The amount of ransom required for ransomware attacks is on the rise, is it affected by hacking incidents that damaged large companies?

Ransomware Attack Vectors shift as New Software Vulnerability Exploits Abound
https://www.coveware.com/blog/ransomware-attack-vectors-shift-as-new-software-vulnerability-exploits-abound
Accellion data breaches drive up average ransom price
https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/accellion-data-breaches-drive-up-average-ransom-price/
Coveware, which supports data recovery for companies affected by ransomware, has an average ransom demand of $ 220,298, central to hackers who launched a ransomware attack in the first quarter of 2021. It reported that the value reached $ 78,398. Compared to the fourth quarter of 2020, the average is up 43% and the median is up 59%.
The graph below shows the average ransom due to ransomware damage in dark blue and the median in light blue. We can see that the amount of damage increased sharply in 2020, decreased in the fourth quarter of 2020, but increased again in the first quarter of 2021.
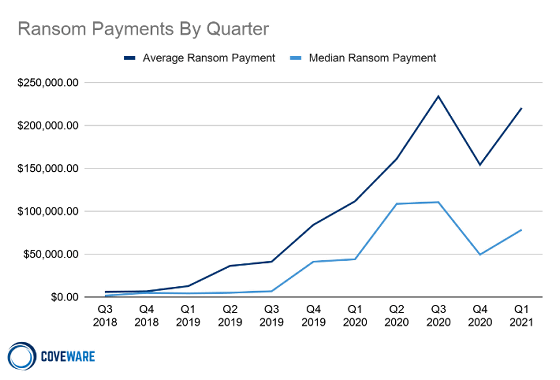
According to Coveware, this number is due to a
Millions of personal information leaked from government agencies and companies, caused by file transfer service vulnerabilities --GIGAZINE

Few companies and institutions used the old file transfer service, and it seems that about 100 companies were damaged. However, among them are Bombardier , which manufactures railroads and aircraft, transportation authorities in New South Wales , Australia, Shell , a major oil company, several universities in the United States, crogers in major supermarkets, the Reserve Bank of New Zealand , and the Washington State Auditorium. Included high-profile companies and institutions.
Some victims who were required to pay a large ransom by Clop accepted the payment to prevent data leakage, while others refused to pay the ransom. It is also reported that Clop has released data on victims who did not pay the ransom, as threatened.
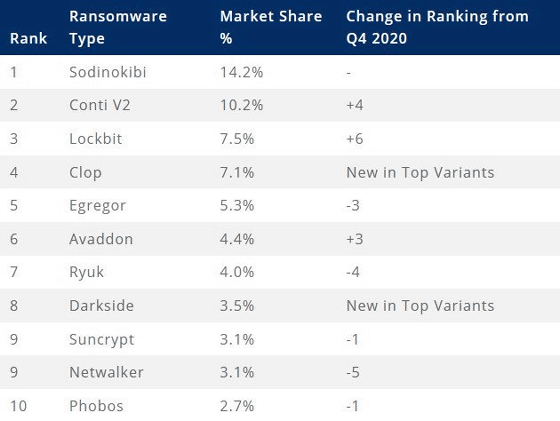
The 'Ransomware Market Share Ranking' announced by Coveware is as follows, and Clop is ranked 4th with 7.1%.
In ransomware ransom negotiations, it is important to have a trusting relationship that 'paying the ransom will restore data or prevent leakage', but in recent years hackers who make technical mistakes due to the overly complicated ransomware attacks. There are also many. In addition to cases where all data was lost due to 'technical flaws in which the victim could not restore the encryption', 'outsourcing of chat makes negotiation difficult' and 'the same target many times There are also increasing acts that damage the relationship of trust, such as 'attacking.'
'We recommend that companies victims of ransomware attacks not pay the attackers,' said Ionut Ilascu , a technology writer specializing in cybersecurity. If you do not pay the ransom, it will be judged that 'attacking this target will not make a profit', and hackers will not be motivated to make repeated attacks. Also, since paying the ransom does not necessarily mean that the hacker will destroy the data, there is a risk that the data will be leaked after the ransom is paid, or the data will be bought and sold on the criminal forum.
Related Posts:
in Security, Posted by log1h_ik







