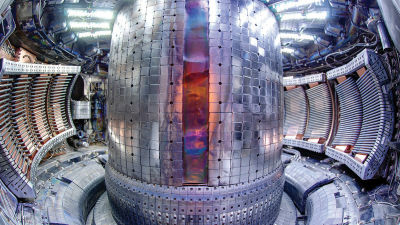
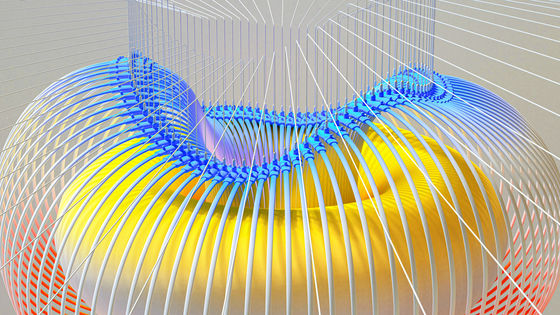
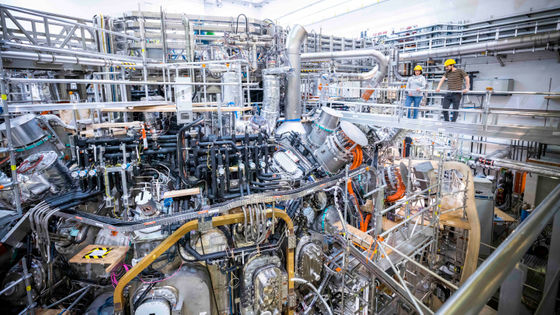
MIT reports that it has set a new world record for 'magnetic field strength of superconducting electromagnets' required for fusion power plants

The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) reported that it has succeeded in creating a new superconducting electromagnet with the strongest magnetic field strength in history through the development of a 'superconducting electromagnet' that has been underway in partnership with a private company since 2015.
MIT-designed project achieves major advance toward fusion energy | MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
https://news.mit.edu/2021/MIT-CFS-major-advance-toward-fusion-energy-0908
Fusion startup builds 10-foot-high, 20-tesla superconducting magnet | Ars Technica
https://arstechnica.com/science/2021/09/mit-backed-fusion-startup-hits-key-milestone-big-superconducting-magnets/
This time, MIT et al. Reported that they have realized the 'world's most powerful superconducting electromagnet,' which is essential for achieving fusion power generation. Nuclear fusion is a type of nuclear reaction in which two atoms are heated into plasma and then fused, and in the process the plasma reaches a high temperature of over 100 million degrees Celsius. At present, it is thought that there is no substance that can maintain a solid state at this level of high temperature, so in the fusion reactor project currently under development, it is said to 'float in a magnetic field' mainly to keep plasma trapped. The method is adopted.
About nuclear fusion: Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
https://www.mext.go.jp/a_menu/shinkou/iter/019.htm
With the conventional method, there was a problem that the device itself became huge in order to keep the plasma heated to hundreds of millions of degrees confined. However, MIT and the fusion system startup Commonwealth Fusion Systems have recently discovered a coil of rare earth barium copper oxide that exhibits superconductivity at 20 kelvin as a power source, and the size of the superconducting electromagnet is 3 meters high and 1.5 in length and width. It was reported that it achieved the magnetic field strength of '20 Tesla ', which is the strongest in history for a high-temperature superconducting fusion magnet, which was the target, while keeping it within meters.
Unlocking SPARC: HTS Magnet for Commercial Fusion Applications --YouTube
This superconducting electromagnet development project started in 2018, and the announcement at that time stated that it would be completed in the next three years, so it seems that the project is proceeding as expected at that time.
MIT's new research aimed at realizing a fusion power plant within 15 years has started --GIGAZINE
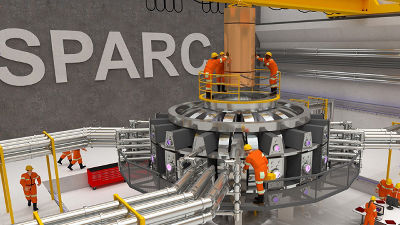
According to the announcement at that time, the final goal of the fusion power plant was to be completed within 15 years, so if steady progress continues, the fusion power plant will be completed by 2030.
This research is a proof-of-concept, which is the pre-stage of the construction of a fusion power plant, but MIT et al. Commented that the completion of this superconducting electromagnet 'exceeded the biggest technical hurdle'. He describes fusion as the 'ultimate clean energy' because it uses only water as fuel, and says he has achieved one of the most important milestones towards the realization of a fusion power plant.
Related Posts: