What antibodies may be able to neutralize all new coronaviruses found so far and unknown coronaviruses?
Several new coronavirus vaccines have been developed, and humankind is trying to stop the spread of the new coronavirus, albeit little by little. However, in order to completely stop the new coronavirus, not only vaccination but also treatment methods that prevent the aggravation of the new coronavirus infection (COVID-19) are required.
SARS-CoV-2 RBD antibodies that maximize breadth and resistance to escape | Nature
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03807-6
Berkeley Lab participates to develop COVID-19 antibody therapy
https://www.dailycal.org/2021/08/18/berkeley-lab-participates-to-develop-covid-19-antibody-therapy/
“Inescapable” COVID-19 Antibody Discovery – Neutralizes All Known SARS-CoV-2 Strains
https://scitechdaily.com/inescapable-covid-19-antibody-discovery-neutralizes-all-known-sars-cov-2-strains/
'Antibody therapy' is one of the treatments used to prevent the aggravation of the new coronavirus in patients with mild to moderate disease. This is to suppress the growth of the new coronavirus in the body by recognizing the spike protein of the new coronavirus and administering an antibody that has the effect of neutralizing the virus. In addition, 'antibody cocktail therapy' in which multiple antibodies are administered at the same time is also performed.
After more than a year of research on antibody drugs against the new coronavirus, three drugs in the United States have been urgently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) at the time of writing. Sotrobimab, the latest antibody drug among the three, was developed by GlaxoSmithKline and Vir Biotechnology and is called 'S309' found in the blood of patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in 2003. Derived from antibodies. When the development team administered sotrobimab to mild to moderate COVID-19-infected individuals, it was confirmed that the rate of aggravation and mortality was reduced by 85% compared to the control group, and it was urgently approved by the FDA in late May. Came down.
And from the results of the experiment, the research team neutralized all known new coronaviruses, including new variants that could not be neutralized by conventional antibody therapy, in addition to S309, and also neutralized closely related viruses. He claims to have found an antibody that may be possible.
Jay Knicks, leader of the Advanced Light Source (ALS) Molecular Biology Consortium at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, said in the early stages of his research that the ALS beamline and the Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource beamline at Stanford University We used it to analyze the X-ray crystal structure of the new coronavirus antibody. As a result, we succeeded in creating a detailed structural map showing how these antibodies bind to the spike protein of the new coronavirus.
It is said that the new coronavirus
As a result, the research team used biochemical and structural analysis, detailed mutation scans, and binding experiments to identify the antibody S2H97, which is highly potent against various strains of the new coronavirus. Knicks said, 'S2H97 has been found to bind to previously unknown regions of the neocoronavirus peplomer. It also contains all of the'Salvecovirus subgenus'viruses, including the neocoronavirus. In addition, it has a binding site in the part of the virus that is difficult to mutate, so it may be possible to deal with the SARS-related coronavirus that may become prevalent in the future. '
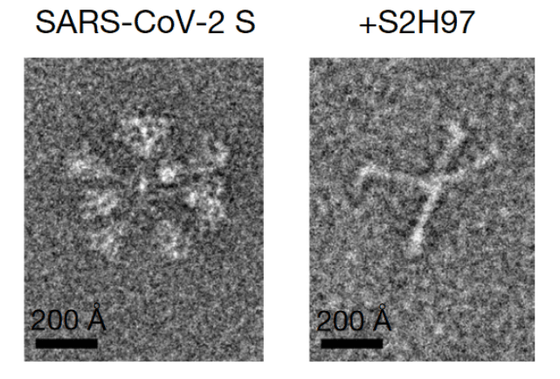
In addition, subsequent experiments with hamsters suggested that prophylactic administration of S2H97 could prevent COVID-19 infection. It was also found that S2H97 hardly competes with infectious and vaccine antibodies.
However, it has not been confirmed whether S2H97 has a direct effect on the delta strain, as the experiment was conducted before
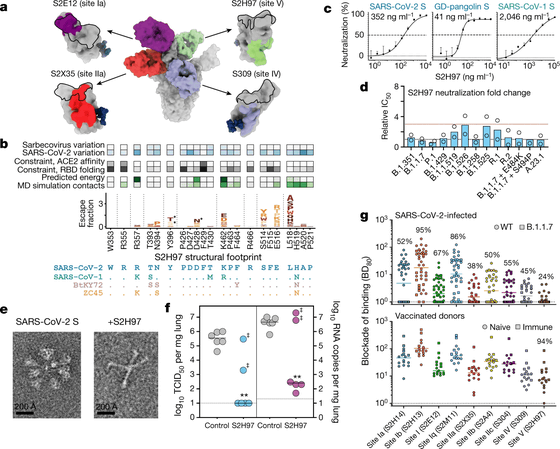
Tyler Star, a member of the research team and a postdoc at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, said, 'Overall, identifying antibodies that respond widely to a variety of strains will spread to humans in the future. It is important in developing antibody therapeutics and vaccines that can pre-immunize potential SARS-related coronavirus strains. '
Related Posts:
in Science, Posted by log1i_yk