It is shown that sunken ships on the seafloor may be affecting deep-sea ecosystems.

It is said that there are
Frontiers | Historic Wooden Shipwrecks Influence Dispersal of Deep-Sea Biofilms | Marine Science
https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2022.873445
New study finds 19th century wooden shipwrecks to be thriving habitats for deep-sea microbiomes – Science & research news | Frontiers
https://blog.frontiersin.org/2022/06/08/new-study-finds-19th-century-wooden-shipwrecks-to-be-thriving-habitats-for-deep-sea-microbiomes/
Millions of Shipwrecks Lost to The Ocean Are Changing Life in The Deep Sea
https://www.sciencealert.com/deep-sea-microbiomes-are-thriving-on-the-ocean-s-submerged-shipwrecks
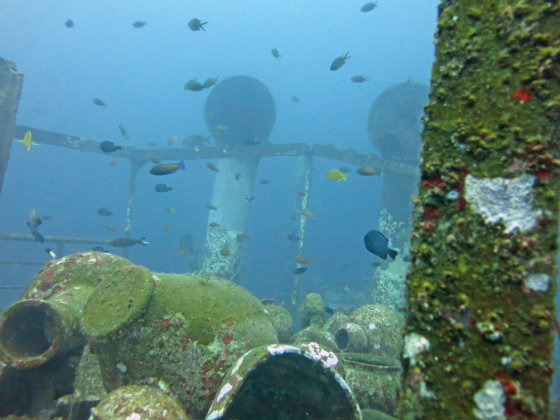
A research team led by Leila Hamdan, a molecular ecologist at the University of South Mississippi , USA, has sunk to the seafloor because it has long been known that trees submerged in rivers and the sea affect biodiversity . I thought that the ship might also affect the ecosystem and conducted an experiment.
In the experiment, the research team chose two 19th-century wooden sailboats that sank in the Gulf of Mexico, placed pine and oak pieces at various locations 0-200 m from the sunken ship, and collected these samples four months later. did. Then, DNA sequencing was performed on the sample to analyze the inhabiting bacteria, archaea , and fungi .
As a result of the analysis, it was found that 'distance from the sunken ship' influences the diversity of microorganisms in addition to factors such as the type and depth of wood and the distance to the Mississippi River, which is a nutrient source. The most microbial diversity was in samples located 125 meters away from the sunken ship, but the research team found that the presence of the sunken ship as a whole enhances microbial diversity in the surrounding water. I am reporting.
Deep-sea microbes form the basis of the food chain in the water, so their changes could affect other marine organisms and ultimately terrestrial ecosystems. thing.
'Awareness and understanding of the microbial community is important to provide early and clear evidence of the changes that human activity has on marine ecosystems,' said Hamdan. 'This study is about the habitats created (by humans). It is the first time that the place / thing that has been made or modified has an effect on the microorganisms that coat these surfaces. '
The results suggest that man-made structures such as oil platforms installed in the ocean may affect the deep-sea microbial flora (so), and the research team needs further research. I think. 'We hope that this study will encourage dialogue that will lead to a study of how the habitats constructed are changing the deep sea,' said Hamdan.

Related Posts:







