Mozilla explains 'How does HTTPS protect people? Is the web safe with HTTPS?'

How does HTTPS protect you (and how doesn't it?) --The Mozilla Blog
https://blog.mozilla.org/en/products/firefox/https-protect/
◆ What role does HTTPS have?
HTTPS refers to a mechanism that encrypts conventional HTTP data communication using the SSL / TLS protocol and performs data communication with a more secure connection. Data communication over HTTPS can prevent malicious attackers from snooping on data sent and received between you and your website.
HTTPS also has the ability to prevent Internet Service Providers (ISPs) from going beyond the top level of your website to see the pages you visit in more detail. For example, an ISP knows that a user has accessed 'https://www.reddit.com ', but even more deeply to ' https://www.reddit.com/r/CatGifs/ '. Can't know.
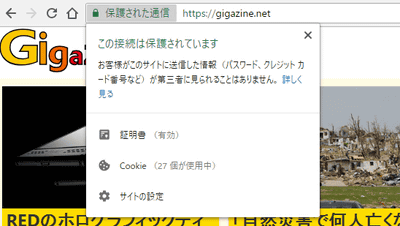
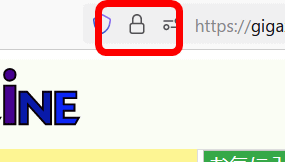
In Firefox, a lock icon is displayed on the left side of the address bar to distinguish whether the connected website is HTTPS or HTTP. If the lock icon is normal, it is an HTTPS connection ...
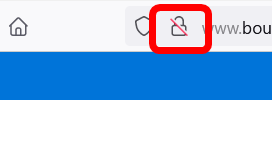
If the icon has a red diagonal line, it is HTTP.
◆ Is HTTPS all-purpose?
Although HTTPS provides secure data communication, Mozilla points out that this does not mean that security on the Internet is perfect. HTTPS only guarantees that your data is encrypted and private, and it doesn't matter if the website itself is fraudulent or malware-laden. Not only reliable and secure websites can provide HTTPS connections, but also websites used for scams, phishing scams, and malware distribution can provide HTTPS.
Mozilla said about HTTPS, 'This is like a phone. The phone company is not responsible for fraudsters calling you and trying to get a credit card number. You are with whom you are. You need to be familiar with what you're talking about. The job of HTTPS is to provide a secure line, and we don't guarantee that you won't talk to fraudsters. '

◆ How to identify fraudulent websites?
To avoid being fooled by scammers, you need to develop your own ability to identify dangerous sites. Mozilla points out that you need to understand that scammers use clever tricks to trick users.
For example, 'A suspicious transaction has been confirmed, so we have frozen the account of Bank A in the name of the customer. If you want to restore the account, please click the link below and enter the password again.' Suppose you receive an email. If you don't have a Bank A account,
However, Mozilla warns that clicking a link in an email is basically a dangerous activity. If you receive such an email, it's better to access your account directly from your browser instead of via email, or call the contact phone number on the official website to verify that the email is genuine. It's safe.
In addition, Firefox has ' protection from spoofed sites and malware ' implemented by default, and it is a mechanism to warn the user when the visited website is reported as a dangerous website. If you are warned by these protections, you should quietly leave the website.

◆ Importance of HTTPS
Although HTTPS does not eliminate scammers who approach you directly, it does help prevent outside communications from being snooped on websites that provide customer logins and the like. In Firefox, you can force HTTPS to be used on websites that support both HTTP and HTTPS by setting it to 'HTTPS-Only', but some websites still do not support HTTPS. Also exists.
Switching to HTTPS is easy with 'Let's Encrypt ', which issues SSL certificates for free. To make the entire web more secure, Mozilla has urged users to switch to HTTPS via email or contact forms if they find a website that doesn't support HTTPS.
Related Posts:
in Web Service, Security, Posted by log1h_ik