in the 1980s and 1990s, and increased a little from the 2000s.
Related Posts:
in Note, Posted by logc_nt