Is ivermectin effective in treating the new corona? Results of analysis based on multiple survey data

Ivermectin: Much More Than You Wanted To Know --Astral Codex Ten
https://astralcodexten.substack.com/p/ivermectin-much-more-than-you-wanted
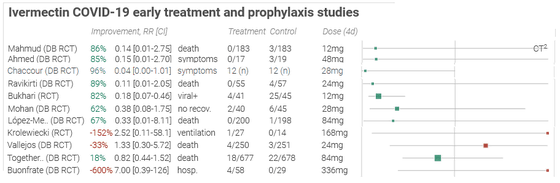
The following data is obtained from Ivermectin for COVID-19 , a site that summarizes the data when ivermectin was administered to COVID-19 patients. 'Data when ivermectin was administered in the early treatment of patients infected with COVID-19' is. Lined up vertically is the name of the facility where ivermectin was administered, and 'Improvement' is the rate at which symptoms improved with ivermectin administration. The improvement rate written in green is the case where the ivermectin-administered group showed a clear improvement in symptoms compared to the placebo group, and the red number was the opposite, and the symptoms worsened more clearly than the placebo group. Thing. Many facilities show that there was an improvement in green, but some are shown in red as '-152%' and '-600%'.
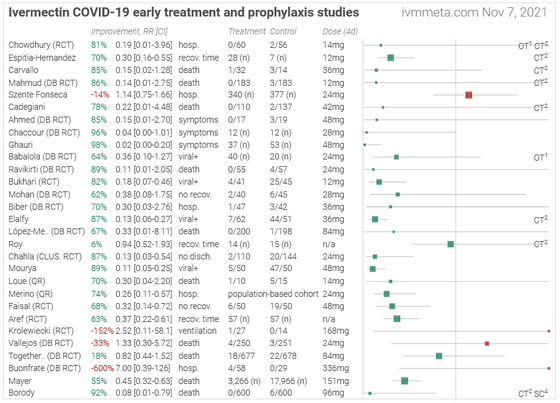
These data were collected from studies such as the administration of ivermectin to COVID-19 patients, and Alexander said, 'One of the most impressive science communications I have ever seen.' 'World Health Organization (WHO) and The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has invested billions of dollars, but still hasn't come up with a clear view of ivermectin. ' Claims the usefulness of the data published in -19.
The data for Ivermectin for COVID-19 is only for cases where ivermectin was used for early treatment of COVID-19 patients. However, it should also be noted that in most study cases, the number of subjects is very small and in fact many COVID-19 patients improve their symptoms. In addition, although the number of deaths in each study is only one or two, the improvement rate will fluctuate significantly in the study group where deaths occurred due to the small number of subjects, so a figure such as minus 600%. Will come out.
'The important fact is that 26 of the 30 studies mentioned above showed that Ibermectin was more effective than the placebo group in improving symptoms,' said Alexander. All studies have focused on viral load, the time it takes for a patient to become negative, the time it takes for a patient's symptoms to disappear, and the result is 'although not statistically significant. , But it is small but effective. '
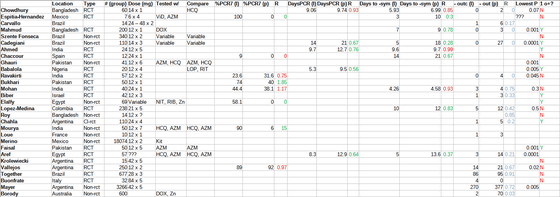
The following is Alexander's adjustment of the data and recreating the table. '# (Group)' is the number of subjects per study and does not include the number of placebo groups. 'Dose' is the dose and number of days of administration of ivermectin, and 'Tested w /' is another drug given with ivermectin. '% PCR7' is the percentage of patients who were negative in the PCR test 7 days after administration, followed by '(I)' is the negative rate of patients who received ivermectin, and '(p)' was given placebo. Represents the negative rate of the patient. 'R' is the ratio of patients receiving ivermectin to those receiving placebo, with green indicating a statistically superior dose of ivermectin and red vice versa. 'Days PCR' is the number of days it took for the PCR test to become negative, 'Days to -sym' is the number of days it took for the symptoms to improve, and '-outc' is the number of cases hospitalized or died due to worsening symptoms. .. And '1 o +?' Indicates whether the survey result was positive or not, 'N' is 'No (not a positive result)' and 'Y' is 'Yse (positive)'. It was the result) '.
Furthermore, if you delete the research that Alexander judged to be incorrect or unhealthy in the research method, it will be as follows.
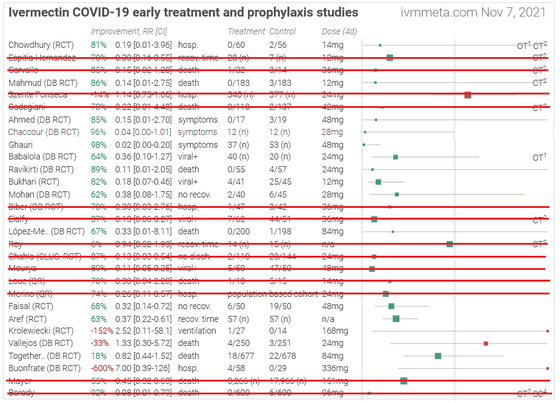
It has been pointed out that there is fraud in the COVID-19 study, except for the ones that
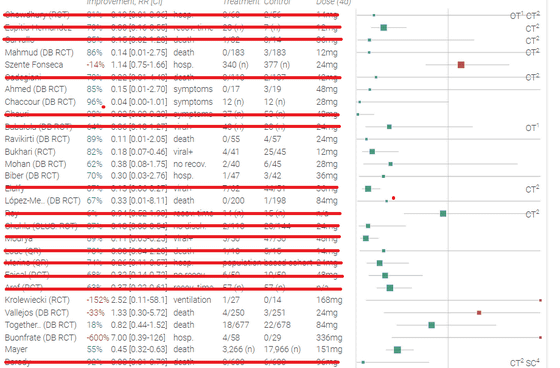
When one of the two found that the study was fraudulent, only the following 11 studies remained useful. Of the 30 studies, 19 were deleted, of which 2 were deleted as fraudulent content, 1 was deleted due to a serious pre-registration violation, and the methodology was incorrect. 10 cases were deleted as being, and 6 cases were judged to be 'suspicious' by Mr. Katz.
Analyzing studies on ivermectin and COVID-19, Alexander noted that about 10-15% of the seemingly superior studies were fraudulent. And even if there is no raw data of the research, there are two ways to check whether the content is fraudulent, '
In addition, Alexander looks at where the studies were found to be useful. 'Mahmud' is a study conducted in Bangladesh, 'Ravakirti' is a study conducted in India, and 'Lopez-Medina' is a study conducted in Colombia.
And the following is a graph showing the prevalence of ascariasis around the world. There are many different types of roundworms, but all together, 25-50% of people in developing countries carry parasites in their bodies.
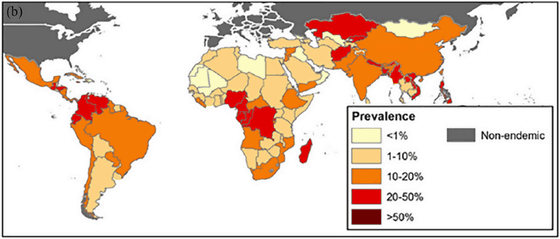
Studies have shown that these parasites can affect the body's immune system to fight the new coronavirus. Studies have pointed out that people infected with ascariasis are more likely to become severely ill with COVID-19, which preventschanges in the intestinal flora associated with ascariasis from effectively responding to the virus in the immune system. It has been pointed out that this is because it will end up. In addition, it has been pointed out that the new coronavirus vaccine is not very effective for patients with ascariasis, and that treatment and prevention of ascariasis may reduce the adverse effects of COVID-19.
Given that ivermectin is an anthelmintic drug by nature, it may be possible to increase the effectiveness of the COVID-19 vaccine by administering ivermectin not as a treatment for COVID-19 but to repel roundworms from the body. Of the roundworms, the species Strongyloides stercoralis can be exterminated from the body by ingesting 200 μg of ivermectin per day.
When the data are scrutinized with this in mind, data from regions with a low prevalence of ascariasis (Vallejos), such as Argentina, show a negative symptom improvement rate after ivermectin administration. On the other hand, data collected in areas with a high prevalence of ascariasis, such as Bangladesh, show a high rate of symptom improvement after ivermectin administration.
Based on these, the 'results of analysis of research data on ivermectin and COVID-19' compiled by Mr. Alexander are as follows.
Ivermectin does not significantly reduce COVID-19 mortality in the absence of parasites in the body. ( Reliability 85-90% )
Parasites have become important confounders in some ivermectin-related studies, and positive results can be obtained even if they are methodologically sound. ( Reliability 50% )
Fraud and data processing errors, as well as P-value hacking and methodological issues, are very important in explaining bad research.
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by logu_ii